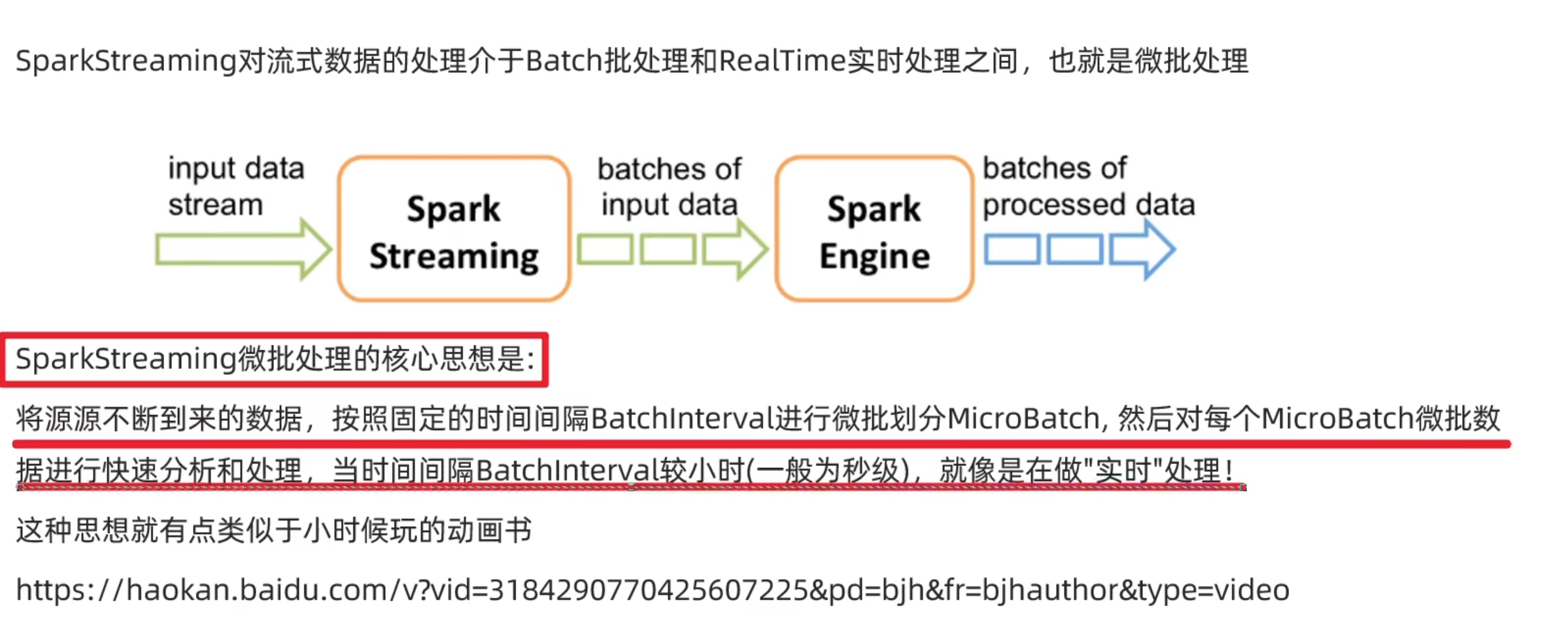
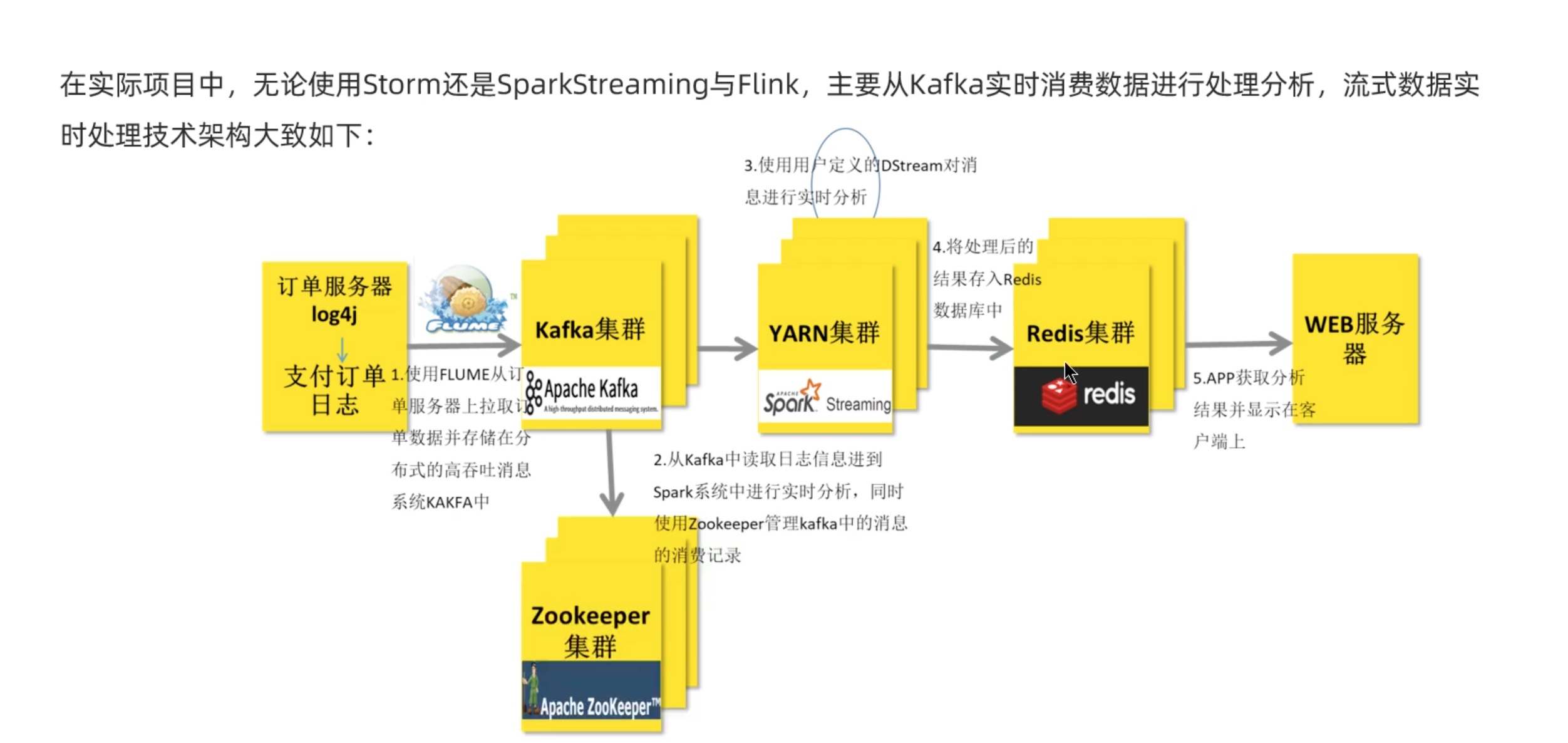
简介
spark streaming 学习
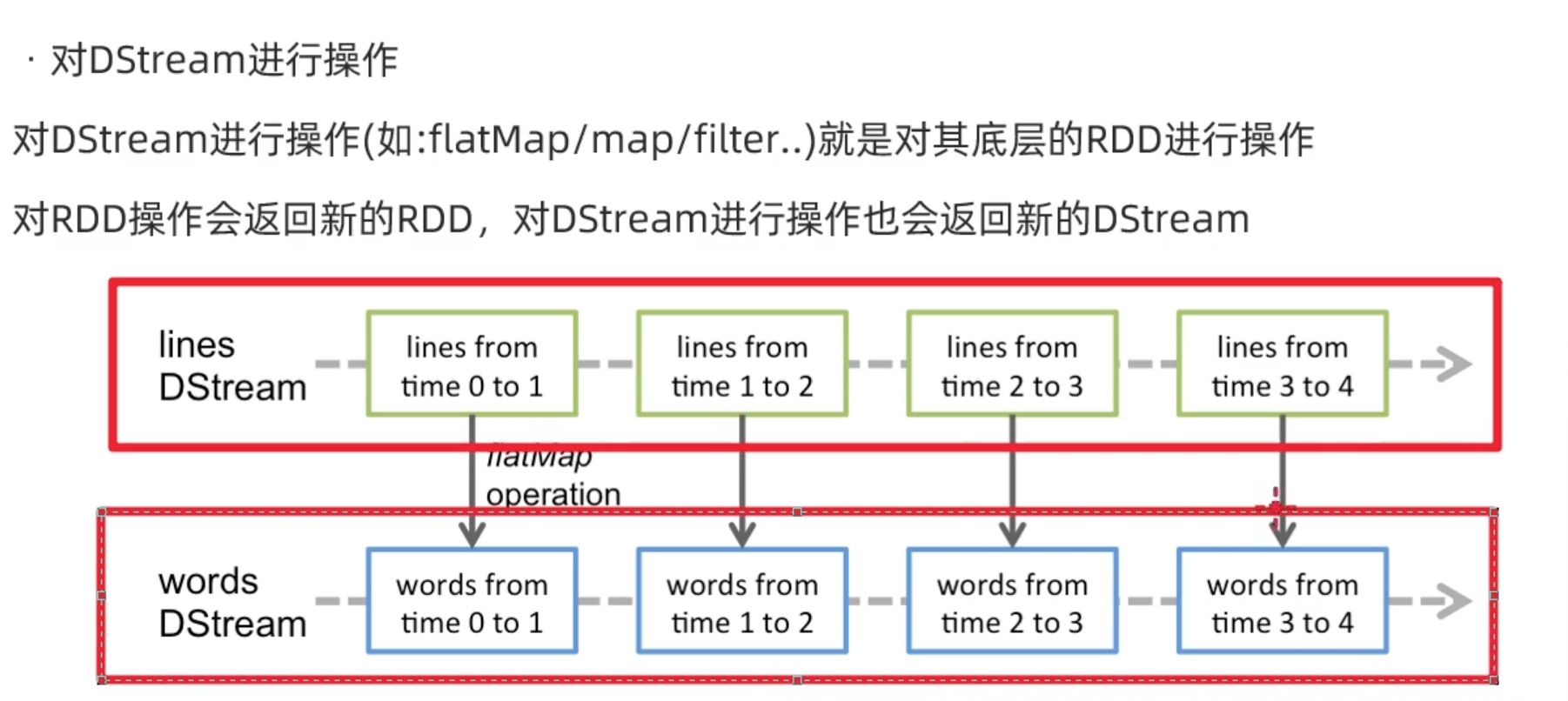
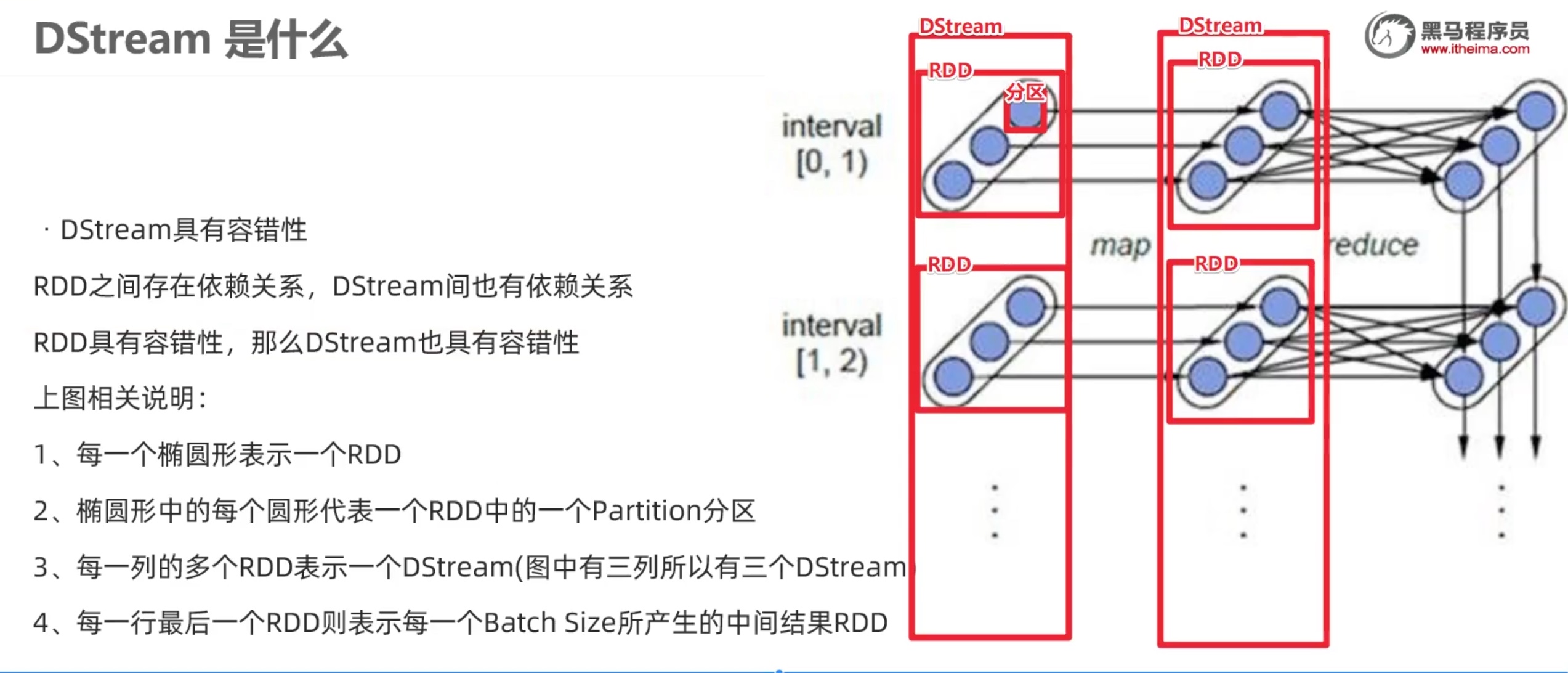
Dstream 数据抽象
Python 版 SparkStreaming 我们在spark官网https://spark.apache.org/examples.html 没看见spark streaming 的python examples,所以我们参考 http://dblab.xmu.edu.cn/blog/1709-2/ 厦大的林子雨老师的 python 版 spark教程。
Spark Streaming程序基本步骤 编写Spark Streaming程序的基本步骤是:
创建StreamingContext对象 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 from pyspark import SparkContext, SparkConffrom pyspark.streaming import StreamingContextconf = SparkConf() conf.setAppName('TestDStream' ) conf.setMaster('local[*]' ) sc = SparkContext(conf = conf) ssc = StreamingContext(sc, 1 )
输入源 一、文件流 在待监听文件夹logfile中新建两个日志文件log1.txt和log2.txt,里面可以随便输入一些内容。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 from pyspark import SparkContext, SparkConffrom pyspark.streaming import StreamingContextconf = SparkConf() conf.setAppName('TestDStream' ) conf.setMaster('local[*]' ) sc = SparkContext(conf = conf) ssc = StreamingContext(sc, 10 ) lines = ssc.textFileStream('file:///opt/data/logfile/logfile' ) words = lines.flatMap(lambda line: line.split(' ' )) wordCounts = words.map (lambda x : (x,1 )).reduceByKey(lambda a,b: a+b) wordCounts.pprint() ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination()
监听程序只监听”logfile”目录下在程序启动后新增的文件,不会去处理历史上已经存在的文件。所以,为了能够让程序读取文件内容并显示到屏幕上,让我们能够看到效果,这时,我们需要到”logfile”目录下再新建一个log3.txt文件,才可见运行后的效果。
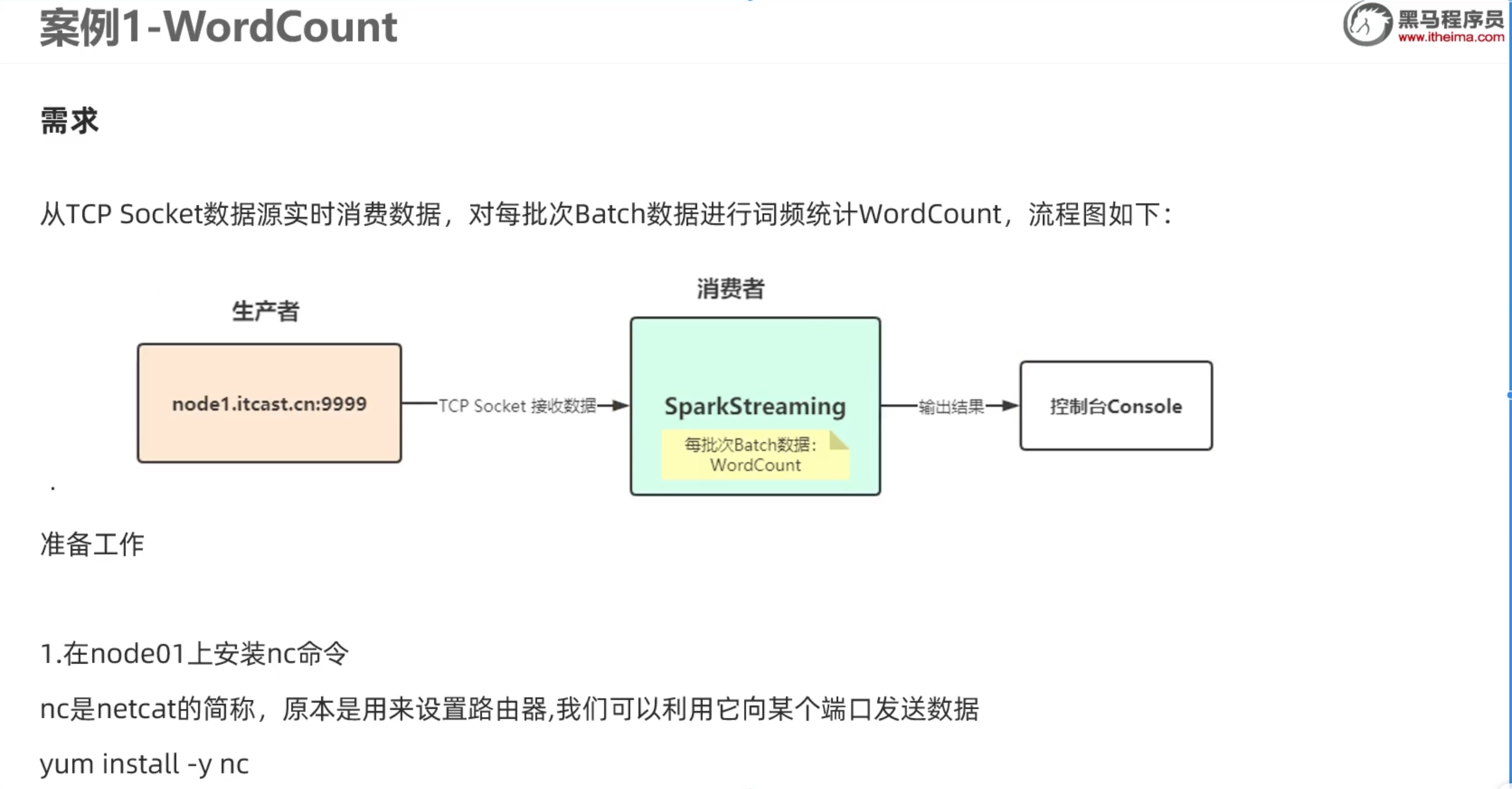
二、套接字流
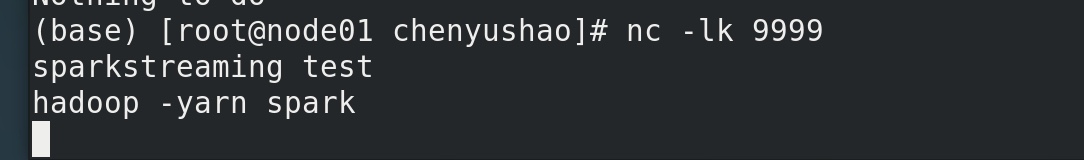
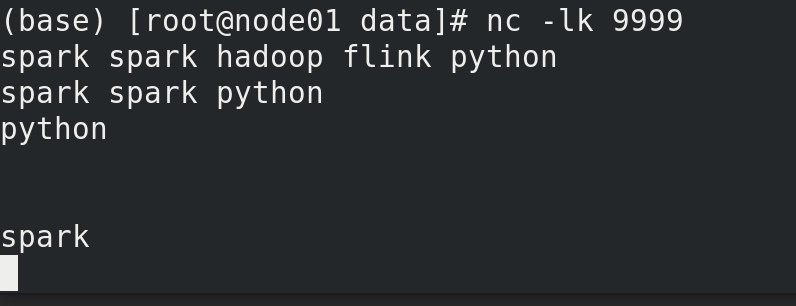
利用nc 在node01机器 用9999端口 向node01 发送内容。模拟流式数据。
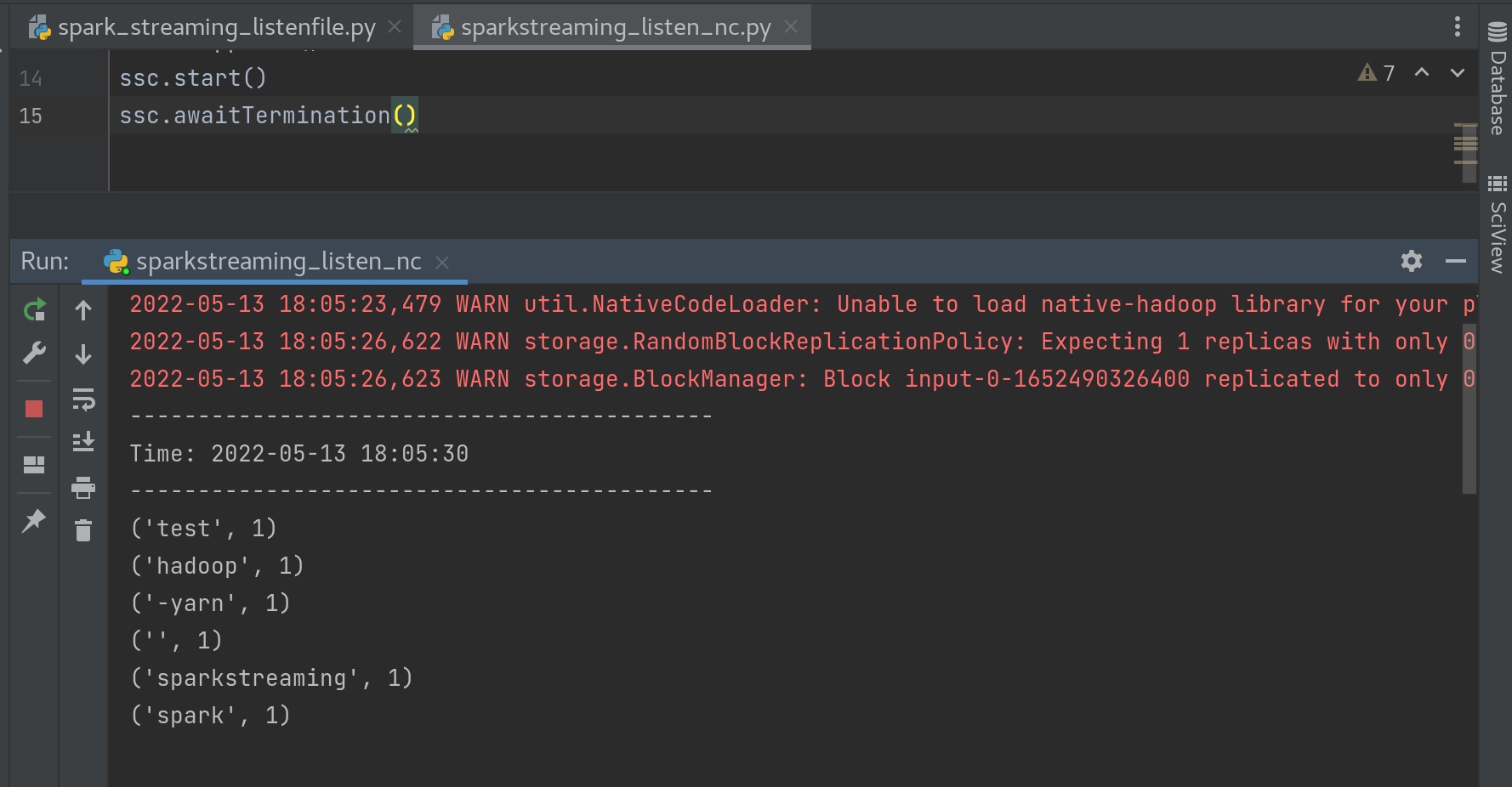
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 from pyspark import SparkContext, SparkConffrom pyspark.streaming import StreamingContextconf = SparkConf() conf.setAppName('TestDStream' ) conf.setMaster('local[*]' ) sc = SparkContext(conf = conf) ssc = StreamingContext(sc, 10 ) lines = ssc.socketTextStream('node01' ,9999 ) counts = lines.flatMap(lambda line:line.split(' ' )).\ map (lambda x: (x,1 )).reduceByKey(lambda a,b: a+b) counts.pprint() ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination()
解释警告的原因:
WARN storage.RandomBlockReplicationPolicy: Expecting 1 replicas with only 0 peer/s.
While a Spark Streaming driver program is running, the system receives data from various sources and and divides it into batches. Each batch of data is treated as an RDD, that is, an immutable parallel collection of data. These input RDDs are saved in memory and replicated to two nodes for fault-tolerance.
The warning in your case means that incoming data from stream are not replicated at all. The reason for that may be that you run the app with just one instance of Spark worker or running in local mode. Try to start more Spark workers and see if the warning is gone.
意思就是sparkstream的容错机制会把 传来的数据复制一份备份,在local模式下可能出现这样的警告,spark on yarn 或者 spark alone的集群应该就不会。
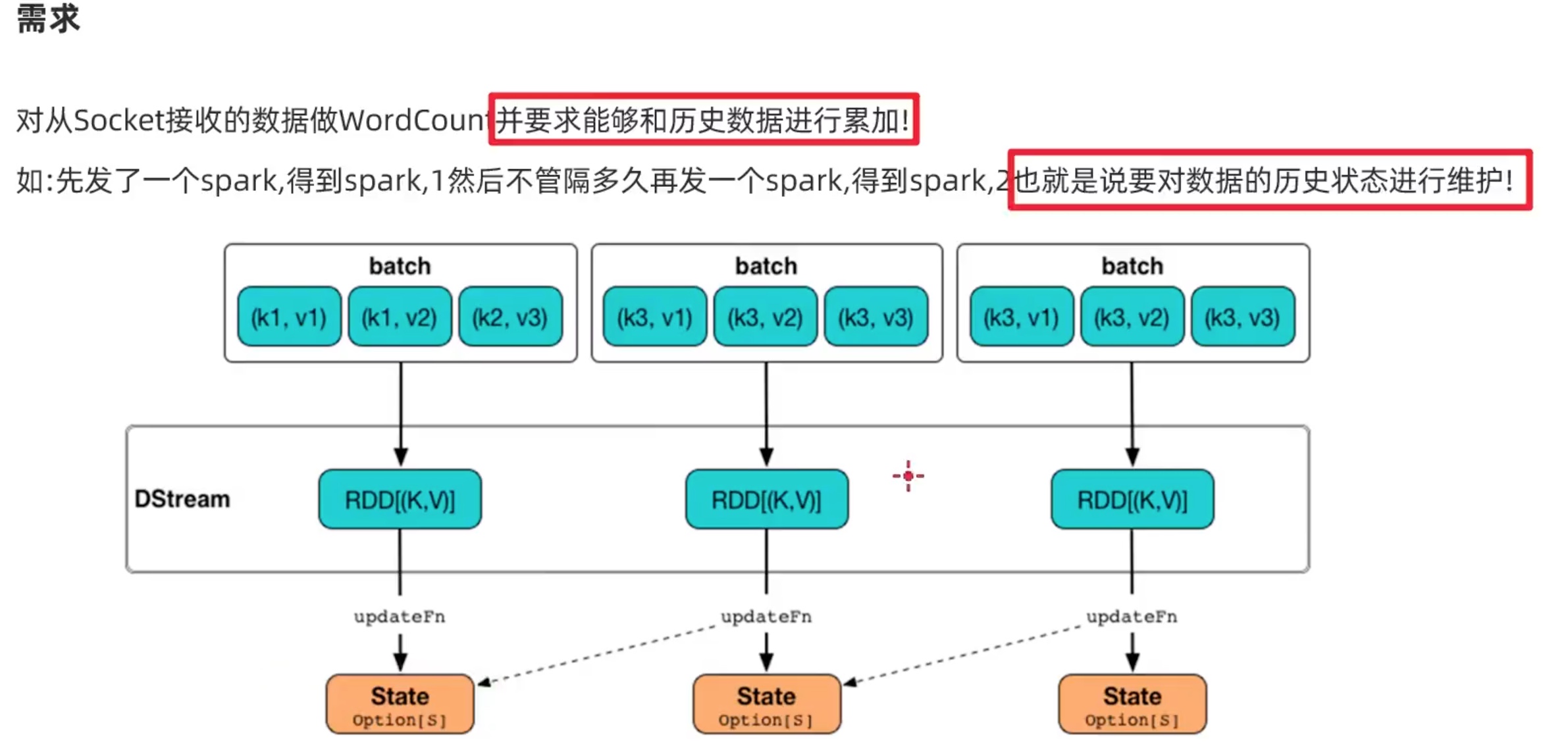
a、增加状态管理
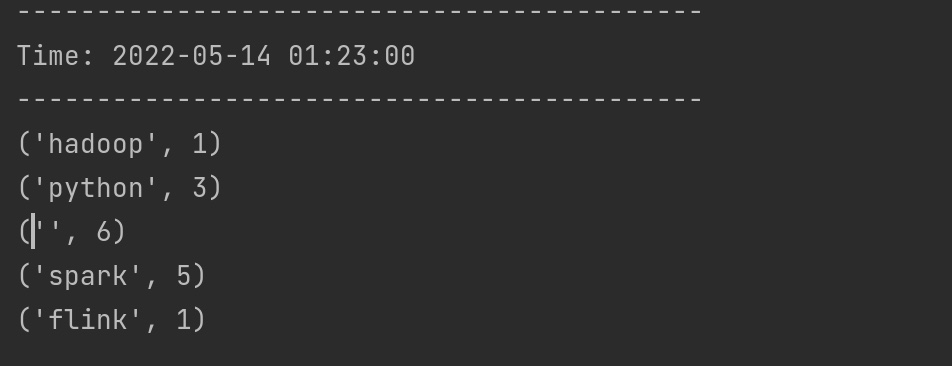
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 from pyspark import SparkContext, SparkConffrom pyspark.streaming import StreamingContextconf = SparkConf() conf.setAppName('TestDStream' ) conf.setMaster('local[*]' ) sc = SparkContext(conf = conf) ssc = StreamingContext(sc, 10 ) ssc.checkpoint(directory='file:///opt/data/sparkstream_checkpoint' ) def updateFunc (currentvalue, historyvalue ): if historyvalue==None : historyvalue = 0 if len (currentvalue)>0 : historyvalue = sum (currentvalue) + int (historyvalue) return historyvalue lines = ssc.socketTextStream('node01' ,9999 ) counts = lines.flatMap(lambda line:line.split(" " )).\ map (lambda x: (x,1 )).\ updateStateByKey(updateFunc) counts.pprint() ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 from pyspark import SparkContext, SparkConffrom pyspark.streaming import StreamingContextdef updateFunc (currentvalue_list, historyvalue ): if historyvalue==None : historyvalue = 0 if len (currentvalue_list)>0 : historyvalue = sum (currentvalue_list) + int (historyvalue) return historyvalue if __name__=='__main__' : conf = SparkConf() conf.setAppName('TestDStream' ) conf.setMaster('local[*]' ) sc = SparkContext(conf=conf) ssc = StreamingContext(sc, 5 ) ssc.checkpoint(directory='file:///opt/data/sparkstream_checkpoint' ) lines = ssc.socketTextStream('node01' ,9999 ) counts = lines.flatMap(lambda line:line.split(" " )). \ map (lambda x: (x,1 )). \ updateStateByKey(updateFunc) counts.pprint() ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() ssc.stop(stopSparkContext=True ,stopGraceFully=True )
可见加入了我们自定义的状态管理方法后,统计了历史状态的全部单词计数。(我不小心打的空格键也被计数记录了进去)。
b、状态恢复 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 from pyspark import SparkContext, SparkConffrom pyspark.streaming import StreamingContextimport timedef updateFunc (currentvalue_list, historyvalue ): if historyvalue==None : historyvalue = 0 if len (currentvalue_list)>0 : historyvalue = sum (currentvalue_list) + int (historyvalue) return historyvalue def setupfunc (): conf = SparkConf() conf.setAppName('TestDStream' ) conf.setMaster('local[*]' ) sc = SparkContext(conf=conf) ssc = StreamingContext(sc, 5 ) ssc.checkpoint(directory='file:///opt/data/sparkstream_checkpoint' ) lines = ssc.socketTextStream('node01' ,9999 ) counts = lines.flatMap(lambda line:line.split(" " )).\ map (lambda x: (x,1 )).\ updateStateByKey(updateFunc) counts.pprint() return ssc if __name__=='__main__' : ssc = StreamingContext.getOrCreate(checkpointPath='file:///opt/data/sparkstream_checkpoint' , setupFunc=setupfunc) ssc.start() time.sleep(5 ) ssc.awaitTermination() ssc.stop(stopSparkContext=True ,stopGraceFully=True )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 from pyspark import SparkContext, SparkConffrom pyspark.streaming import StreamingContextdef updateFunc (currentvalue_list, historyvalue ): if historyvalue==None : historyvalue = 0 if len (currentvalue_list)>0 : historyvalue = sum (currentvalue_list) + int (historyvalue) return historyvalue def setupfunc (): conf = SparkConf() conf.setAppName('TestDStream' ) conf.setMaster('local[*]' ) sc = SparkContext(conf=conf) ssc = StreamingContext(sc, 5 ) ssc.checkpoint(directory='file:///opt/data/sparkstream_checkpoint' ) lines = ssc.socketTextStream('node01' ,9999 ) counts = lines.flatMap(lambda line:line.split(" " )).\ map (lambda x: (x,1 )).\ updateStateByKey(updateFunc) counts.pprint() return ssc if __name__=='__main__' : ssc = StreamingContext.getOrCreate(checkpointPath='file:///opt/data/sparkstream_checkpoint' , setupFunc=setupfunc) ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() ssc.stop(stopSparkContext=True ,stopGraceFully=True )
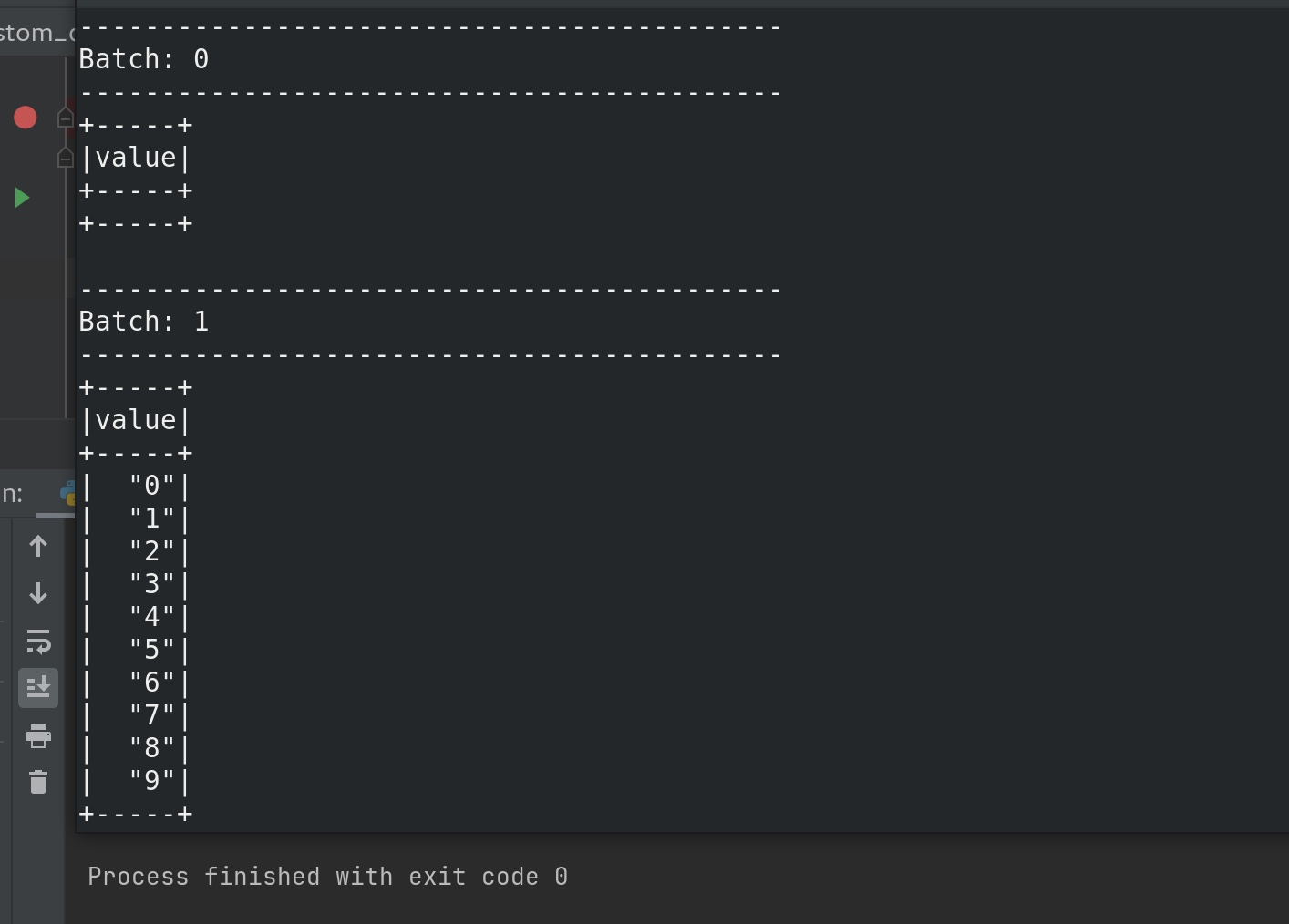
我们先在nc 中输入 spark spark spark hadoop 。
sparkstreaming的程序显示 【spark 3 hadoop 1】
故意把sparkstreaming的程序关闭。
重新运行sparkstreaming的程序,状态恢复!可见【spark 3 hadoop 1】再次被显示。
然后在nc 中输入 spark spark
sparkstreaming的程序显示 【spark 5 hadoop 1】
状态恢复成功,后续sparkstream统计词汇的程序正常运行。
三、rdd 队列流 重新介绍算子 parallelize ,将一个存在的集合,变成一个RDD。
1 2 3 4 var array = List (1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 )var rdd = sc.parallelize(array,3 )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 from pyspark import SparkContext, SparkConffrom pyspark.streaming import StreamingContextconf = SparkConf() conf.setAppName('Test_rddqueue_Stream' ) conf.setMaster('local[*]' ) sc = SparkContext(conf=conf) ssc = StreamingContext(sc, 5 ) a = [i for i in range (1 ,10 )] rdd = sc.parallelize(a,1 ) rdd2 = ssc.sparkContext.parallelize([11 ,12 ,13 ],2 ) b = ssc.queueStream([rdd,rdd2]) b = b.map (lambda x: (x,1 )) r_b = b.reduceByKey(lambda a,b: a+b) r_b.pprint() ssc.start() ssc.stop(stopSparkContext=True ,stopGraceFully=True )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 ------------------------------------------- Time: 2022 -05-13 19 :25 :45 ------------------------------------------- (2 , 1 ) (4 , 1 ) (6 , 1 ) (8 , 1 ) (1 , 1 ) (3 , 1 ) (5 , 1 ) (7 , 1 ) (9 , 1 ) ------------------------------------------- Time: 2022 -05-13 19 :25 :50 ------------------------------------------- (12 , 1 ) (11 , 1 ) (13 , 1 )
四、kafuka(Structured Streaming 实现)
或者是
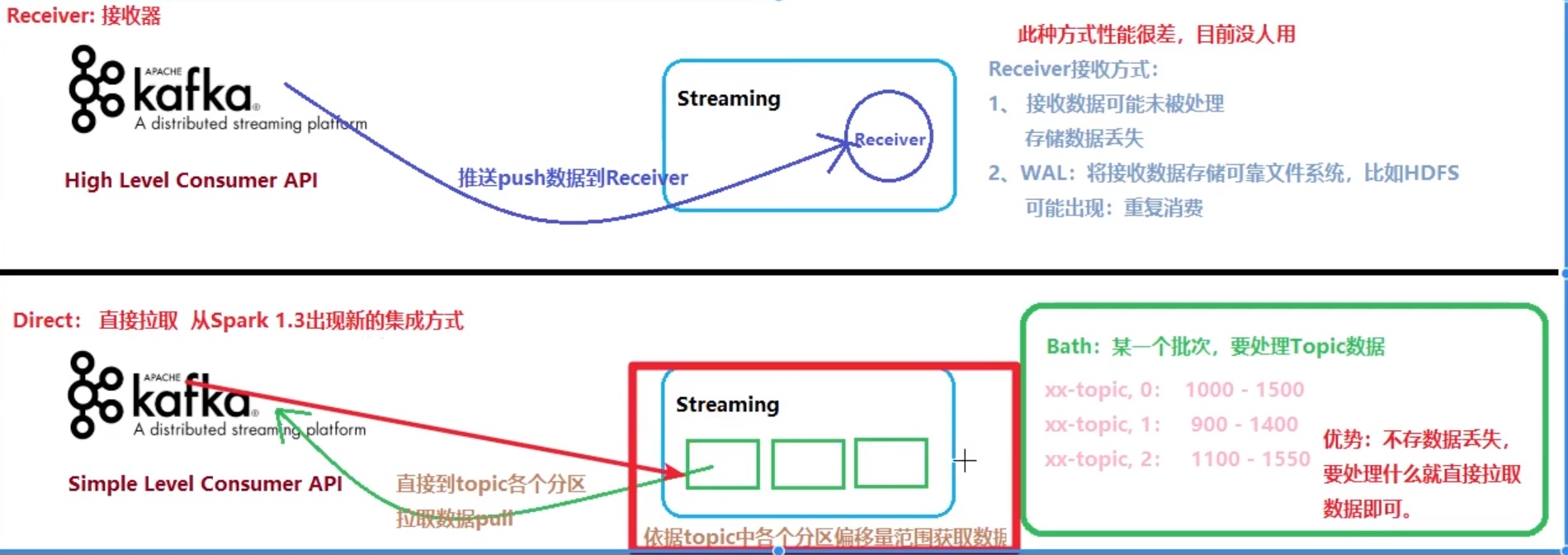
Approach 2: Direct Approach (No Receivers) 直连kafka模式在Spark1.3中支持Scala和Java,在1.4中可以支持Python。
4.1 structured接收kafka消息 可以参考:
https://juejin.cn/post/6844903460169580558 ,
https://www.cnblogs.com/leimu/p/15179692.html,
https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/structured-streaming-kafka-integration.html 这是我们接下来用到的structured-streaming介绍 。
我们知道了,自Spark 2.4起,Spark Streaming已被逐步弃用,尤其是pyspark,在spark3之后 from pyspark.streaming.kafka import KafkaUtils 就已经没法用了,因为spark3之后spark文件夹中的pyspark.streaming下面已经没有 kafuka.py了。
Apache基金会 已经把发展重点放在了 Spark Structured Streaming,我们这里直接用Spark Structured Streaming 来代替 sparkstreaming。
Structured Streaming 的关键思想是将持续不断的数据当做一个不断追加的表 。这使得[流式计算]模型与批处理计算引擎十分相似。使用类似对于静态表的批处理方式来表达流计算,然后 Spark 以在无限表上的增量计算来运行。continuous mode 是传统的流处理模式,通过运行一个 long-running 的 operator 用来处理数据。之前 Spark Streaming是基于 micro-batch 模式的,就被很多人诟病不是“真正的”流式处理。
Structured Streaming (结构化流)是一种基于 Spark SQL 引擎构建的可扩展且容错的 stream processing engine (流处理引擎)。可以使用Dataset/DataFrame API 来表示 streaming aggregations (流聚合), event-time windows (事件时间窗口), stream-to-batch joins (流到批处理连接) 等。简而言之,Structured Streaming 提供快速,可扩展,容错,end-to-end exactly-once stream processing (端到端的完全一次性流处理),且无需用户理解 streaming 。
1.导入依赖: Kafka和Flume等高级输入源,需要依赖独立的库(jar文件)。按 照我们前面安装好的Spark版本安装。我们查看自己的Scala和kafka、 spark版本号。
cd /opt/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.1.0/libs/opt/spark/spark/bin/pyspark
可见 kafka_2.13-3.1.0.jar,前面是Scala版本2.13后面是kafka版本 3.1.0,spark是3.2.1。但是我们去spark 的spark-shell 运行,可知其实运 行在spark中的scala是2.12版本!!!所以我们实际导入的jar包要求是 Scala2.12版本!!!
在以下网站下载spark和Scala对应版本的 spark- streaming-kafka 补丁,我的是
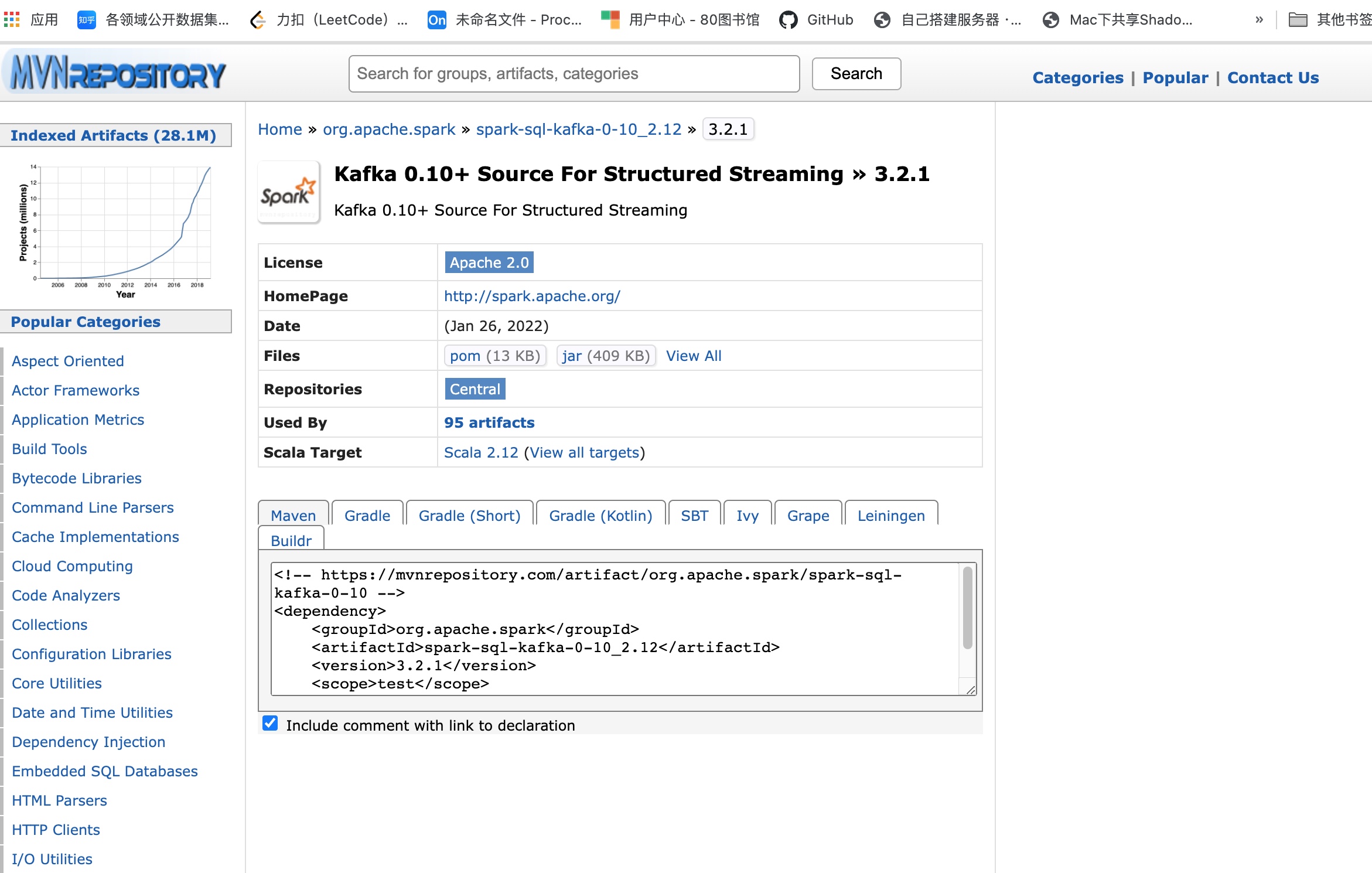
https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.spark/spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.12/3.2.1
把 spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.13-3.2.1.jar 放入 /opt/anaconda3/envs/pyspark/lib/python3.8/site-packages/pyspark/jars/ 下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 # 有的教程会说要添加某某的 pom依赖,举个例子来解释: # 搭建开发环境需要引入kafka的jar包,一种方式是将Kafka安装包中lib下的jar包加入到项目的classpath中,这种比较简单了。不过我们使用另一种更加流行的方式:使用maven管理jar包依赖。 # 创建好maven项目后,在pom.xml中添加以下依赖: <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.spark/spark-sql-kafka-0-10 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId> <artifactId>spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.13</artifactId> <version>3.2.1</version> </dependency>
pyspark中调用包间接使用maven,不用在pom.xml文件中配置,但是每次用要 用如下写法间接调用maven的jar包,有点麻烦额,毕竟python只是干儿子。
1 2 3 4 5 bin/spark-submit --packages org.apache.spark:spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.12:3.2.1 /opt/data/sparkstreaming/structured_receive_from_kafuka.py # --packages 后面跟的是maven格式中的groupId:artifactId:version,中间用 : 隔开。 # 运行一次以后,我们不用去管,等待一阵子,maven会被自动下载好,并且上面的相关依赖jar包也会下载好。 # 之后程序正常运行。
2.建立kafka生产者 1 2 3 4 # 启动zookeeper集群,在每台机器上开启。 /opt/zookeeper/bin/zkServer.sh start # 集群各节点 启动 kafka 服务。 /opt/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.1.0/bin/kafka-server-start.sh -daemon /opt/kafka/kafka_2.13-3.1.0/config/server.properties
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server node01:9092 --create --topic kafka-produce-topic --partitions 3 --replication-factor 2 vim kafka-produce.py from kafka import KafkaProducerfrom kafka.errors import kafka_errorsimport tracebackimport jsondef create_producer (): producer = KafkaProducer( bootstrap_servers=['node01:9092' ], acks=1 , key_serializer=lambda k: json.dumps(k).encode(), value_serializer=lambda v: json.dumps(v).encode() ) for i in range (0 ,10 ): future = producer.send( 'kafka-produce-topic' , key='count_num' , value=str (i), partition=2 ) print ('send {}' .format (str (i))) try : future.get(timeout=10 ) print ( 'producer send %d is ok! ' %(i)) print (type (future)) except kafka_errors: traceback.format_exc() producer.close() if __name__ == '__main__' : create_producer()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 # 运行kafka生产者 python kafka-produce.py # 查看topic列表 kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server node01:9092 --list # 验证创建的 topic kafka-topics.sh --describe --topic kafka-produce-topic --bootstrap-server node01:9092
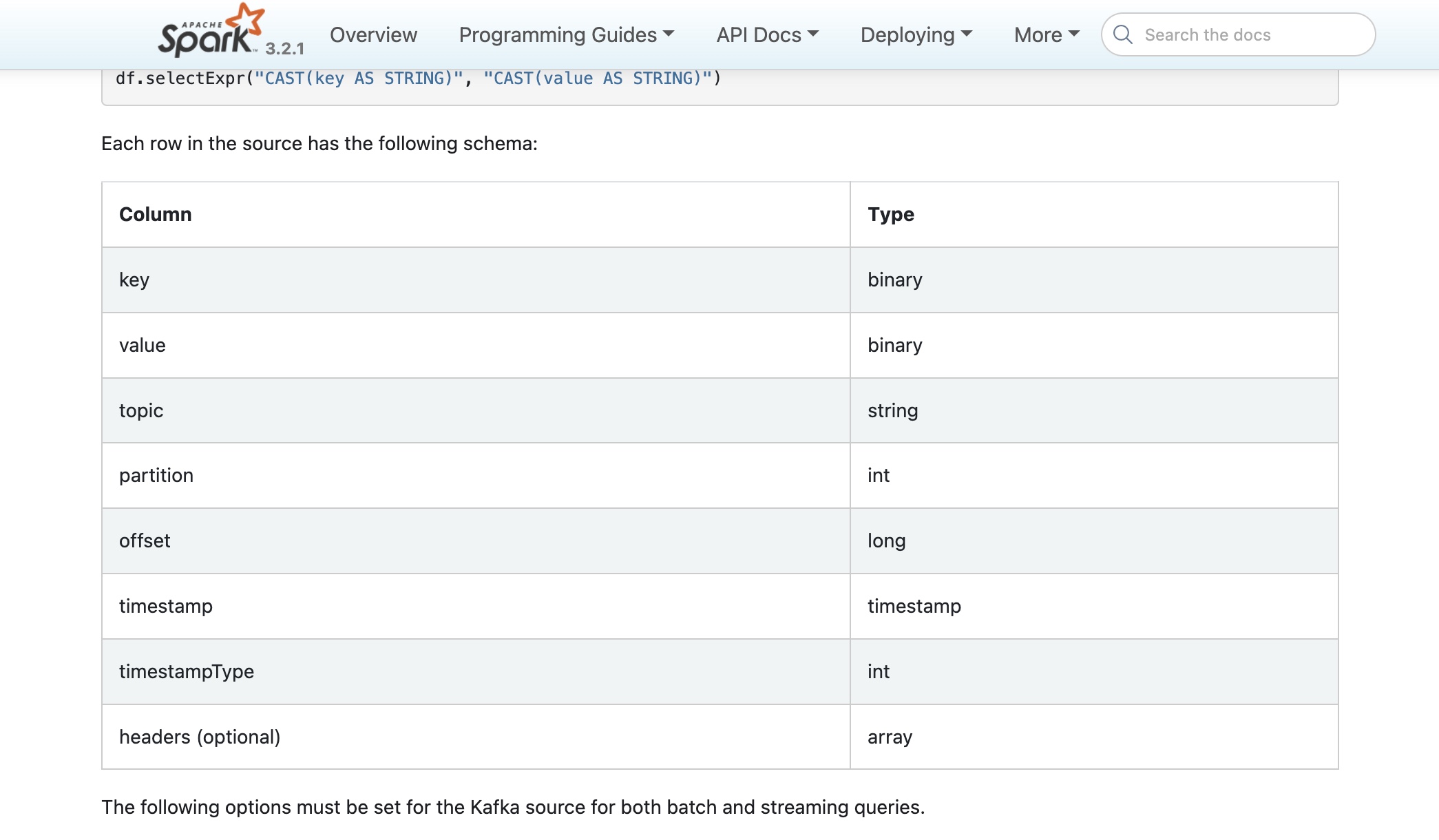
3.收取kafka数据 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 from pyspark.sql import SparkSessionfrom pyspark.sql import functions as Ffrom pyspark.storagelevel import StorageLevelfrom pyspark.sql.types import StringType,StructType''' Reading Data from Kafka Creating a Kafka Source for Streaming Queries ''' if __name__=='__main__' : spark = SparkSession.builder.appName('structured_receive_kafka' ).\ master('local[*]' ).config('spark.sql.shuffle.partitions' ,'2' ).\ getOrCreate() df = spark.readStream.format ('kafka' ).\ option('kafka.bootstrap.servers' ,'node01:9092' ).\ option('subscribe' ,'kafka-produce-topic' ).\ load() nums = df.selectExpr( "CAST(value AS STRING)" ) print (type (df),df) query = nums.writeStream \ .format ('console' )\ .outputMode('append' )\ .start() query.awaitTermination()
执行步骤:
1、运行pyspark的structure-stream接收程序。
bin/spark-submit --packages org.apache.spark:spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.12:3.2.1 /opt/data/sparkstreaming/structured_receive_from_kafuka.py
2、运行kafka的生产程序。
python kafka-produce.py
终端可见成功接收kafka生产的数据:
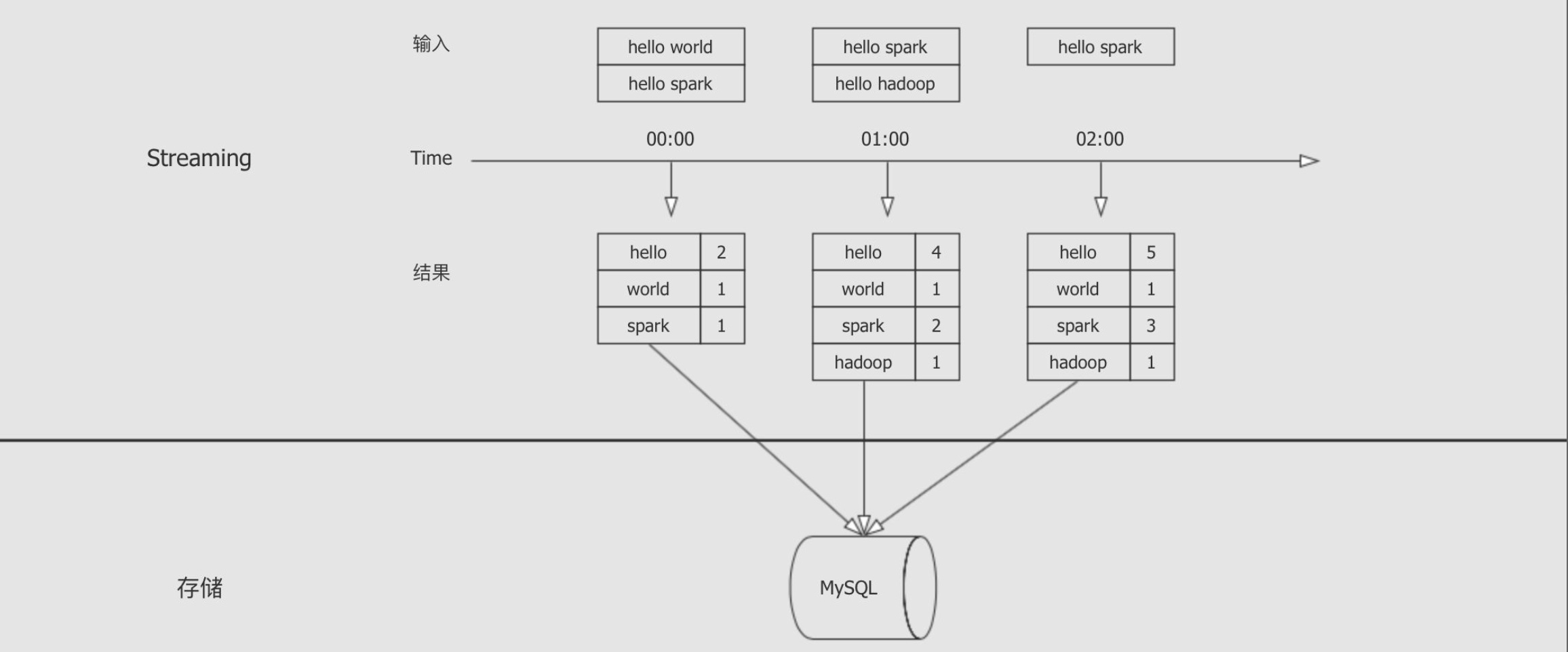
SparkStreaming 应用窗口计算
这里的窗口和 hive 、spark 之前说的窗口函数不是一回事,这里的意思是用一个窗口把一个时间段框起来,每隔多久,用Dstream 来计算一次。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 from pyspark import SparkContext, SparkConffrom pyspark.streaming import StreamingContextif __name__=='__main__' : conf = SparkConf() conf.setAppName('TestDStream' ) conf.setMaster('local[*]' ) sc = SparkContext(conf=conf) ssc = StreamingContext(sc, 5 ) ssc.checkpoint(directory='file:///opt/data/sparkstream_checkpoint' ) lines = ssc.socketTextStream('node01' ,9999 ) counts = lines.flatMap(lambda line:line.split(" " )). \ map (lambda x: (x,1 )). \ reduceByKeyAndWindow(func=lambda a,b:a+b,invFunc=None ,windowDuration=10 ,slideDuration=5 ) counts.pprint() ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() ssc.stop(stopSparkContext=True ,stopGraceFully=True )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 ''' 上海分阶段复商复市 上海分阶段复商复市 上海分阶段复商复市 上海分阶段复商复市 上海分阶段复商复市 上海分阶段复商复市 四川邻水一周现499例感染者 已外溢 四川邻水一周现499例感染者 已外溢 围观火爆全网的国字脸猴子 粮食是国之大者咱们一起端稳热 粮食是国之大者咱们一起端稳热 粮食是国之大者咱们一起端稳热 鸡鸭吃泡酒桑葚醉死 主人含泪吃3碗 1992年茅台起拍价3999万元新 河北磁县回应农民春耕办不了通行证 河北磁县回应农民春耕办不了通行证 男子购买“疫情险” 男子购买“疫情险” 男子购买“疫情险” 男子购买“疫情险” 男子购买“疫情险” 男子购买“疫情险” 男子购买“疫情险” 男子购买“疫情险” 学生反映饭菜难吃被回复没良心新 夫人锐利一眼 韩总统放下酒杯 记者实拍亚速钢铁厂激烈交战 成都天空现黑圈 官方:电力设施故障新 成都天空现黑圈 官方:电力设施故障新 成都天空现黑圈 官方:电力设施故障新 成都天空现黑圈 官方:电力设施故障新 苍山13人差一两公里就到飞机坠毁地 央媒:“井盖吃人”顽疾必须治 不明原因儿童急性肝炎最新发现 俄军在乌每天消耗61亿元人民币 ''' from pyspark import SparkContext, SparkConffrom pyspark.streaming import StreamingContextdef dstream_sorted (rdd ): rdd2 = rdd.sortBy(lambda x: x[1 ],ascending=False ,numPartitions=1 ) rdd2_top3_list = rdd2.take(3 ) print ('===== top3 =====' ) print (rdd2_top3_list) print ('===== top3 =====' ) return rdd2 if __name__=='__main__' : conf = SparkConf() conf.setAppName('TestDStream' ) conf.setMaster('local[*]' ) sc = SparkContext(conf=conf) ssc = StreamingContext(sc, 5 ) ssc.checkpoint(directory='file:///opt/data/sparkstream_checkpoint' ) lines = ssc.socketTextStream('node01' ,9999 ) counts = lines.flatMap(lambda line:line.split(" " )). \ map (lambda x: (x,1 )). \ reduceByKeyAndWindow(func=lambda a,b:a+b,invFunc=None ,windowDuration=10 ,slideDuration=5 ) counts_sorted = counts.transform(dstream_sorted) counts_sorted.pprint() ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() ssc.stop(stopSparkContext=True ,stopGraceFully=True )
在nc 输入 上述 百度热搜榜单后,可见一个窗口时间内输出如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 ===== top3 ===== [('男子购买“疫情险”' , 8 ), ('上海分阶段复商复市' , 6 ), ('官方:电力设施故障新' , 4 )] ===== top3 ===== ------------------------------------------- Time: 2022 -05-16 03:33 :15 ------------------------------------------- ('男子购买“疫情险”' , 8 ) ('上海分阶段复商复市' , 6 ) ('官方:电力设施故障新' , 4 ) ('成都天空现黑圈' , 4 ) ('粮食是国之大者咱们一起端稳热' , 3 ) ('河北磁县回应农民春耕办不了通行证' , 2 ) ('四川邻水一周现499例感染者' , 2 ) ('已外溢' , 2 ) ('围观火爆全网的国字脸猴子' , 1 ) ('鸡鸭吃泡酒桑葚醉死' , 1 ) ... ===== top3 ===== [] ===== top3 ===== ------------------------------------------- Time: 2022 -05-16 03:36 :10 ------------------------------------------- ===== top3 ===== [] ===== top3 ===== ------------------------------------------- Time: 2022 -05-16 03:36 :15 -------------------------------------------
自定义输出 dstream的pprint() 源代码就是调用了foreachRDD()方法,自定义输出就是我们自己用 foreachRDD() 方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 ''' 上海分阶段复商复市 上海分阶段复商复市 上海分阶段复商复市 上海分阶段复商复市 上海分阶段复商复市 上海分阶段复商复市 四川邻水一周现499例感染者 已外溢 四川邻水一周现499例感染者 已外溢 围观火爆全网的国字脸猴子 粮食是国之大者咱们一起端稳热 粮食是国之大者咱们一起端稳热 粮食是国之大者咱们一起端稳热 鸡鸭吃泡酒桑葚醉死 主人含泪吃3碗 1992年茅台起拍价3999万元新 河北磁县回应农民春耕办不了通行证 河北磁县回应农民春耕办不了通行证 男子购买“疫情险” 男子购买“疫情险” 男子购买“疫情险” 男子购买“疫情险” 男子购买“疫情险” 男子购买“疫情险” 男子购买“疫情险” 男子购买“疫情险” 学生反映饭菜难吃被回复没良心新 夫人锐利一眼 韩总统放下酒杯 记者实拍亚速钢铁厂激烈交战 成都天空现黑圈 官方:电力设施故障新 成都天空现黑圈 官方:电力设施故障新 成都天空现黑圈 官方:电力设施故障新 成都天空现黑圈 官方:电力设施故障新 苍山13人差一两公里就到飞机坠毁地 央媒:“井盖吃人”顽疾必须治 不明原因儿童急性肝炎最新发现 俄军在乌每天消耗61亿元人民币 ''' from pyspark import SparkContext, SparkConffrom pyspark.streaming import StreamingContextfrom pyspark.storagelevel import StorageLevelfrom pyspark.sql import SparkSessionimport timeimport redef dstream_sorted (rdd ): rdd2 = rdd.sortBy(lambda x: x[1 ],ascending=False ,numPartitions=1 ) rdd2_top3_list = rdd2.take(3 ) print ('===== top3 =====' ) print (rdd2_top3_list) print ('===== top3 =====' ) return rdd2 def cdo (datetime,rdd ): print ('===== constomer defined output =====' ) print (datetime) print ('===== constomer defined output =====' ) rdd.persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_ONLY) rdd.foreach(lambda x: print (x)) datetime_str = re.sub('[-: ]' ,'' ,str (datetime)) print (datetime_str) print (type (rdd),'\n has toDF Func? :' ,hasattr (rdd,'toDF' )) if rdd.isEmpty() == False : rdd.repartition(1 ).saveAsTextFile('hdfs://node01:9000/spark_study/sparkstream_study/' +datetime_str) df = rdd.toDF(['key' ,'num_of_search' ]) df.write.mode('overwrite' ). \ format ('jdbc' ). \ option('url' ,'jdbc:mysql://node01:3306/spark_databases?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true' ). \ option('dbtable' ,'hotsearch_table' +datetime_str). \ option('user' ,'root' ). \ option('password' ,'cys123456' ). \ save() rdd.unpersist() if __name__=='__main__' : conf = SparkConf() conf.setAppName('TestDStream' ) conf.setMaster('local[*]' ) sc = SparkContext(conf=conf) sparksession = SparkSession(sc) ssc = StreamingContext(sc, 5 ) ssc.checkpoint(directory='file:///opt/data/sparkstream_checkpoint' ) lines = ssc.socketTextStream('node01' ,9999 ) counts_stream = lines.flatMap(lambda line:line.split(" " )). \ map (lambda x: (x,1 )). \ reduceByKeyAndWindow(func=lambda a,b:a+b,invFunc=None ,windowDuration=10 ,slideDuration=5 ) counts_sorted_stream = counts_stream.transform(dstream_sorted) counts_sorted_stream.pprint() counts_sorted_stream.foreachRDD(cdo) ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() ssc.stop(stopSparkContext=True ,stopGraceFully=True )
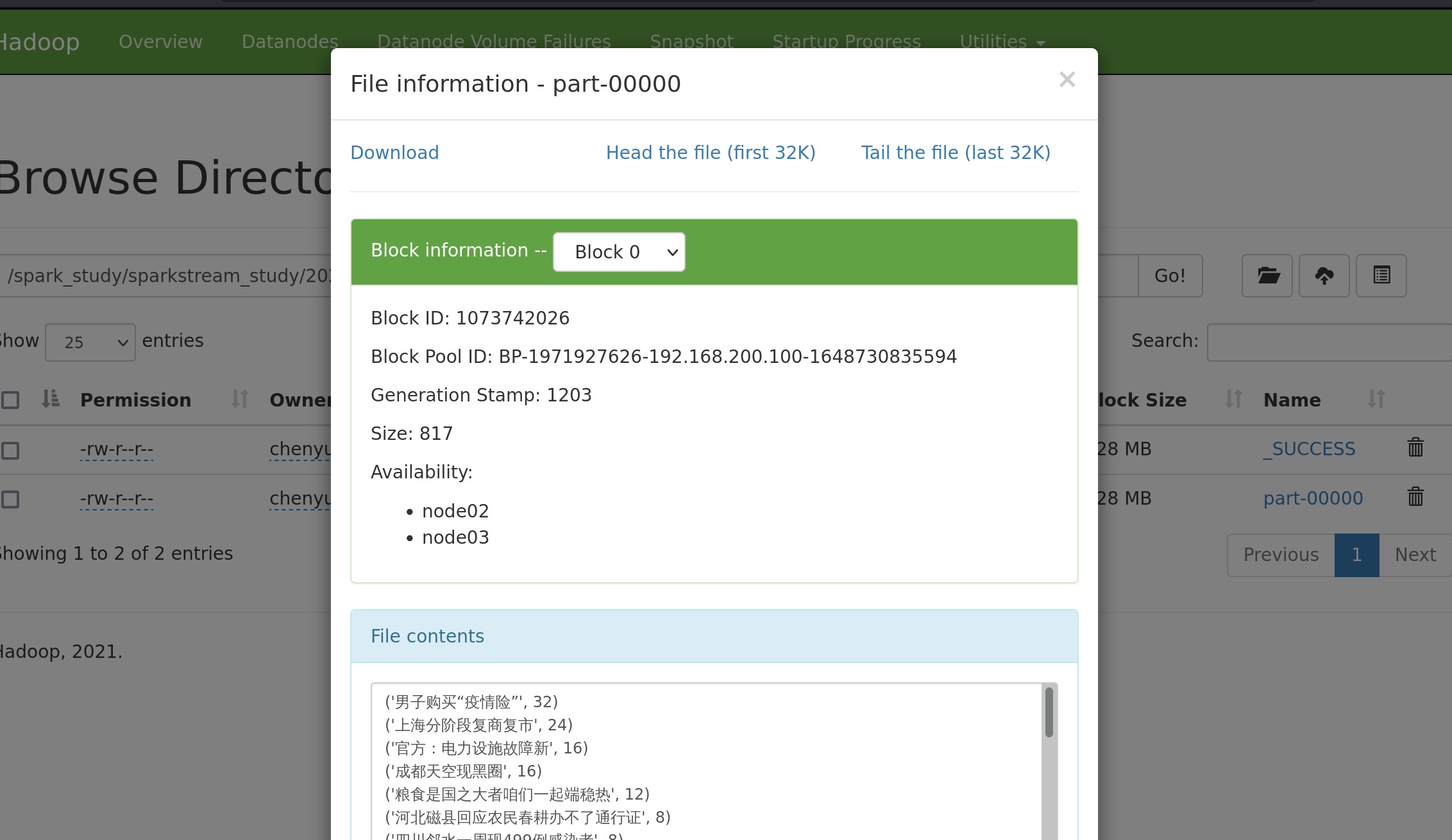
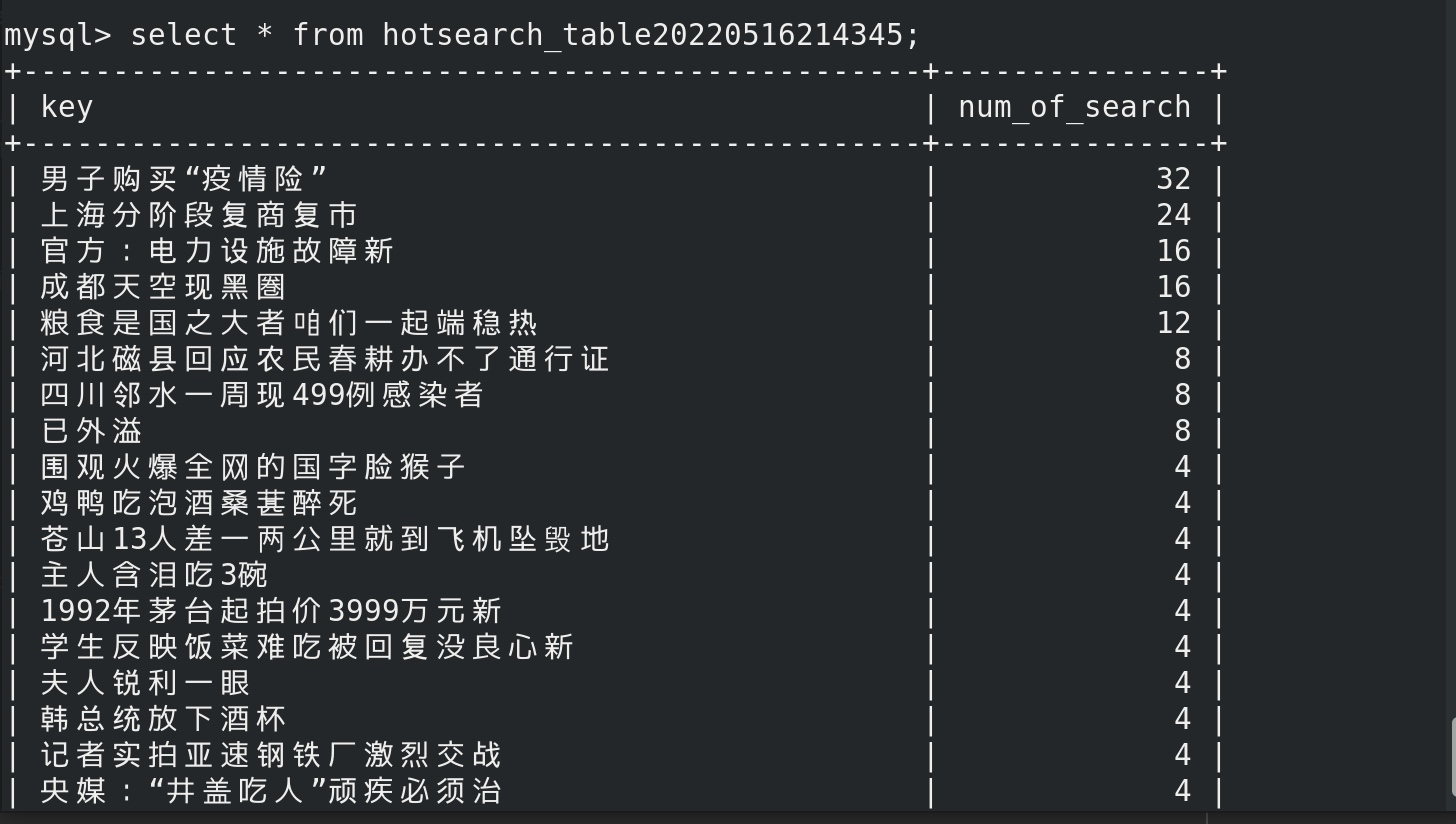
在nc端, 10秒钟之内输入上述热搜内容4次,在mysql对应文件夹和hdfs对应文件夹内可见:
然后随着时间的推移,窗口向后滑动5秒,counts_stream把10秒钟内的历史rdd再都算一遍。男子购买“疫情险” num_of_search 可能会变成32、24、16、8、或者为rdd为空不再储存……
再随着时间的推移,窗口向后滑动5秒,counts_stream把10秒钟内的历史rdd再都算一遍。发现counts_stream内的rdd为空,不再储存。其他key 依此类推。
spark- structure-stream学习 前面在spark接收kafka数据的案例中已经用过了spark-structure-stream ,但是在这里我们在补充一些案例。
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33689414/article/details/86469267
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_35154281/article/details/116883816?spm=1001.2101.3001.6650.1&utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-2%7Edefault%7ECTRLIST%7ERate-1-116883816-blog-86469267.pc_relevant_antiscanv3&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-2%7Edefault%7ECTRLIST%7ERate-1-116883816-blog-86469267.pc_relevant_antiscanv3&utm_relevant_index=2
https://spark.apache.org/docs/3.2.1/structured-streaming-kafka-integration.html
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1WV411y7NQ?p=6&spm_id_from=pageDriver
kafka- streaming vim kafka_structure_streaming.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 from pyspark.sql import SparkSessionfrom pyspark.sql import functions as Ffrom pyspark.sql.types import TimestampTypespark = SparkSession.builder\ .appName('structure_word_count' )\ .getOrCreate() sc = spark.sparkContext sc.setLogLevel('WARN' ) df = spark.readStream\ .format ('kafka' )\ .option('kafka.bootstrap.servers' ,'node01:9092' )\ .option('subscribe' ,'kafka-structure-stream' )\ .load() df.writeStream \ .format ('console' ) \ .outputMode('update' ) \ .option('truncate' ,False )\ .start() \ .awaitTermination() spark.stop()
kafka 有标准的输出模式
1 2 3 4 5 kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server node01:9092 --create --topic kafka-structure-stream --partitions 3 --replication-factor 2 kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list node01:9092 --topic kafka-structure-stream spark-submit --packages org.apache.spark:spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.12:3.2.1 /opt/data/spark-structure-streaming/kafka_structure_streaming.py
可见kafka标准输出格式。
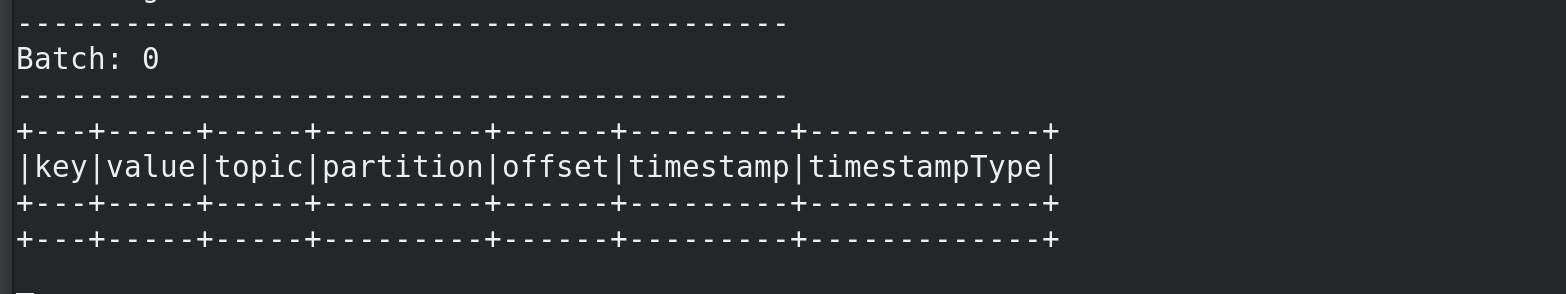
在kafka的生产者输入 a b c spark终端可见:
可以看见kafka的标准输入数据类型。所以一般我们在接收kafka数据时给个类型转换。
一个最简单的流式词频统计,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 from pyspark.sql import SparkSessionfrom pyspark.sql import functions as Ffrom pyspark.sql.types import TimestampTypespark = SparkSession.builder\ .appName('structure_word_count' )\ .getOrCreate() sc = spark.sparkContext sc.setLogLevel('WARN' ) df = spark.readStream\ .format ('kafka' )\ .option('kafka.bootstrap.servers' ,'node01:9092' )\ .option('subscribe' ,'kafka-structure-stream' )\ .load()\ .selectExpr('cast(value as string)' ) df = df.select(F.explode( F.split(df.value,' ' )).alias('value' ))\ .groupBy('value' )\ .count() df.writeStream \ .format ('console' ) \ .outputMode('update' ) \ .option("truncate" ,False ) \ .start() \ .awaitTermination() spark.stop()
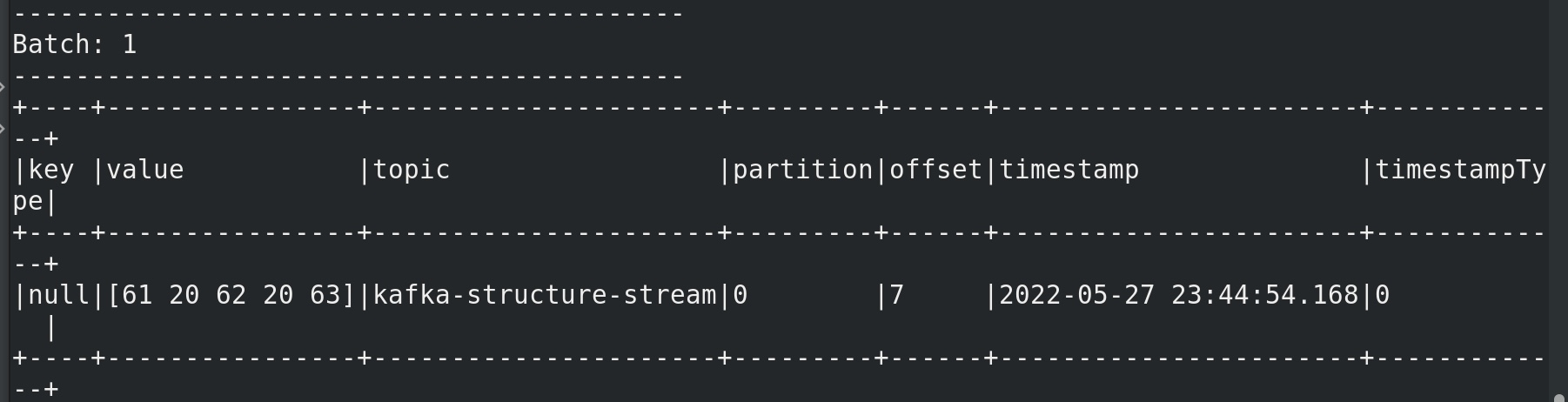
在 kafka生产者输入 a b c a ,终端可见
一个最简单的批处理batch query,词频统计,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 from pyspark.sql import SparkSessionfrom pyspark.sql import functions as Ffrom pyspark.sql.types import TimestampTypespark = SparkSession.builder\ .appName('structure_word_count' )\ .getOrCreate() sc = spark.sparkContext sc.setLogLevel('WARN' ) df = spark.read\ .format ('kafka' )\ .option('kafka.bootstrap.servers' ,'node01:9092' )\ .option('subscribe' ,'kafka-structure-stream' )\ .option('startingOffsets' ,'earliest' )\ .option('endingOffsets' ,'latest' )\ .load()\ .selectExpr('cast(value as string)' ) df = df.select(F.explode( F.split(df.value,' ' )).alias('value' ))\ .groupBy('value' )\ .count() df.write \ .format ('console' ) \ .option("truncate" ,False ) \ .save()
终端可见,kafka生产者还没有新输入内容,kafka的topic内的旧内容被批处理输出了:
批处理是一次性算完的,没有流式计算的流式。
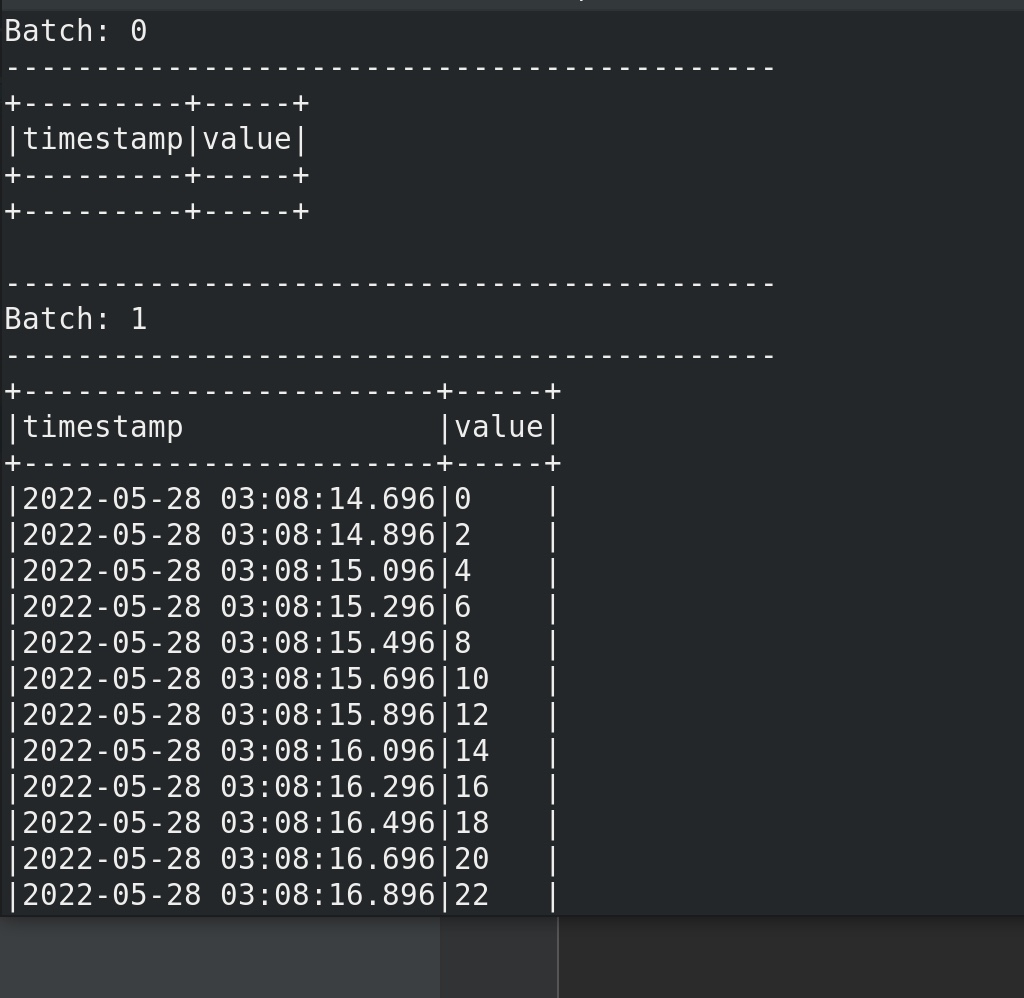
ratesource 以固定的速率生成固定的格式的数据,用以检测structure streaming 的性能。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 from pyspark.sql import SparkSessionfrom pyspark.sql import functions as Ffrom pyspark.sql.types import TimestampTypespark = SparkSession.builder \ .appName('structure_word_count' ) \ .getOrCreate() sc = spark.sparkContext sc.setLogLevel('WARN' ) df = spark.readStream \ .format ('rate' ) \ .option('rowsPerSecond' ,'100' ) \ .option('rampUpTime' ,1 ) \ .option('numPartitions' ,3 )\ .load() \ df.writeStream \ .format ('console' ) \ .outputMode('update' ) \ .option("truncate" ,False ) \ .start() \ .awaitTermination() spark.stop()
spark-submit --packages org.apache.spark:spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.12:3.2.1 /opt/data/spark-structure-streaming/rate_source_test.py
控制台可见
window操作 structure-streaming 的window操作一定要求数据有时间戳timestamp。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 from pyspark.sql import SparkSessionfrom pyspark.sql import functions as Ffrom pyspark.sql.types import TimestampTypespark = SparkSession.builder \ .appName('structure_test' ) \ .getOrCreate() sc = spark.sparkContext sc.setLogLevel('WARN' ) df = spark.readStream \ .format ('kafka' ) \ .option('kafka.bootstrap.servers' ,'node01:9092' ) \ .option('subscribe' ,'kafka-structure-stream' ) \ .load() df.selectExpr('cast(value as string)' ,'timestamp' )\ .writeStream \ .format ('console' ) \ .outputMode('update' ) \ .option("truncate" ,False ) \ .start() \ .awaitTermination() spark.stop()
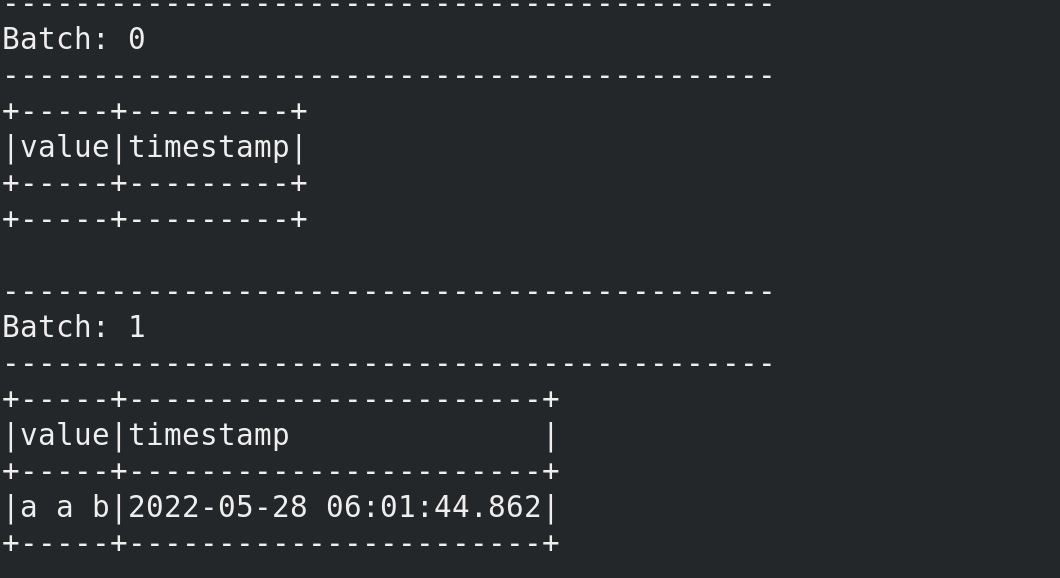
注意:上面的时间戳 实际是spark收到数据的时间点,spark拿收到数据时的时间点 假定为事件发生时间event-time。下图的time就是spark收到数据的时间– 伪event-time。
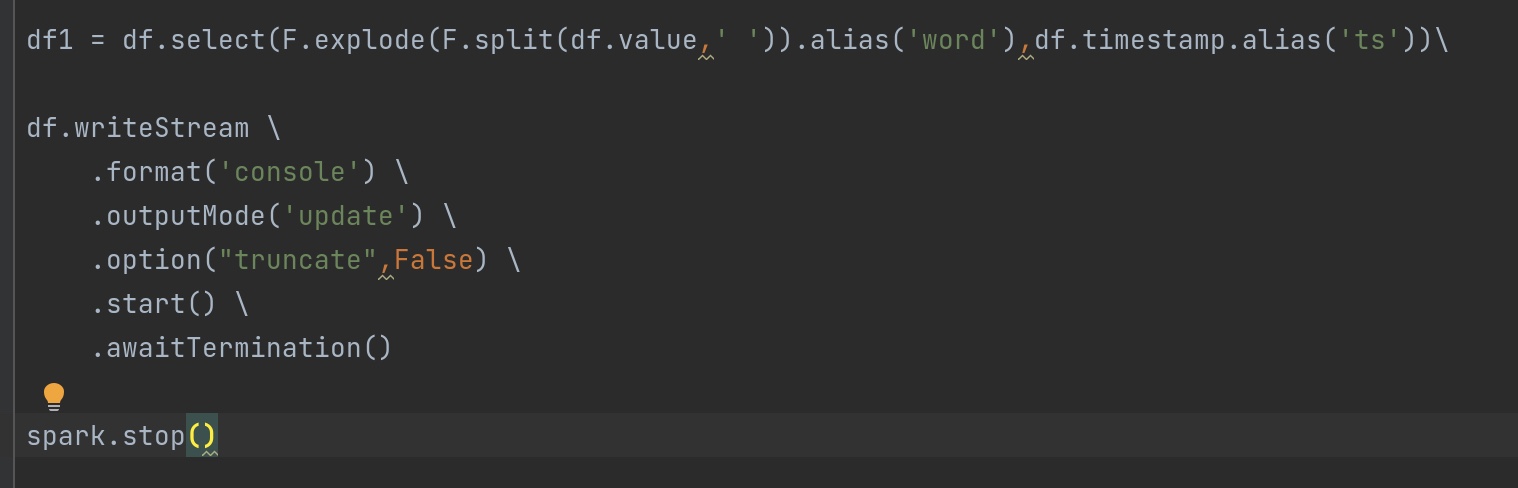
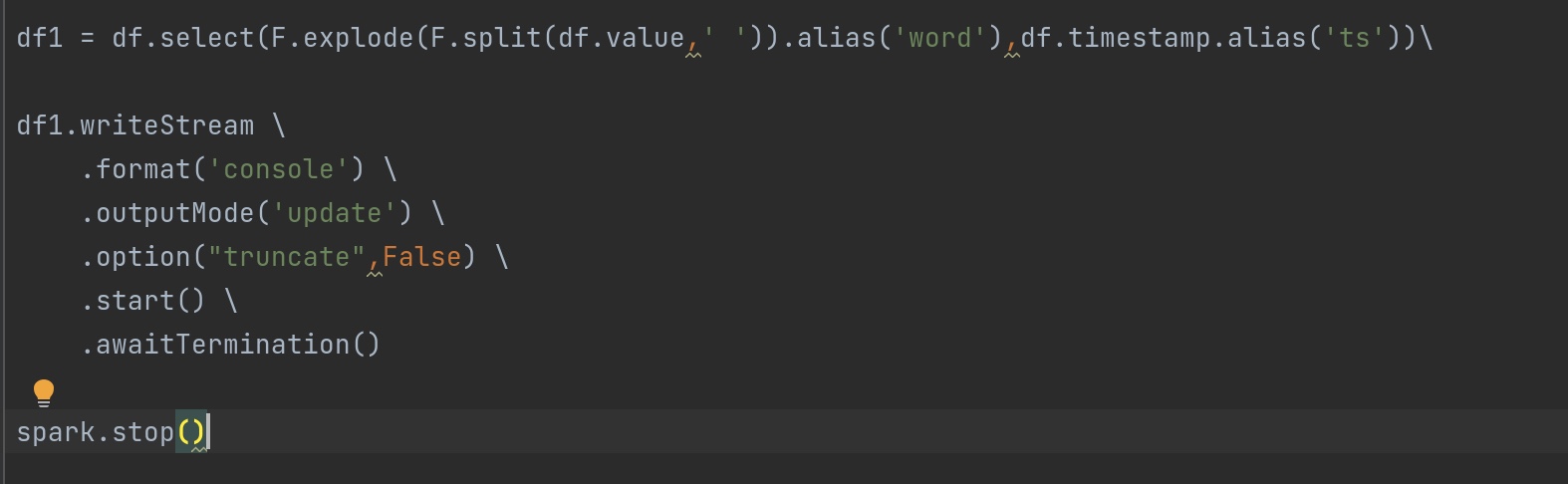
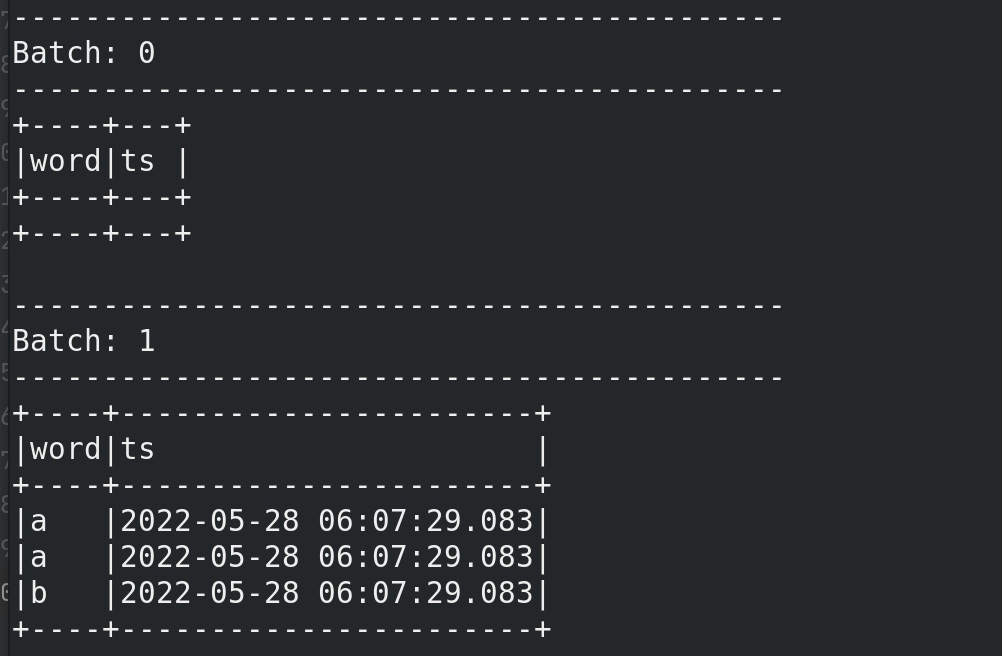
对比一下 以下修改dataframe前后的输出结果:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 from pyspark.sql import SparkSessionfrom pyspark.sql import functions as Ffrom pyspark.sql.types import TimestampTypespark = SparkSession.builder \ .appName('structure_test' ) \ .getOrCreate() sc = spark.sparkContext sc.setLogLevel('WARN' ) df = spark.readStream \ .format ('kafka' ) \ .option('kafka.bootstrap.servers' ,'node01:9092' ) \ .option('subscribe' ,'kafka-structure-stream' ) \ .load()\ .selectExpr('cast(value as string)' ,'cast(timestamp as string)' ) df1 = df.select(F.explode(F.split(df.value,' ' )).alias('word' ),df.timestamp.alias('ts' )) df2 = df1.groupBy(F.window(df1.ts,'1 minutes' ,'1 minutes' ),df1.word)\ .count() df2.writeStream \ .format ('console' ) \ .outputMode('update' ) \ .option("truncate" ,False ) \ .start() \ .awaitTermination() spark.stop()
spark-submit --packages org.apache.spark:spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.12:3.2.1 /opt/data/spark-structure-streaming/window_test.py
在kafka生产者输入 a a b ,终端可见:
一个常见的错误:
org.apache.spark.sql.AnalysisException: resolved attribute(s)
这是由于 df1 是由前一个df派生出来的,一旦df和df1的属性混乱,会出现这类报错。按照我们上面的例子, df1.groupBy(F.window(df1.ts,'1 minutes','1 minutes'),df1.word) 写成了 df1.groupBy(F.window(df.ts,'1 minutes','1 minutes'),df.word) 就会报此类错误。
另外补充一个知识点:
流式计算过程中是不能有dataframe转rdd的操作
不然会出现报错:
Queries with streaming sources must be executed with writeStream.start()
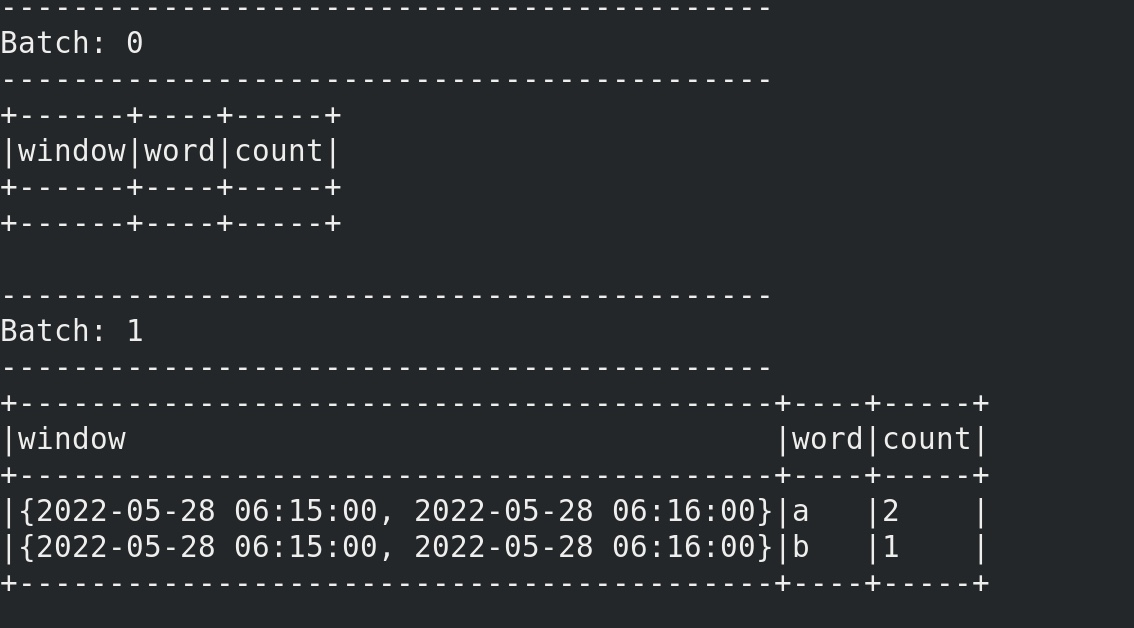
最大窗口数(重叠数) 最大窗口数maxnumoverlapping = 「窗口长度/滑动长度」()向上取整
maxnumoverlapping 英文其实更加准确一些,是最大滞留的数目,比如说 windowsduration=10,slideduration=5,那么maxnumoverlapping=10/5向上取整=2,某个时间点最大滞留在两个窗口内,比如:12最大滞留在两个窗口区间内。
我们用一个例子解释上述伪代码:
windowsduration=10,slideduration=5,starttime秒数=00,
timestamp现在的时间戳=52分12秒,
maxnumoverlapping=10/5向上取整=2。
windowid = 52.12/5 = 11
for 循环 会循环出 最大的滞留窗口数:
第一个windowstart = 11 * 5 + (0-2)*5 + 00 = 45.00
第二个windowstart = 11 * 5 + (1-2)*5 +00 = 50.00
也就是说 52.00 这个时间点接收了一个hello单词这个 事件,会出现在两个窗口区间内:
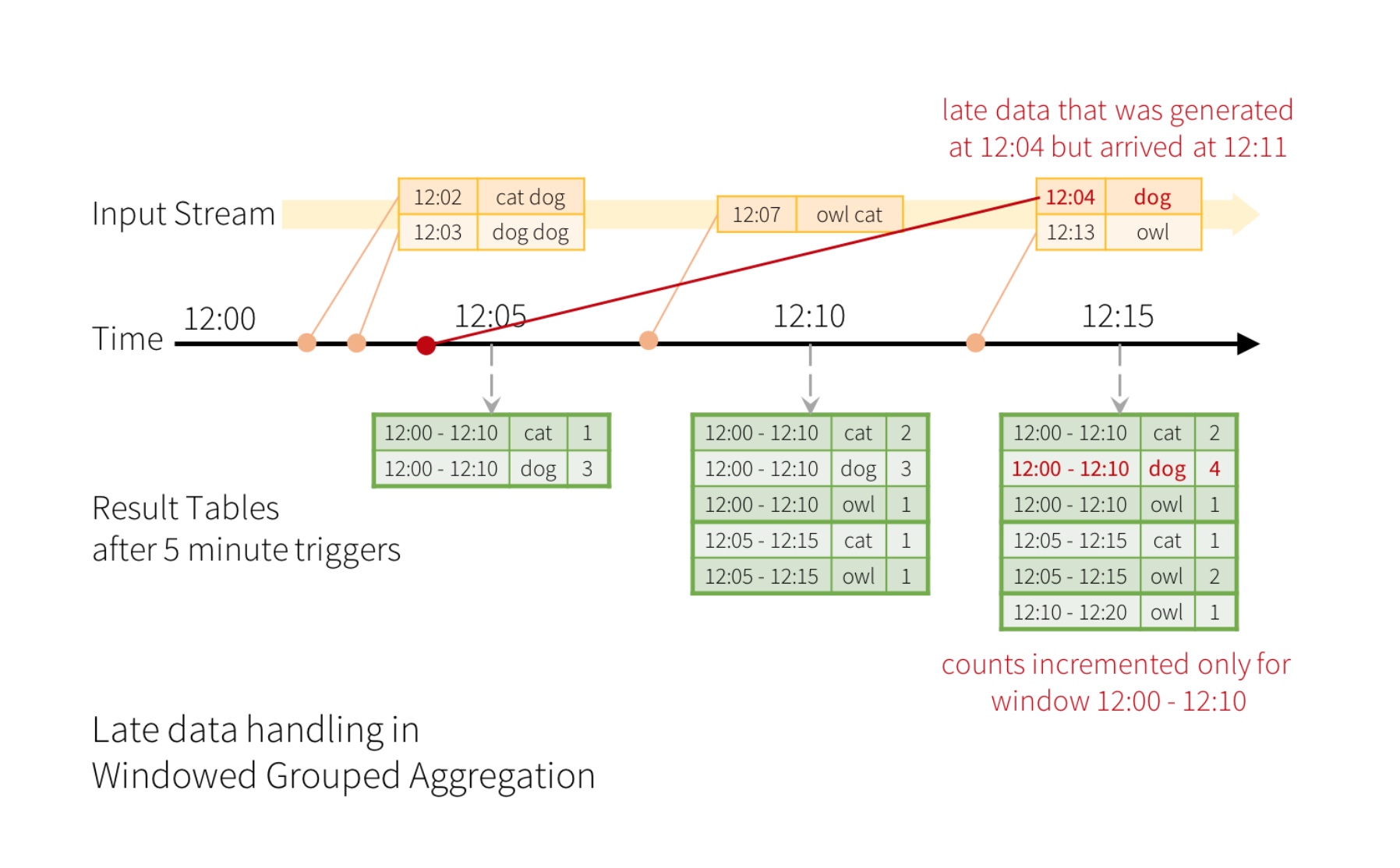
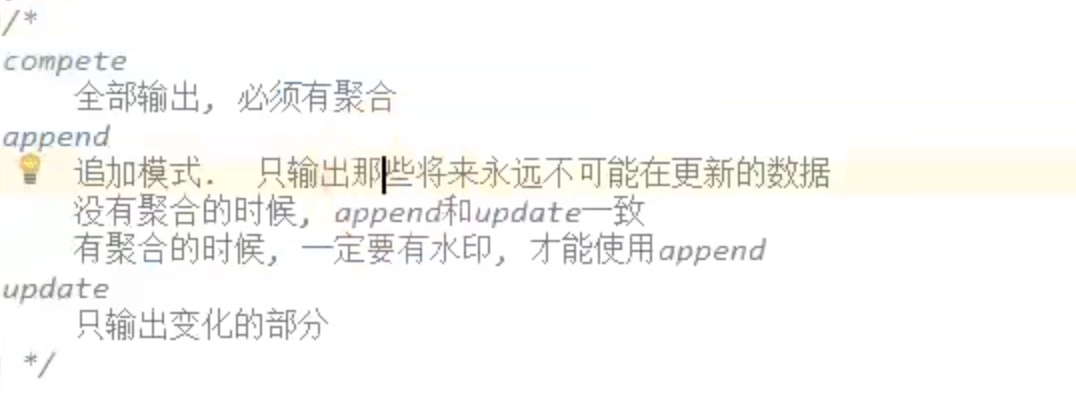
update模式下加watermask 水印相当于往前找回 迟到的数据返回应该在的位置,水印规定了这个最大的可找回的时间范围。
例如,说在12:04(即事件时间)生成的一个字可以在12:11被应用程序接收。应用程序应该使用12:04而不是12:11来更新窗口的较旧计数12:00 - 12:10。这在我们基于窗口的分组中自然发生 - 结构化流可以长时间维持部分聚合的中间状态,以便后期数据可以正确地更新旧窗口的聚合,如下所示。
就是把落下的数据加到它本来应该在的位置
在complete模式下,加水印是没有意义的,因为水印本身是为了舍弃一些超时太久的数据,而complete模式是全输出,根本没有舍弃。
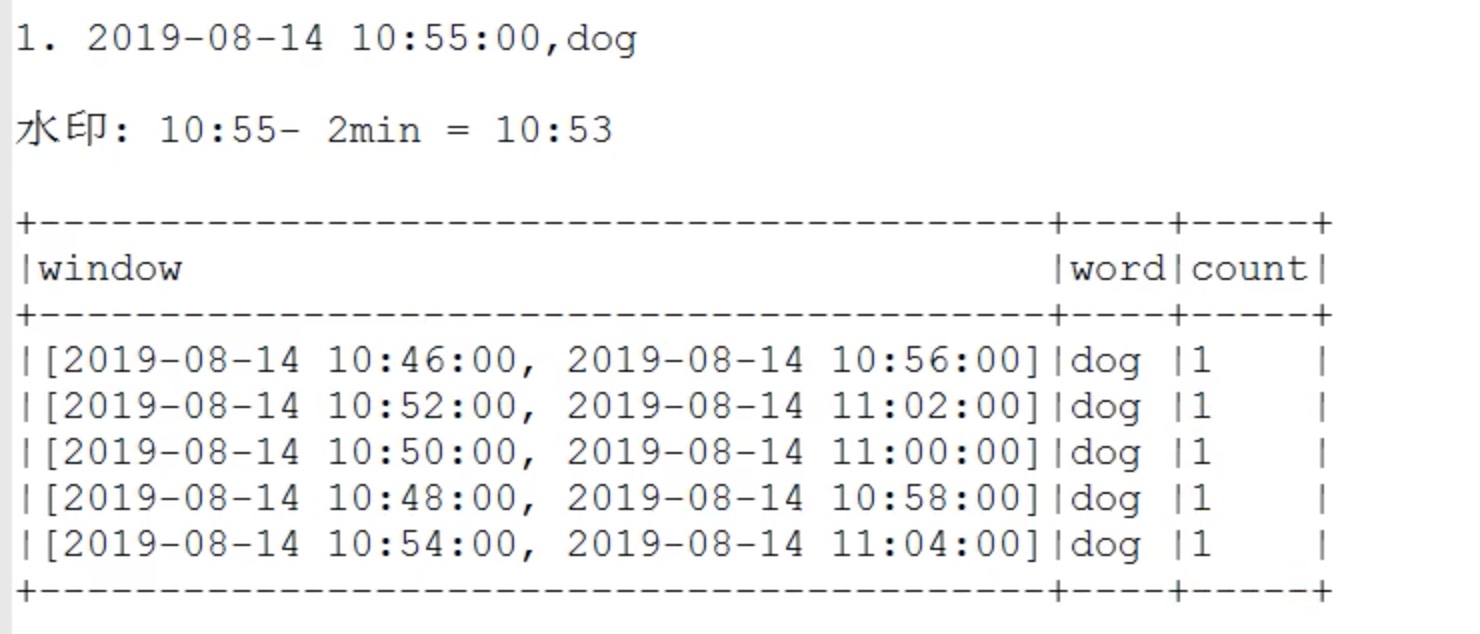
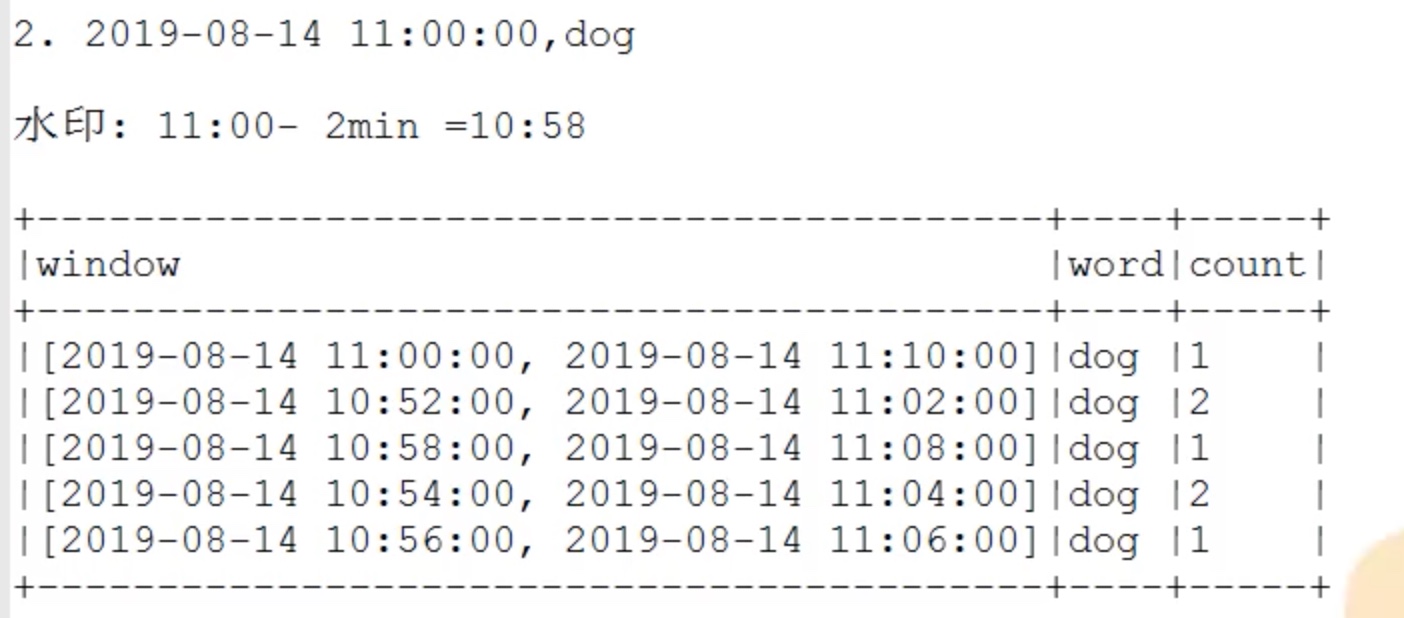
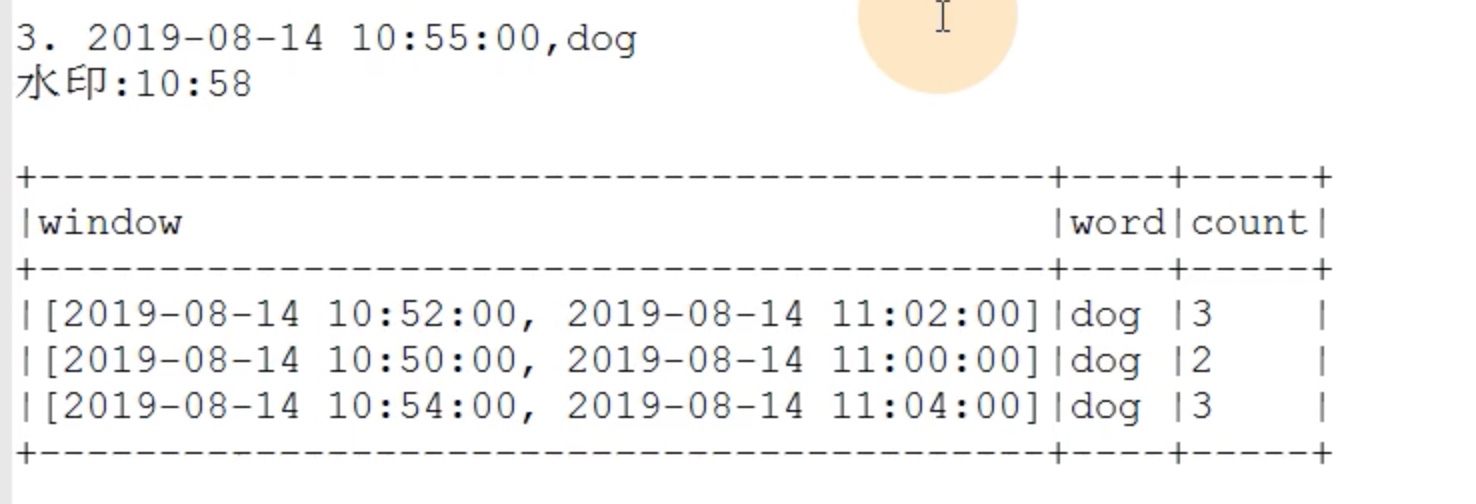
以下例子(update模式下的水印):
windowsduration = 10,sildeduration = 2,watermark = 2,最大滞留窗口数=10/2=5。
我们在10:55输入两个dog,在11:00输入一个dog,但是10:55输入的一个dog迟到了。被水印找补回来了。
尽管10.55的消息在11.00补发来了,但是水印还是保持在之前的10:58。update模式下的水印用于剔除掉水印时间范围之外的窗口 ,最终显示的是满足两种要求的窗口 :
1、水印时间范围之内(这个窗口内包扩了水印);
2、内容发生了变化。
append模式下加watermask 有聚合操作时;
还是上面的例子,append模式是输出那些不可能变化的窗口 ,某种意义上和update正好相反,比如说watermask 过期了,update模式会把这样的窗口剔除,而append模式会把这样的窗口输出,因为watermask过期了,窗口不可能再发生变化了。
没有聚合操作时;
append和update一致,也是只输出更新窗口,水印淘汰超水印时间数据。
水印机制总结
去重算子 dropDuplicates(arg=iterable)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 from pyspark.sql import SparkSessionfrom pyspark.sql import functions as Ffrom pyspark.sql.types import TimestampTypespark = SparkSession.builder \ .appName('structure_test' ) \ .getOrCreate() sc = spark.sparkContext sc.setLogLevel('WARN' ) df = spark.readStream \ .format ('kafka' ) \ .option('kafka.bootstrap.servers' ,'node01:9092' ) \ .option('subscribe' ,'kafka-structure-stream' ) \ .load() \ .selectExpr('cast(value as string)' ,'timestamp' ) df1 = df.select(df.value.alias('word' ),df.timestamp.alias('ts' )) df2 = df1.withWatermark('ts' ,'2 minutes' )\ .dropDuplicates(['word' ]) df2.writeStream \ .format ('console' ) \ .outputMode('append' ) \ .option("truncate" ,False ) \ .trigger(processingTime='2 seconds' ) \ .start() \ .awaitTermination() spark.stop()
1 spark-submit --packages org.apache.spark:spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.12:3.2.1 /opt/data/spark-structure-streaming/dropDuplicates_test.py
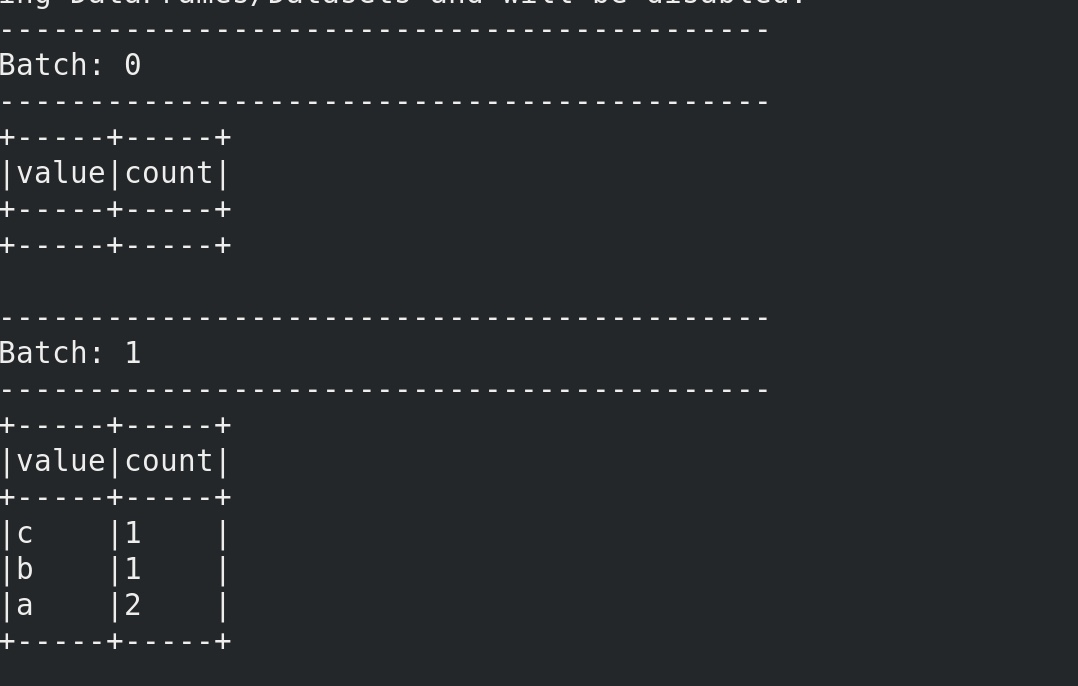
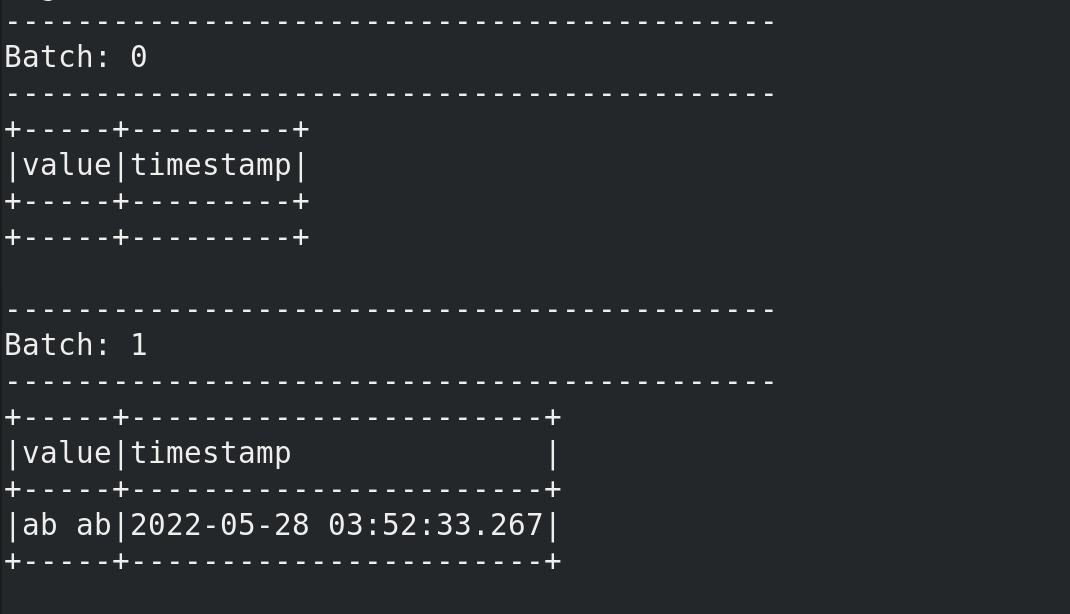
在kafka生产者输入 a 等4秒再 输入a。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 ------------------------------------------- Batch: 3 ------------------------------------------- +----+-----------------------+ |word|ts | +----+-----------------------+ |a |2022-05-31 02:33:01.487| +----+-----------------------+ 22/05/31 02:33:10 WARN ProcessingTimeExecutor: Current batch is falling behind. The trigger interval is 2000 milliseconds, but spent 6482 milliseconds ------------------------------------------- Batch: 4 ------------------------------------------- +----+---+ |word|ts | +----+---+ +----+---+ # 可见第二次输入的a ,被去重了,没有出现在输出中。
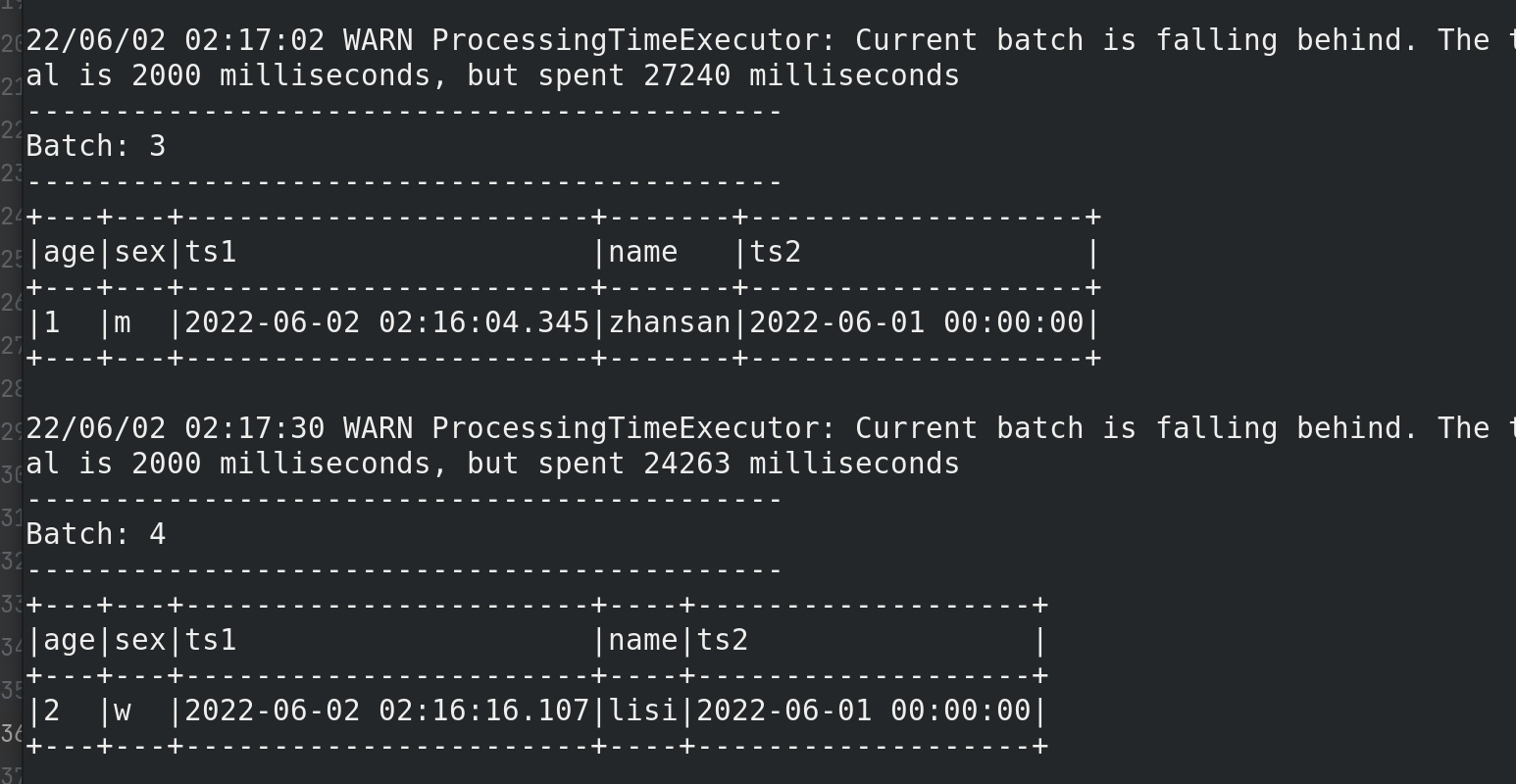
流与静态数据join 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 from pyspark.sql import SparkSessionfrom pyspark.sql import functions as Ffrom pyspark.sql.types import TimestampType,StructType,IntegerType,StringTypespark = SparkSession.builder \ .appName('structure_test' ) \ .getOrCreate() sc = spark.sparkContext sc.setLogLevel('WARN' ) df = spark.readStream \ .format ('kafka' ) \ .option('kafka.bootstrap.servers' ,'node01:9092' ) \ .option('subscribe' ,'kafka-structure-stream' ) \ .load() \ .selectExpr('cast(value as string)' ,'timestamp' ) df_stream = df.select(F.split(df.value,' ' )[0 ].alias('age' ), F.split(df.value,' ' )[1 ].alias('sex' )) schema = StructType().add('name' ,StringType()).add('age' ,IntegerType()) rdd = spark.sparkContext.parallelize([['zhansan' ,23 ],['lisi' ,24 ]]) df_static = spark.createDataFrame(rdd,schema=schema) df_join = df_stream.join(df_static,'age' ,'left' ) df_join.writeStream \ .format ('console' ) \ .outputMode('update' ) \ .option("truncate" ,False ) \ .trigger(processingTime='2 seconds' ) \ .start() \ .awaitTermination() spark.stop()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 >23 m >24 w >22 m > ------------------------------------------- Batch: 1 左连接 匹配成功。 ------------------------------------------- +---+---+-------+ |age|sex|name | +---+---+-------+ |23 |m |zhansan| +---+---+-------+ 22 /05/31 03:42 :12 WARN ProcessingTimeExecutor: Current batch is falling behind. The trigger interval is 2000 milliseconds, but spent 4184 milliseconds------------------------------------------- Batch: 2 左连接匹配成功。 ------------------------------------------- +---+---+----+ |age|sex|name| +---+---+----+ |24 |w |lisi| +---+---+----+ 22 /05/31 03:42 :27 WARN ProcessingTimeExecutor: Current batch is falling behind. The trigger interval is 2000 milliseconds, but spent 3375 milliseconds------------------------------------------- Batch: 3 左连接匹配失败,自动填null。 ------------------------------------------- +---+---+----+ |age|sex|name| +---+---+----+ |22 |m |null| +---+---+----+
流与流join
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 from pyspark.sql import SparkSessionfrom pyspark.sql import functions as Ffrom pyspark.sql.types import TimestampType,StructType,IntegerType,StringTypespark = SparkSession.builder \ .appName('structure_test' ) \ .getOrCreate() sc = spark.sparkContext sc.setLogLevel('WARN' ) df_1 = spark.readStream \ .format ('kafka' ) \ .option('kafka.bootstrap.servers' ,'node01:9092' ) \ .option('subscribe' ,'kafka-structure-stream' ) \ .load() \ .selectExpr('cast(value as string)' ,'timestamp' ) df_kafka = df_1.select(F.split(df_1.value,' ' )[0 ].alias('age' ), F.split(df_1.value,' ' )[1 ].alias('sex' ), df_1.timestamp.alias('ts1' ))\ .withWatermark('ts1' ,'2 minutes' ) df_socket = spark.readStream\ .format ('socket' )\ .option('host' ,'node01' )\ .option('port' ,'9999' )\ .load() df_socket = df_socket.select(F.split(df_socket.value,' ' )[0 ].alias('name' ), F.split(df_socket.value,' ' )[1 ].alias('age' ), F.split(df_socket.value,' ' )[2 ].alias('ts2' )) \ .withColumn('ts2' ,F.to_timestamp('ts2' ))\ .withWatermark('ts2' ,'1 minutes' ) df_join = df_kafka.join(df_socket,'age' ) df_join.writeStream \ .format ('console' ) \ .outputMode('append' ) \ .option("truncate" ,False ) \ .trigger(processingTime='2 seconds' ) \ .start() \ .awaitTermination() spark.stop()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 # 在 nc 端输入 zhansan 1 2022-06-01 lisi 2 2022-06-01 # 在kafka生产者端输入 1 m 2 w
输出如下:
流与流的outjoin 可以参考 https://docs.databricks.com/_static/notebooks/stream-stream-joins-python.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 df_kafka = df_1.select(F.split(df_1.value,' ' )[0 ].alias('kafka_age' ), F.split(df_1.value,' ' )[1 ].alias('sex' ), df_1.timestamp.alias('ts1' )) \ .withWatermark('ts1' ,'4 minutes' ) df_socket = spark.readStream \ .format ('socket' ) \ .option('host' ,'node01' ) \ .option('port' ,'9999' ) \ .load() df_socket = df_socket.select(F.split(df_socket.value,' ' )[0 ].alias('name' ), F.split(df_socket.value,' ' )[1 ].alias('socket_age' ), F.split(df_socket.value,' ' )[2 ].alias('ts2' )) \ .withColumn('ts2' ,F.to_timestamp('ts2' )) \ .withWatermark('ts2' ,'2 minutes' ) df_join = df_kafka.join(df_socket,F.expr('''socket_age == kafka_age AND ts1 > ts2 + interval 1 minutes''' ),"leftouter" )
但是我实践以后发现,这个outerjoin 和 inner join 效果是一样的,也没有对空位置补null。
Support matrix for joins in streaming queries
Left Input
Right Input
Join Type
Static
Static
All types
Supported, since its not on streaming data even though it can be present in a streaming query
Stream
Static
Inner
Supported, not stateful
Left Outer
Supported, not stateful
Right Outer
Not supported
Full Outer
Not supported
Left Semi
Supported, not stateful
Static
Stream
Inner
Supported, not stateful
Left Outer
Not supported
Right Outer
Supported, not stateful
Full Outer
Not supported
Left Semi
Not supported
Stream
Stream
Inner
Supported, optionally specify watermark on both sides + time constraints for state cleanup
Left Outer
Conditionally supported, must specify watermark on right + time constraints for correct results, optionally specify watermark on left for all state cleanup
Right Outer
Conditionally supported, must specify watermark on left + time constraints for correct results, optionally specify watermark on right for all state cleanup
Full Outer
Conditionally supported, must specify watermark on one side + time constraints for correct results, optionally specify watermark on the other side for all state cleanup
Left Semi
Conditionally supported, must specify watermark on right + time constraints for correct results, optionally specify watermark on left for all state cleanup
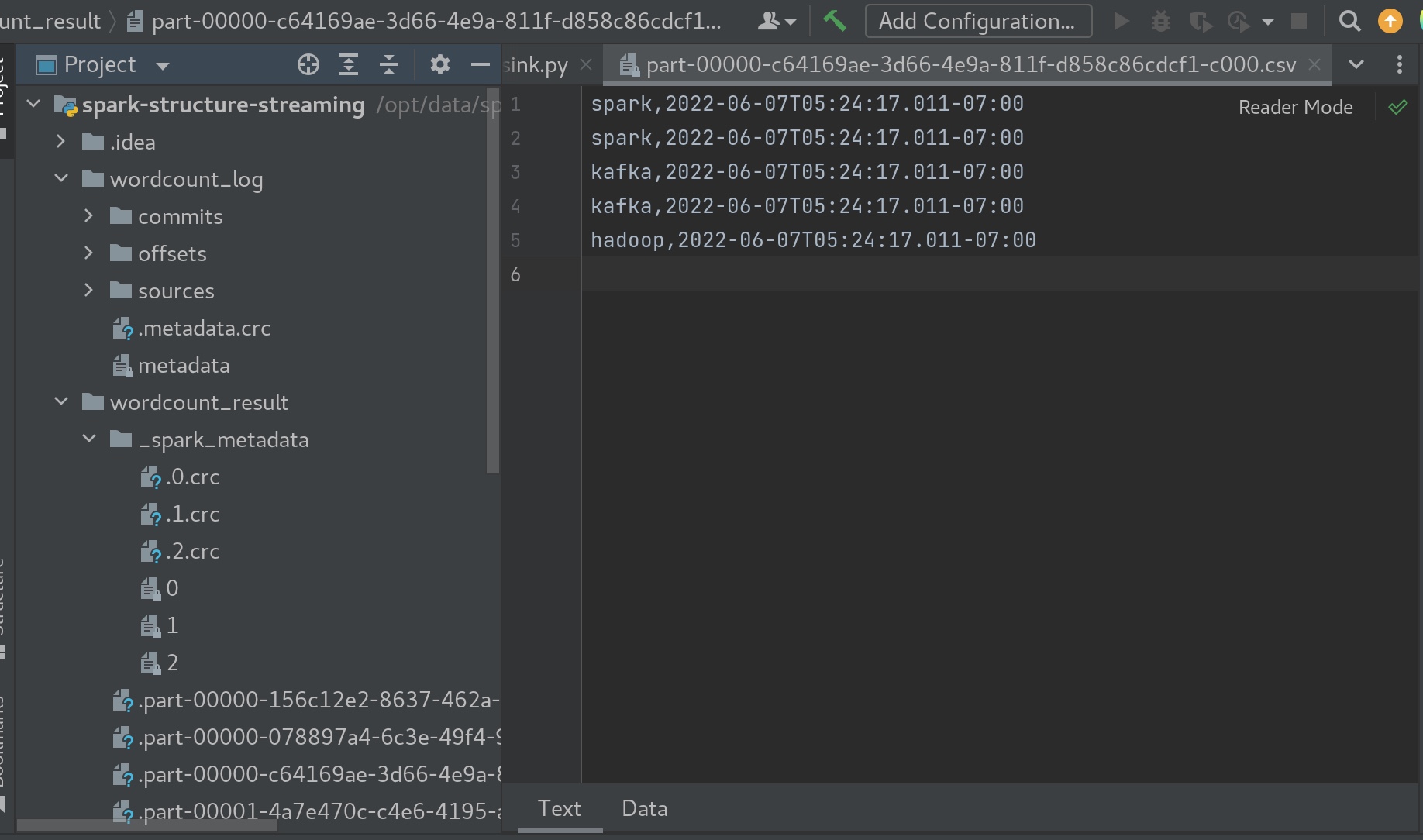
sink hdfs sink(or 本地) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 from pyspark.sql import SparkSessionfrom pyspark.sql import functions as Ffrom pyspark.sql.types import TimestampTypespark = SparkSession.builder \ .appName('structure_word_count' ) \ .getOrCreate() sc = spark.sparkContext sc.setLogLevel('WARN' ) df = spark.readStream \ .format ('kafka' ) \ .option('kafka.bootstrap.servers' ,'node01:9092' ) \ .option('subscribe' ,'kafka-structure-stream' ) \ .load() \ .selectExpr('cast(value as string)' ,'timestamp' ) df = df.select(F.explode( F.split(df.value,' ' )).alias('value' ), df.timestamp.alias('ts' )) df.writeStream \ .format ('csv' ) \ .option('path' ,'file:///opt/data/spark-structure-streaming/wordcount_result' ) \ .option('checkpointLocation' ,'file:///opt/data/spark-structure-streaming/wordcount_log' ) \ .option("truncate" ,False ) \ .start() \ .awaitTermination() spark.stop()
kafka sink 从 Kafka topic1 中获取数据, 简单处理, 再次放入 Kafka的 topic2 。
1 2 3 4 5 kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server node01:9092 --create --topic structure-stream-kafka --partitions 3 --replication-factor 2 kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server node01:9092 --topic structure-stream-kafka spark-submit --packages org.apache.spark:spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.12:3.2.1 /opt/data/spark-structure-streaming/kafka_sink.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 from pyspark.sql import SparkSessionfrom pyspark.sql import functions as Ffrom pyspark.sql.types import TimestampTypespark = SparkSession.builder \ .appName('structure_word_count' ) \ .getOrCreate() sc = spark.sparkContext sc.setLogLevel('WARN' ) df = spark.readStream \ .format ('kafka' ) \ .option('kafka.bootstrap.servers' ,'node01:9092' ) \ .option('subscribe' ,'kafka-structure-stream' ) \ .load() \ .selectExpr('cast(value as string)' ,'timestamp' ) df = df.select(F.explode( F.split(df.value,' ' )).alias('value' ), df.timestamp.alias('ts' )) df.writeStream \ .format ('kafka' ) \ .option('kafka.bootstrap.servers' ,'node01:9092' ) \ .option('topic' ,'structure-stream-kafka' ) \ .option('checkpointLocation' ,'file:///opt/data/spark-structure-streaming/wordcount_log' ) \ .option("truncate" ,False ) \ .start() \ .awaitTermination() spark.stop()
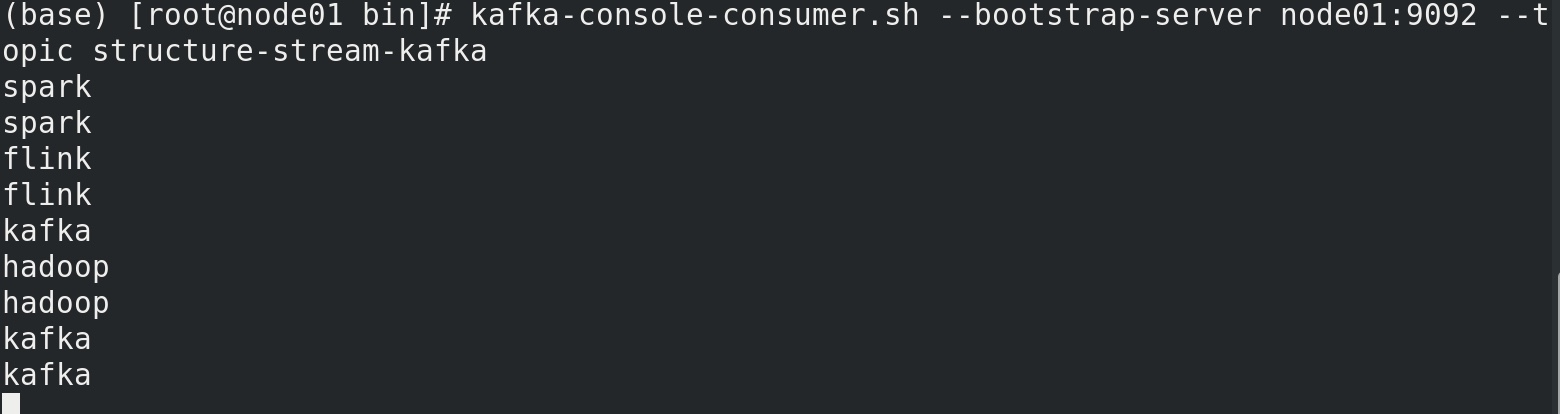
kafka的生产者内输入:
1 2 > spark spark flink flink kafka > hadoop hadoop kafka kafka
在kafka topic (structure-stream-kafka)中可见时间戳被隐藏了。
Foreach writer (mysql)
观察:foreach 的 统计自带了回顾前面内容的能力。
相当于,把所有前面 多次 输入的内容,重新 一次 逐条输入进去,foreach 就是每个都输入一遍,包括过去的输入内容。
foreach() 参数是一个类,这个类要重写open连接mysql 方法;重写close断开连接mysql方法;重写process处理df的方法。
process方法 传入的参数 row, 是 【foreach 每个都输入一遍,包括过去的输入的内容】运行完的结果df中的一行转化的row对象。例如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 # 截取部分代码 df = df.select(F.explode( F.split(df.value,' ')).alias('word'))\ .groupBy('word')\ .count() class Row_to_mysql(): def __init__(self): self.db = None def open(self, partition_id, epoch_id): # 连接mysql pass def process(self,row): print(row) def close(self,error): # 断开mysql连接 pass df.writeStream \ .outputMode('update') \ .foreach(Row_to_mysql()) # 我们来看看row到底是什么。 # row 是把多次的输入一次性每一个都输入一遍,运行完的df 结果,取每一行,变成了row对象。因为这里是update 模式,row只是df 结果变化的一行。 # 在kafka的生产者输入: > spark spark # output Row(word='spark', count=2) # 在kafka的生产者输入: > hive hive hive # output Row(word='hive', count=3) # 在kafka的生产者输入: > hive hive # output Row(word='hive', count=5)
在mysql 中新建一个table。
1 2 3 create database structure_stream_mysql; use structure_stream_mysql; create table structure_stream_mysql_table(word char(20),counted int);
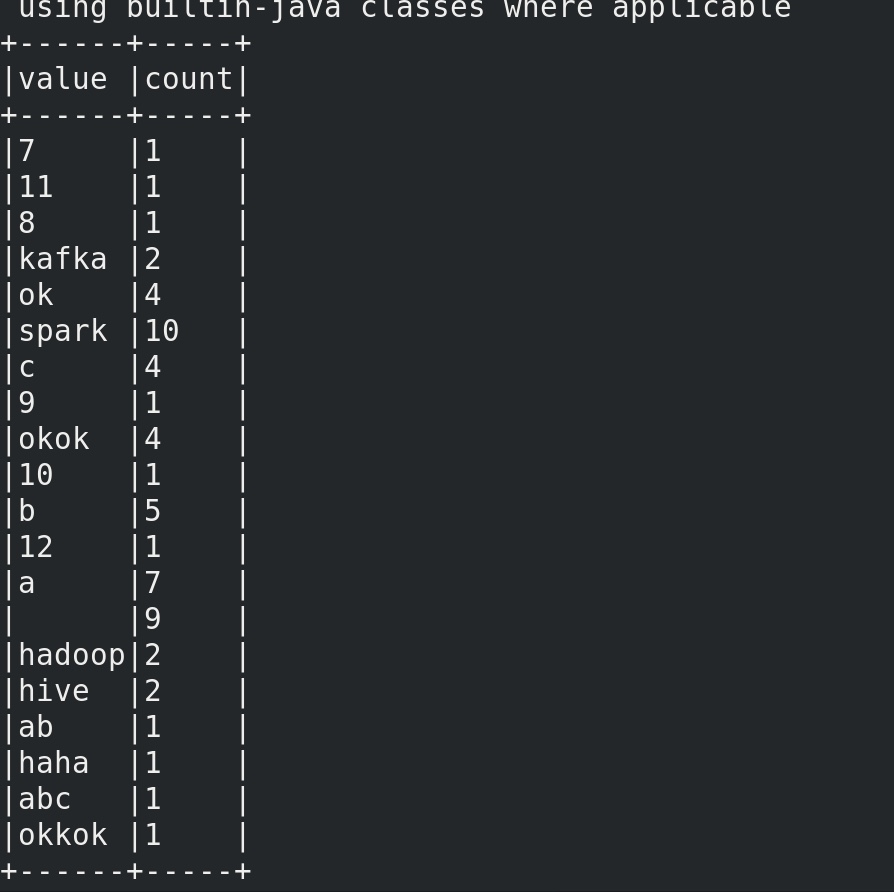
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 from pyspark.sql import SparkSession,Rowfrom pyspark.sql import functions as Ffrom pyspark.sql.types import TimestampTypeimport pymysqlspark = SparkSession.builder \ .appName('structure_word_count' ) \ .getOrCreate() sc = spark.sparkContext sc.setLogLevel('WARN' ) df = spark.readStream \ .format ('kafka' ) \ .option('kafka.bootstrap.servers' ,'node01:9092' ) \ .option('subscribe' ,'kafka-structure-stream' ) \ .load() \ .selectExpr('cast(value as string)' ,'timestamp' ) df = df.select(F.explode( F.split(df.value,' ' )).alias('word' ))\ .groupBy('word' )\ .count() class Row_to_mysql (): def __init__ (self ): self.db = None def open (self, partition_id, epoch_id ): self.db = pymysql.connect(host='node01' , user='root' , password='密码' , database='structure_stream_mysql' ) return self.db!=None def process (self,row ): print (row) cursor = self.db.cursor() sql = "insert into structure_stream_mysql_table(word,counted) values (%s,%s) on duplicate key update counted=%s;" cursor.execute(sql,[row['word' ],row['count' ],row['count' ]]) self.db.commit() def close (self,error ): self.db.close() df.writeStream \ .outputMode('update' ) \ .foreach(Row_to_mysql()) \ .start() \ .awaitTermination() spark.stop()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 # 在kafka的生产者输入: > spark spark spark kafka kafka hive hive > spark kafka hive > hadoop > spark > select * from structure_stream_mysql_table; # output +--------+---------+ | word | counted | +--------+---------+ | kafka | 2 | | spark | 3 | | hive | 2 | | kafka | 3 | | spark | 5 | | hadoop | 1 | | hive | 3 | +--------+---------+ 7 rows in set (0.02 sec)
Foreachbatch 1、Reuse existing batch data sources
2、Write to multiple locations
3、Apply additional DataFrame operations
**(foreachbatch 把流式的df变成了静态的df,大大拓展了算子的应用。)**
scala 标准写法
1 2 3 4 5 streamingDF.writeStream.foreachBatch { (batchDF: DataFrame , batchId: Long ) => batchDF.persist() batchDF.write.format(...).save(...) batchDF.write.format(...).save(...) batchDF.unpersist()}
python
1 2 3 4 5 def foreach_batch_function (df, epoch_id ): pass streamingDF.writeStream.foreachBatch(foreach_batch_function).start()
foreachbatch 案例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 from pyspark.sql import SparkSessionfrom pyspark.sql import functions as Ffrom pyspark.sql.types import TimestampTypespark = SparkSession.builder \ .appName('structure_word_count' ) \ .getOrCreate() sc = spark.sparkContext sc.setLogLevel('WARN' ) df = spark.readStream \ .format ('kafka' ) \ .option('kafka.bootstrap.servers' ,'node01:9092' ) \ .option('subscribe' ,'kafka-structure-stream' ) \ .load() \ .selectExpr('cast(value as string)' ) def foreachBatch_func (df,batchId ): df2 = df.select(F.explode( F.split(df.value,' ' )).alias('value' )) \ .groupBy('value' ) \ .count() df2.persist() df2.write.mode('overwrite' )\ .format ('json' )\ .save('file:///opt/data/spark-structure-streaming/repository_test/json' ) df2.write.mode('overwrite' )\ .format ('jdbc' ) \ .option('url' ,'jdbc:mysql://node01:3306/structure_stream_mysql?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true' ) \ .option('dbtable' ,'foreachbatch_table' ) \ .option('user' ,'root' ) \ .option('password' ,'密码' ) \ .save() df2.unpersist() df.writeStream \ .outputMode('update' ) \ .foreachBatch(foreachBatch_func)\ .start() \ .awaitTermination() spark.stop()
当然,处理df的过程可以放进foreachBatch_func方法内,也可以放在外面,放外面的话,用complete输出模式会适用一些。
Trigger(触发器)
Trigger Type
Description
unspecified (default) 没有显示的设定触发器, 表示使用 micro-batch mode, 尽可能块的处理每个批次的数据. 如果无数据可用, 则处于阻塞状态, 等待数据流入
Fixed interval micro-batches 固定周期的微批处理查询会在微批处理模式下执行, 其中微批处理将以用户指定的间隔执行. 1. 如果以前的微批处理在间隔内完成, 则引擎会等待间隔结束, 然后开启下一个微批次 2. 如果前一个微批处理在一个间隔内没有完成(即错过了间隔边界), 则下个微批处理会在上一个完成之后立即启动(不会等待下一个间隔边界) 3. 如果没有新数据可用, 则不会启动微批次. 适用于流式数据的批处理作业
One-time micro-batch 一次性微批次查询将在所有可用数据上执行一次微批次处理, 然后自行停止. 如果你希望定期启动集群, 然后处理集群关闭期间产生的数据, 然后再关闭集群. 这种情况下很有用. 它可以显著的降低成本. 一般用于非实时的数据分析
Continuous with fixed checkpoint interval (experimental 2.3 引入*)* 连续处理以超低延迟处理数据,(但是可能很多前面的流式处理的算子不支持)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import org.apache.spark.sql.streaming.Trigger df.writeStream .format("console" ) .start() df.writeStream .format("console" ) .trigger(Trigger .ProcessingTime ("2 seconds" )) .start() df.writeStream .format("console" ) .trigger(Trigger .Once ()) .start() df.writeStream .format("console" ) .trigger(Trigger .AvailableNow ()) .start() df.writeStream .format("console" ) .trigger(Trigger .Continuous ("1 second" )) .start()
实践案例(写入redis) 代码生成数据-> kafka -> streaming消费 -> redis\mysql...
模拟数据 因为python总是要在控制台里用submit这样的方法运行写的脚本,有点麻烦,Scala写的代码在maven 里配置好spark-sql-kafka就可以在idea中直接运行程序,方便不少。
所以这个实践案例我们干脆用Scala来写。
先随机生成一些数据写入到kafka。
新建一个maven的项目。在maven项目中写Scala代码。
把maven相关的依赖pom.xml都配置好,刷新一下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.spark</groupId > <artifactId > spark-core_2.13</artifactId > <version > 3.2.1</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.spark</groupId > <artifactId > spark-sql_2.13</artifactId > <version > 3.2.1</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.spark</groupId > <artifactId > spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.13</artifactId > <version > 3.2.1</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.kafka</groupId > <artifactId > kafka_2.13</artifactId > <version > 3.1.0</version > </dependency > </dependencies >
mock_data_from_scope.scala
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 package kafka_to_spark_test.mockimport java.util.Random import scala.collection.mutableobject RandomNumUtil val random = new Random () def randomInt Int ,to:Int ):Int ={ if (from > to) throw new IllegalArgumentException (s"from is $from should < to = $to " ) random.nextInt(to-from+1 ) + from } def randomMultiInt Int ,to:Int ,count:Int ,canReat:Boolean = true ):List [Int ]={ if (canReat){ (1 to count).map( _ => randomInt(from, to)).toList }else { if ((to - from)+1 < count ) throw new IllegalArgumentException ("count must < num of regulations when canReat state " ) val set: mutable.Set [Int ] = mutable.Set [Int ]() while (set.size < count){ set += randomInt(from, to) } set.toList } } def main Array [String ]): Unit ={ println(randomMultiInt(10 ,14 ,5 ,true )) println(randomMultiInt(10 ,14 ,5 ,false )) } }
mock_data_proportion.scala
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 package kafka_to_spark_test.mockimport scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer import scala.util.Random object mock_data_proportion def apply T ](opts: (T ,Int )*):mock_data_proportion[T ]={ val randomoptions = new mock_data_proportion[T ]() randomoptions.totalWeight = (0 /: opts)(_+_._2) opts.foreach { case (value,weight)=>{ randomoptions.options ++= (1 to weight).map(_ => value )}} randomoptions } def main Array [String ]): Unit ={ val opts: mock_data_proportion[String ] = mock_data_proportion(("zhangsan" , 1 ), ("lisi" , 10 )) println(opts.getRandomOption()) println(opts.getRandomOption()) } } class mock_data_proportion [T ] var totalWeight:Int = _ private val options: ListBuffer [T ] = ListBuffer [T ]() def getRandomOption T ={ val random = new Random () options(random.nextInt(options.length)) } }
cityInfo
1 2 3 4 5 package kafka_to_spark_test.mockcase class cityInfo (city_id: Long , city_name: String , area: String )
mockRealTime
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 package kafka_to_spark_test.mockimport org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.{KafkaProducer , ProducerRecord }import java.util.Properties import scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer object mockRealTime def mockRealTimeData ArrayBuffer [String ] = { var array = ArrayBuffer [String ]() var randomOpts: mock_data_proportion[cityInfo] = mock_data_proportion( (cityInfo(1 , "北京" , "华北" ), 30 ), (cityInfo(2 , "上海" , "华东" ), 30 ), (cityInfo(3 , "广州" , "华南" ), 10 ), (cityInfo(4 , "深圳" , "华南" ), 20 ), (cityInfo(5 , "杭州" , "华中" ), 10 ), ) (1 to 5 ).foreach { i => { val timestamp = System .currentTimeMillis() val cityInfo = randomOpts.getRandomOption() val area = cityInfo.area val adid = cityInfo.city_id val city = cityInfo.city_name val userid = RandomNumUtil .randomInt(100 , 106 ) array += s"$timestamp ,$userid ,$area ,$city ,$adid " Thread .sleep(10 ) } } array } def createKafkaProducer KafkaProducer [String , String ] = { val props = new Properties props.put("bootstrap.servers" , "node01:9092" ) props.put("key.serializer" , "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer" ) props.put("value.serializer" , "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer" ) new KafkaProducer [String , String ](props) } def main Array [String ]): Unit = { val topic = "ads_log" val producer: KafkaProducer [String , String ] = createKafkaProducer while (true ) { mockRealTimeData().foreach { msg => { producer.send(new ProducerRecord (topic, msg)) Thread .sleep(1000 ) } } Thread .sleep(5000 ) } } }
AdsInfo(从 kafka 读取数据, 为了方便后续处理, 封装数据到 AdsInfo 样例类中)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 package kafka_to_spark_test.beanimport java.sql.Timestamp case class AdsInfo ( timestamp: Timestamp , dayString: String , hmString: String , area: String , city: String , userId: String , adsId: String )
RealtimeApp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 package kafka_to_spark_test.appimport java.sql.Timestamp import java.text.SimpleDateFormat import java.util.Date import kafka_to_spark_test.bean.AdsInfo import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession import org.apache.spark.sql._object RealtimeApp def main Array [String ]): Unit ={ val spark: SparkSession = SparkSession .builder() .master("local[*]" ) .appName("realtimeApp" ) .getOrCreate() spark.sparkContext.setLogLevel("WARN" ) import spark.implicits._ val dayStringFormatter = new SimpleDateFormat ("yyyy-MM-dd" ) val hmStringFormatter = new SimpleDateFormat ("HH:mm" ) val adsInfoDS: Dataset [AdsInfo ] = spark.readStream .format("kafka" ) .option("kafka.bootstrap.servers" , "node01:9092" ) .option("subscribe" , "ads_log" ) .load .select("value" ) .as[String ] .map(v => { val split: Array [String ] = v.split("," ) val date = new Date (split(0 ).toLong) AdsInfo ( new Timestamp (split(0 ).toLong), dayStringFormatter.format(date), hmStringFormatter.format(date), split(2 ), split(3 ), split(1 ), split(4 ) ) }) adsInfoDS.writeStream .format("console" ) .outputMode("update" ) .option("truncate" ,"false" ) .start .awaitTermination() } }
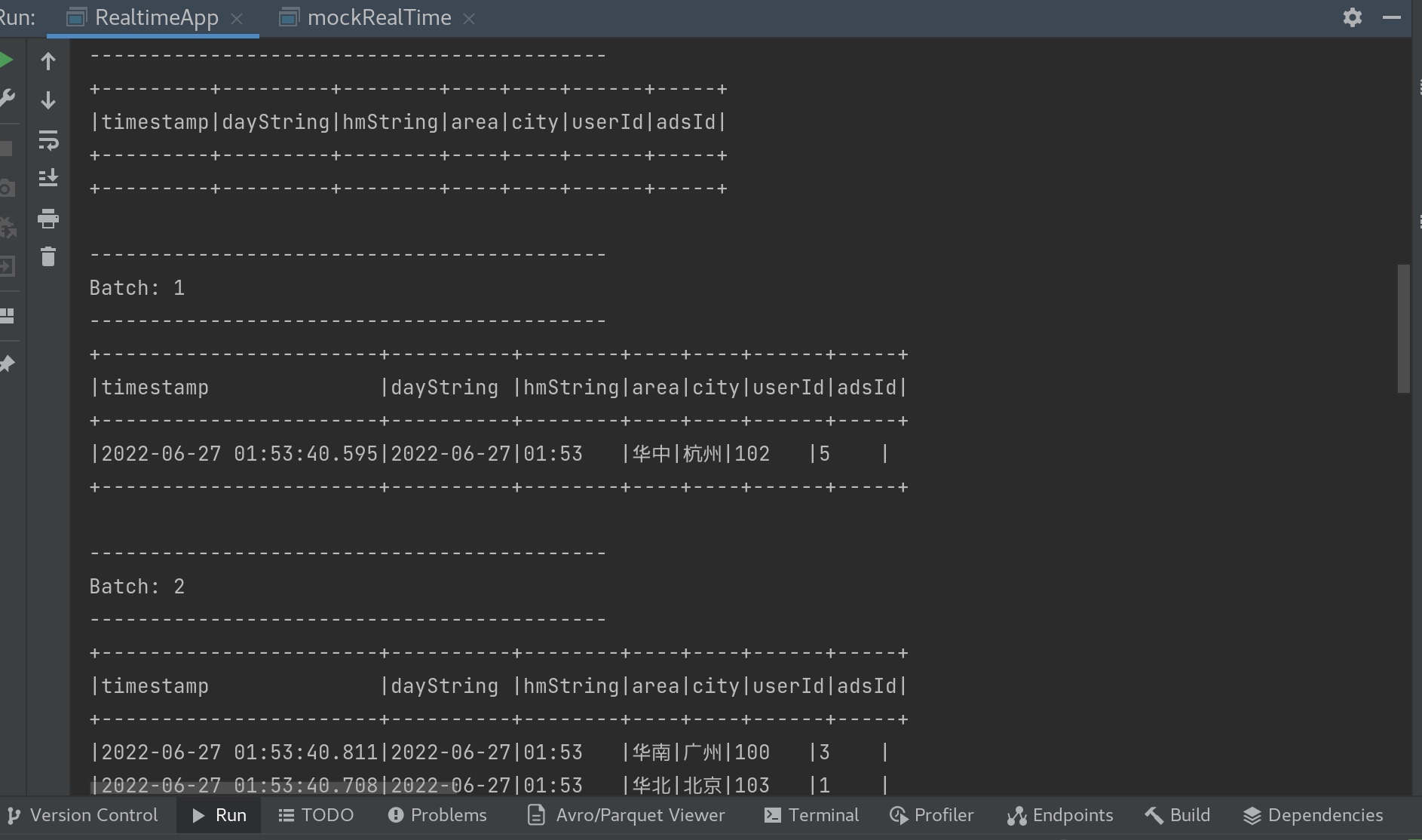
先在kafka 内打开一个 topic ads_log。
我们先运行RealtimeApp 用spark structure接收kafka 的数据。 再运行 mockRealTime 生产数据进入kafka,可见如下:
黑名单实时统计 (需求)
实现实时的动态黑名单检测机制:将每天对某个广告点击超过阈值(比如:100次)的用户拉入黑名单。 1. 黑名单应该是每天更新一次. 如果昨天进入黑名单, 今天应该重新再统计 2. 把黑名单写入到 redis 中, 以供其他应用查看 3. 已经进入黑名单的用户不再进行检测(提高效率)
(思路)
黑名单存放在 redis 中, 使用 set, set 中的每个元素表示一个用户。通过 sql 查询过滤出来每天每广告点击数超过阈值的用户, 然后使用 foreach 写入到 redis 即可。
(技法)
在spark structure streaming 的编写上,要注意:
1、编写步骤上、应先用console的形式输出到控制台,再一点一点去完善代码。
2、spark处理数据的时间间隔最好要 小于 kafka等数据流生成的时间间隔。
3、awaitTermiation() 放的位置是 流式处理的最后一个writestreaming后尾作为收尾标志的,若之前有多次流式处理,写到start() 即可,运行起来以找到 awaitTermiation() 作为一整个流式处理的结束。
4、如果运行一直没结果,又不明不白的停滞了,jps 检查一下看看hadoop 有没有 /tmp/hsperf 错误,zookeeper、kafka、hadoop都重来一遍,checkpointLocation删除重新生成一个新的。再来一遍。
*** 先安装一下 redis***
wget https://github.com/redis/redis/archive/7.0.2.tar.gz
tar -zvxf 7.0.2.tar.gz
cd redis-7.0.2/
make // 编译
make PREFIX=/opt/redis-7.0.2 install // 安装
vim redis.conf aemonize yes // 打开远程登录功能
./bin/redis-server& ./redis.conf // 启动redis服务
netstat -an | grep 6379 // 检查6379端口是否被监听
redis-cli // 启用redis的客户端
flushall // 清空redis的内容
keys * //查看
smembers
sadd key value* // 往set里面写key和value
客户端内 可关闭redis服务 shutdown,退出客户端 exit
在maven 内配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 <dependency > <groupId > redis.clients</groupId > <artifactId > jedis</artifactId > <version > 4.2.3</version > </dependency >
注意几个redis相关bug 的处理:
1、redis-sentinel "DENIED Redis is running in protected mode
先把redis配置文件conf 中的 protected-mode yes 改成 protected-mod no, 再手动开启redis服务时不开启保护模式 ./bin/redis-server --protected-mode no & ./redis.conf ;
2、 There is insufficient memory for the Java Runtime Environment to continue
Java虚拟机内存空间不够了,我们 cd /etc/security/limits.d 将文件 xxxx.config 的 * soft nproc xxxx 注释掉;
3、[java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig.setMinEvictableIdleTime](https://www.cnblogs.com/live41/p/15790868.html)
这是访问redis 时报的错,原因可能有两个:一:Maven中有其它组件依赖了旧版的jedis,需要排除;二:JedisPoolConfig和JedisSentinelPool使用了apache.commons的commons-pool2包(怀疑是用反射使用的原因);在maven 中改如下两个配置。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 <dependencies > <dependency > <exclusions > <exclusion > <groupId > redis.clients</groupId > <artifactId > jedis</artifactId > </exclusion > </exclusions > <groupId > redis.clients</groupId > <artifactId > jedis</artifactId > <version > 4.2.3</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.commons</groupId > <artifactId > commons-pool2</artifactId > <version > 2.11.1</version > </dependency > </dependencies >
Redis_Util.scala
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 package kafka_to_spark_test.utilimport redis.clients.jedis.{Jedis , JedisPool , JedisPoolConfig }object RedisUtil private val jedisPoolConfig: JedisPoolConfig = new JedisPoolConfig () jedisPoolConfig.setMaxTotal(100 ) jedisPoolConfig.setMaxIdle(20 ) jedisPoolConfig.setMinIdle(20 ) jedisPoolConfig.setBlockWhenExhausted(true ) jedisPoolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(500 ) jedisPoolConfig.setTestOnBorrow(true ) private val jedisPool: JedisPool = new JedisPool (jedisPoolConfig, "node01" , 6379 ) def getJedisClient Jedis = { jedisPool.getResource } }
BlackListApp.scala
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 package kafka_to_spark_test.appimport kafka_to_spark_test.bean.AdsInfo import kafka_to_spark_test.util.RedisUtil import org.apache.spark.sql._import org.apache.spark.sql.streaming.Trigger import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis import java.utilimport scala.collection.IterableOnce .iterableOnceExtensionMethodsobject BlackListApp def startBlackList SparkSession ,adsInfoDS:Dataset [AdsInfo ]):Dataset [AdsInfo ]={ import spark.implicits._ def filter_func Dataset [AdsInfo ]):Dataset [AdsInfo ]={ adsInfoDS1.mapPartitions(adsInfoItera => { val adsInfoList: List [AdsInfo ] = adsInfoItera.toList if (adsInfoList.isEmpty) { adsInfoList.toIterator } else { val client: Jedis = RedisUtil .getJedisClient val blackList: util.Set [String ] = client.smembers(s"day:blacklist:${adsInfoList(0).dayString} " ) adsInfoList.filter(adsInfo => { !blackList.contains(adsInfo.userId) }).toIterator } }) adsInfoDS1 } var filtered_adsInfoDS: Dataset [AdsInfo ] = filter_func(adsInfoDS) filtered_adsInfoDS.createOrReplaceTempView("tb_adsinfo" ) val result1: DataFrame = spark.sql( """ |select | userId, | dayString |from tb_adsinfo |group by userId,dayString,adsId |having count(1)>5 """ .stripMargin) result1.writeStream .outputMode("update" ) .trigger(Trigger .ProcessingTime ("2 seconds" )) .foreach(new ForeachWriter [Row ] { var client : Jedis = _ override def open Long , epochId: Long ): Boolean = { client = RedisUtil .getJedisClient client != null } override def process Row ): Unit = { val dayString: String = value.getString(1 ) val userId: String = value.getString(0 ) client.sadd(s"day:blacklist:$dayString " ,userId) } override def close Throwable ): Unit = { if (client!=null ) client.close() } }) .option("checkpointLocation" ,"/opt/data/maven_scala_test/src/scalaCode/kafka_to_spark_test/blacklist_log" ) .start() .awaitTermination() filtered_adsInfoDS = filter_func(filtered_adsInfoDS) filtered_adsInfoDS } }
RealtimeApp1.scala
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 package kafka_to_spark_test.appimport kafka_to_spark_test.app.BlackListApp import kafka_to_spark_test.bean.AdsInfo import org.apache.spark.sql._import java.sql.Timestamp import java.text.SimpleDateFormat import java.util.Date object RealtimeApp1 def main Array [String ]): Unit ={ val spark: SparkSession = SparkSession .builder() .master("local[*]" ) .appName("realtimeApp" ) .getOrCreate() spark.sparkContext.setLogLevel("WARN" ) import spark.implicits._ val dayStringFormatter = new SimpleDateFormat ("yyyy-MM-dd" ) val hmStringFormatter = new SimpleDateFormat ("HH:mm" ) val adsInfoDS: Dataset [AdsInfo ] = spark.readStream .format("kafka" ) .option("kafka.bootstrap.servers" , "node01:9092" ) .option("subscribe" , "ads_log" ) .load .select("value" ) .as[String ] .map(v => { val split: Array [String ] = v.split("," ) val date = new Date (split(0 ).toLong) AdsInfo ( new Timestamp (split(0 ).toLong), dayStringFormatter.format(date), hmStringFormatter.format(date), split(2 ), split(3 ), split(1 ), split(4 ) ) }) .withWatermark("timestamp" ,"24 hours" ) val filtered_adsInfoDS: Dataset [AdsInfo ] = BlackListApp .startBlackList(spark, adsInfoDS) } }
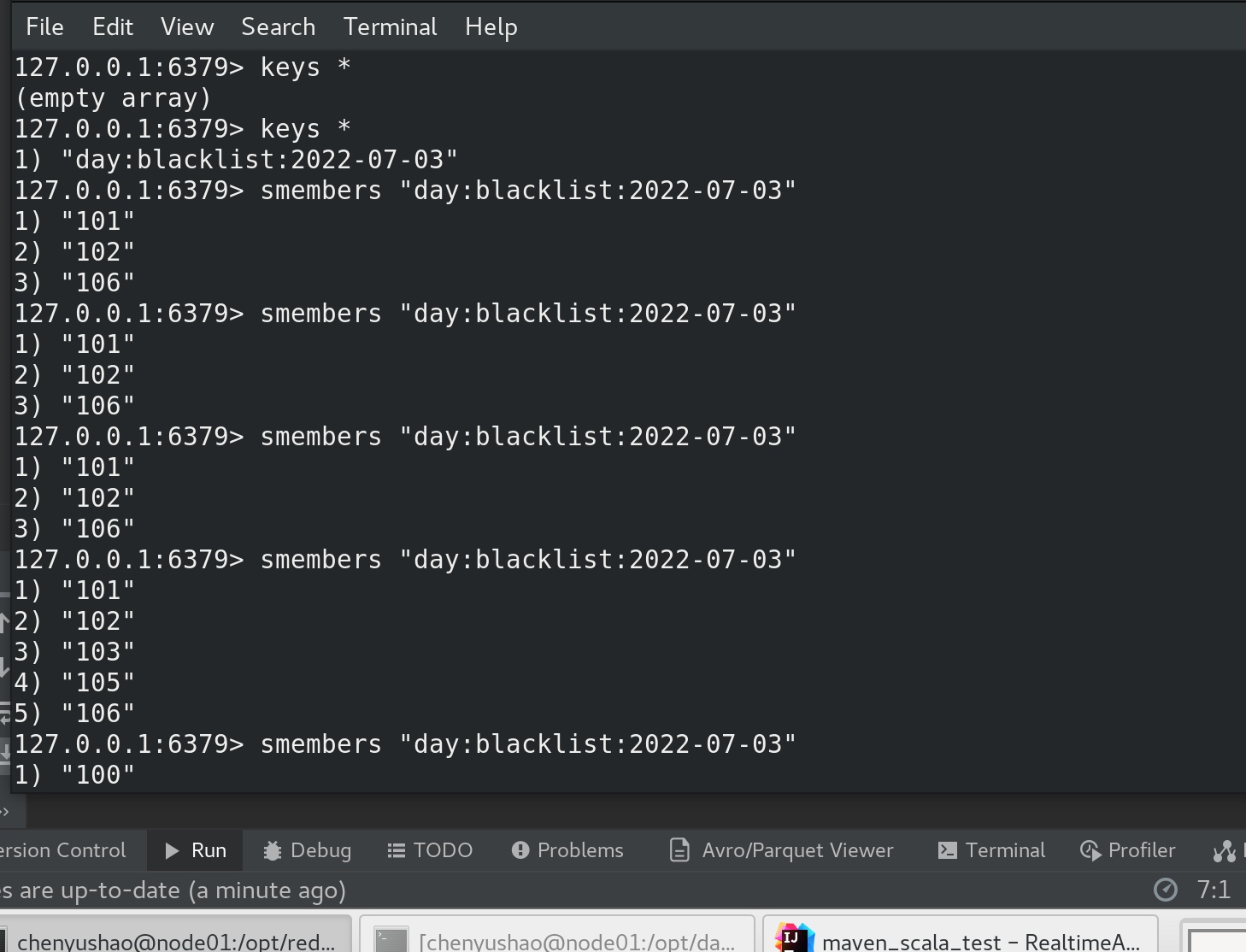
此时在 redis-cli 中查看 redis内容,可见 黑名单 里的数据越来越多了。
统计广告点击量 (需求)
每天每地区每城市每广告的点击流量实时统计
(技法)
在spark structure streaming 的编写上,要注意:
1、编写步骤上、应先用console的形式输出到控制台,再一点一点去完善代码。
2、spark处理数据的时间间隔最好要 小于 kafka等数据流生成的时间间隔。
3、awaitTermiation() 放的位置是 流式处理的最后一个writestreaming后尾作为收尾标志的,若之前有多次流式处理,写到start() 即可,运行起来以找到 awaitTermiation() 作为一整个流式处理的结束。
4、如果运行一直没结果,又不明不白的停滞了,jps 检查一下看看hadoop 有没有 /tmp/hsperf 错误,zookeeper、kafka、hadoop都重来一遍,checkpointLocation删除重新生成一个新的。再来一遍。
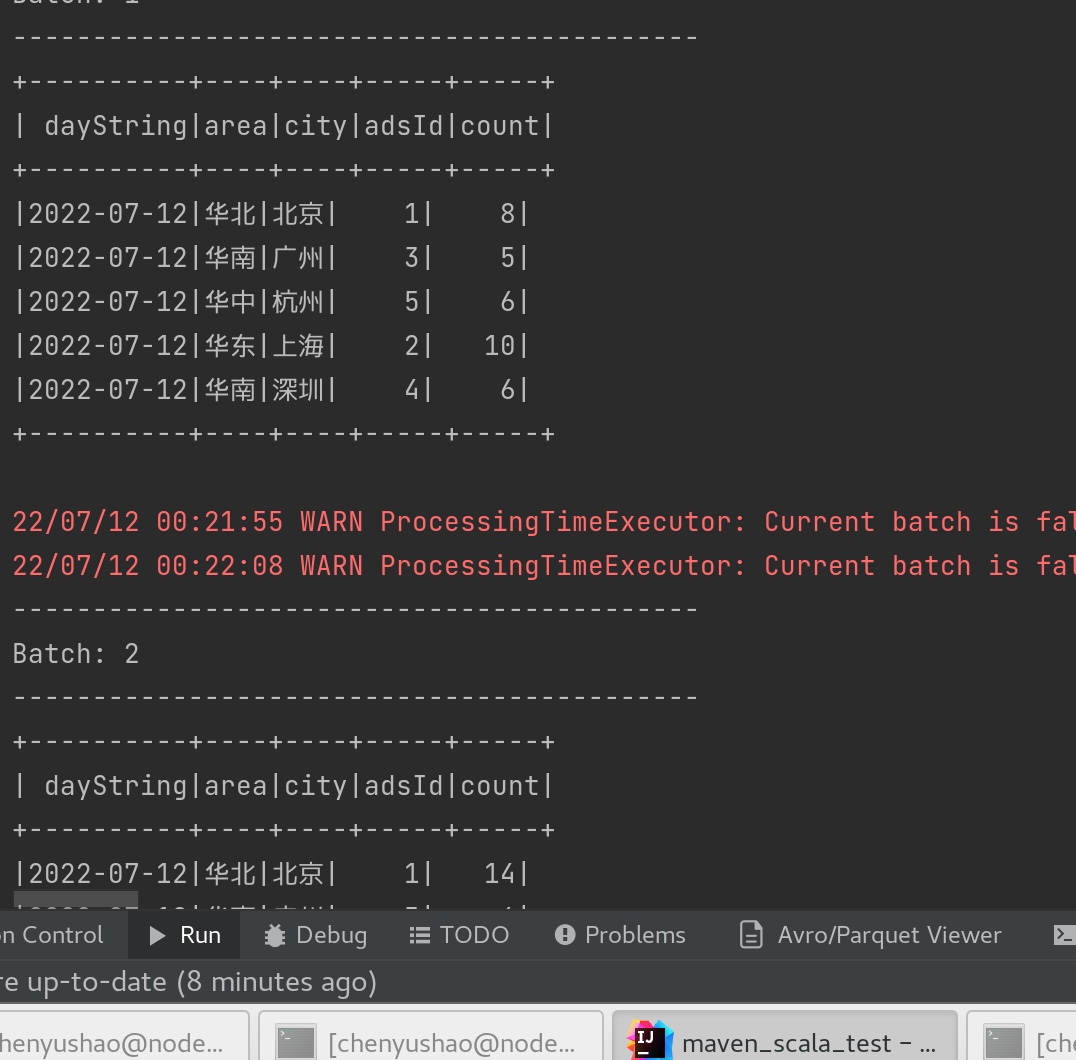
先在控制台console 中检查数据。如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 package kafka_to_spark_test.appimport kafka_to_spark_test.bean.AdsInfo import org.apache.spark.sql.streaming.Trigger import org.apache.spark.sql.{DataFrame , Dataset , SparkSession }object AdsClickCountApp def statClickCount SparkSession ,filtered_adsInfoDS:Dataset [AdsInfo ]):Unit ={ val resultDF: DataFrame = filtered_adsInfoDS .groupBy("dayString" , "area" , "city" , "adsId" ) .count() resultDF.writeStream .format("console" ) .outputMode("complete" ) .trigger(Trigger .ProcessingTime ("2 seconds" )) .start() .awaitTermination() } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 package kafka_to_spark_test.appimport kafka_to_spark_test.app.{BlackListApp ,AdsClickCountApp }import kafka_to_spark_test.bean.AdsInfo import org.apache.spark.sql._import java.sql.Timestamp import java.text.SimpleDateFormat import java.util.Date object RealtimeApp1 def main Array [String ]): Unit ={ val spark: SparkSession = SparkSession .builder() .master("local[*]" ) .appName("realtimeApp" ) .getOrCreate() spark.sparkContext.setLogLevel("WARN" ) import spark.implicits._ val dayStringFormatter = new SimpleDateFormat ("yyyy-MM-dd" ) val hmStringFormatter = new SimpleDateFormat ("HH:mm" ) val adsInfoDS: Dataset [AdsInfo ] = spark.readStream .format("kafka" ) .option("kafka.bootstrap.servers" , "node01:9092" ) .option("subscribe" , "ads_log" ) .load .select("value" ) .as[String ] .map(v => { val split: Array [String ] = v.split("," ) val date = new Date (split(0 ).toLong) AdsInfo ( new Timestamp (split(0 ).toLong), dayStringFormatter.format(date), hmStringFormatter.format(date), split(2 ), split(3 ), split(1 ), split(4 ) ) }) .withWatermark("timestamp" ,"24 hours" ) val filtered_adsInfoDS: Dataset [AdsInfo ] = BlackListApp .startBlackList(spark, adsInfoDS) AdsClickCountApp .statClickCount(spark, filtered_adsInfoDS) } }
运行 模拟生成器 和 RealtimeApp1,在console可见
用foreachebatch来写入redis。
注意事项:
1、spark structure streaming最好先 jps 检查一下 有无 【进程号】 – process information unavailable 这个错误,如果有,则删除 /tmp/hsperfdata_{username} 那几个文件夹,再重启hadoop、zookeeper、Kafka;
2、jvm 空间不足,除了我们 cd /etc/security/limits.d 将文件 xxxx.config 的 * soft nproc xxxx 注释掉以外;reboot也可以解决;
3、总是提示 foreachBatch \ foreachPartition 的参数 类型缺失missing parameter type,我们要手动补全,像这样 foreachBatch{ (df:DataFrame,batchId:Long)=>{ df.foreachPartition((rowIt: Iterator[Row]) => { ;可以看官网,也可以在idea中ctrl+p 查看参数提示,以官网为准;
4、hmset 之类的hash格式在python中写入dict即可,scala中需要把scala的map转化成java的map,dataframe中可以保存map格式的数据,df 需要使用getAs写一下Map[…,…]类型,否则Map中的类型无法自动识别,像这样 row.getAs[Long](4);
5、redis 存map需要的是Java 类型的map,scala的map需要先转成Java的map才能存,现在转的途径只有javaconverter配合asjava,而 javaconversion已经不用了;
6、报错java.lang.ClassCastException: java.lang.Long cannot be cast to java.lang.String 这是因为 java toString 的强制类型转换可能报这个错,用 String.valueOf() 这样强转 不会报错。
7、一个非常让我费解的错误 [Overloaded method foreachBatch with alternatives] ,foreachbatch重载后分不清找哪一个, 解决方法我是在这里看到的https://stackoverflow.com/questions/63137538/overloaded-method-foreachbatch-with-alternatives在 foreachbatch 的最后,也就是解除持久化 df.unpersist() 下面加上一个 “ () ” 符号,就能解决问题,我现在也不明白为什么,但是可以解决问题。
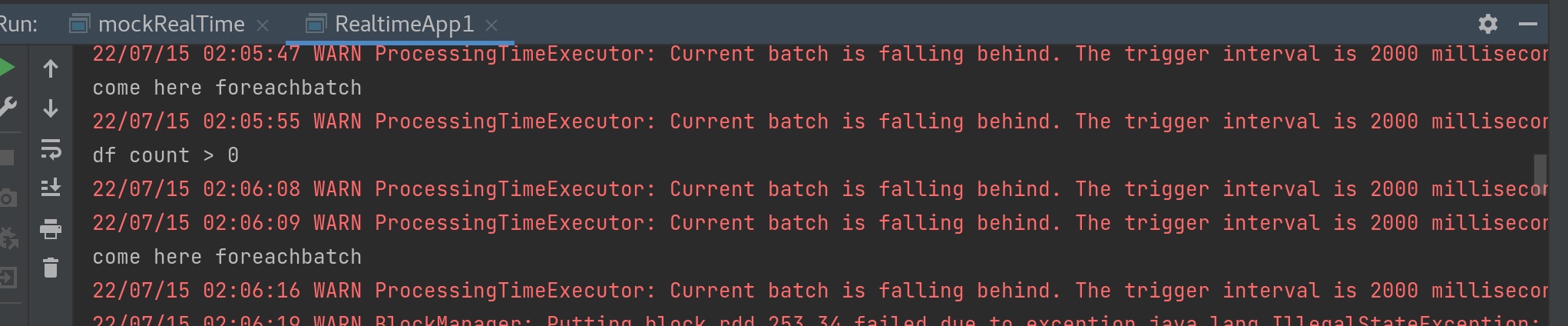
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 package kafka_to_spark_test.appimport kafka_to_spark_test.bean.AdsInfo import kafka_to_spark_test.util.RedisUtil import org.apache.spark.sql.streaming.Trigger import org.apache.spark.sql.{DataFrame , Dataset , Row , SparkSession }import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis import java.utilobject AdsClickCountApp def statClickCount SparkSession ,filtered_adsInfoDS:Dataset [AdsInfo ]):Unit ={ val resultDF: DataFrame = filtered_adsInfoDS .groupBy("dayString" , "area" , "city" , "adsId" ) .count() import spark.implicits._ resultDF.writeStream .outputMode("complete" ) .foreachBatch{ (df:DataFrame ,batchId:Long )=>{ df.persist() println("come here foreachbatch" ) if (df.count()>0 ){ println("df count > 0" ) df.foreachPartition((rowIt: Iterator [Row ]) => { val client: Jedis = RedisUtil .getJedisClient var dayString:String = "" val dict_map_asValue: Map [String , String ] = rowIt.map(row => { dayString = row.getString(0 ) val area: String = row.getString(1 ) val city: String = row.getString(2 ) val adsId: String = row.getString(3 ) val count: String = String .valueOf(row.getAs[Long ](4 )) (s"$area :$city :$adsId " , count) }).toMap if (dict_map_asValue.size>0 ){ import scala.collection.JavaConverters ._ val dict_map_asValue1: java.util.Map [String , String ] = dict_map_asValue.asJava client.hmset(s"date:area:city:ads:$dayString " ,dict_map_asValue1) } client.close() }) } df.unpersist() () }} .trigger(Trigger .ProcessingTime ("2 seconds" )) .start() .awaitTermination() } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 package kafka_to_spark_test.appimport kafka_to_spark_test.app.{BlackListApp ,AdsClickCountApp }import kafka_to_spark_test.bean.AdsInfo import org.apache.spark.sql._import java.sql.Timestamp import java.text.SimpleDateFormat import java.util.Date object RealtimeApp1 def main Array [String ]): Unit ={ val spark: SparkSession = SparkSession .builder() .master("local[*]" ) .appName("realtimeApp" ) .getOrCreate() spark.sparkContext.setLogLevel("WARN" ) import spark.implicits._ val dayStringFormatter = new SimpleDateFormat ("yyyy-MM-dd" ) val hmStringFormatter = new SimpleDateFormat ("HH:mm" ) val adsInfoDS: Dataset [AdsInfo ] = spark.readStream .format("kafka" ) .option("kafka.bootstrap.servers" , "node01:9092" ) .option("subscribe" , "ads_log" ) .load .select("value" ) .as[String ] .map(v => { val split: Array [String ] = v.split("," ) val date = new Date (split(0 ).toLong) AdsInfo ( new Timestamp (split(0 ).toLong), dayStringFormatter.format(date), hmStringFormatter.format(date), split(2 ), split(3 ), split(1 ), split(4 ) ) }) .withWatermark("timestamp" ,"24 hours" ) val filtered_adsInfoDS: Dataset [AdsInfo ] = BlackListApp .startBlackList(spark, adsInfoDS) AdsClickCountApp .statClickCount(spark, filtered_adsInfoDS) } }
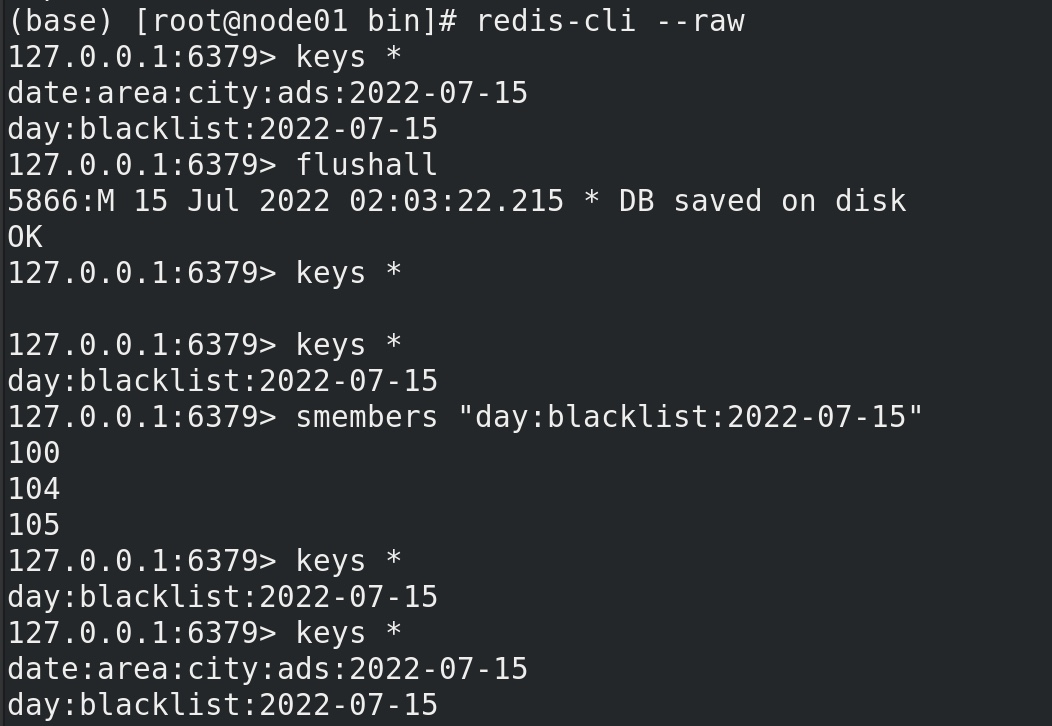
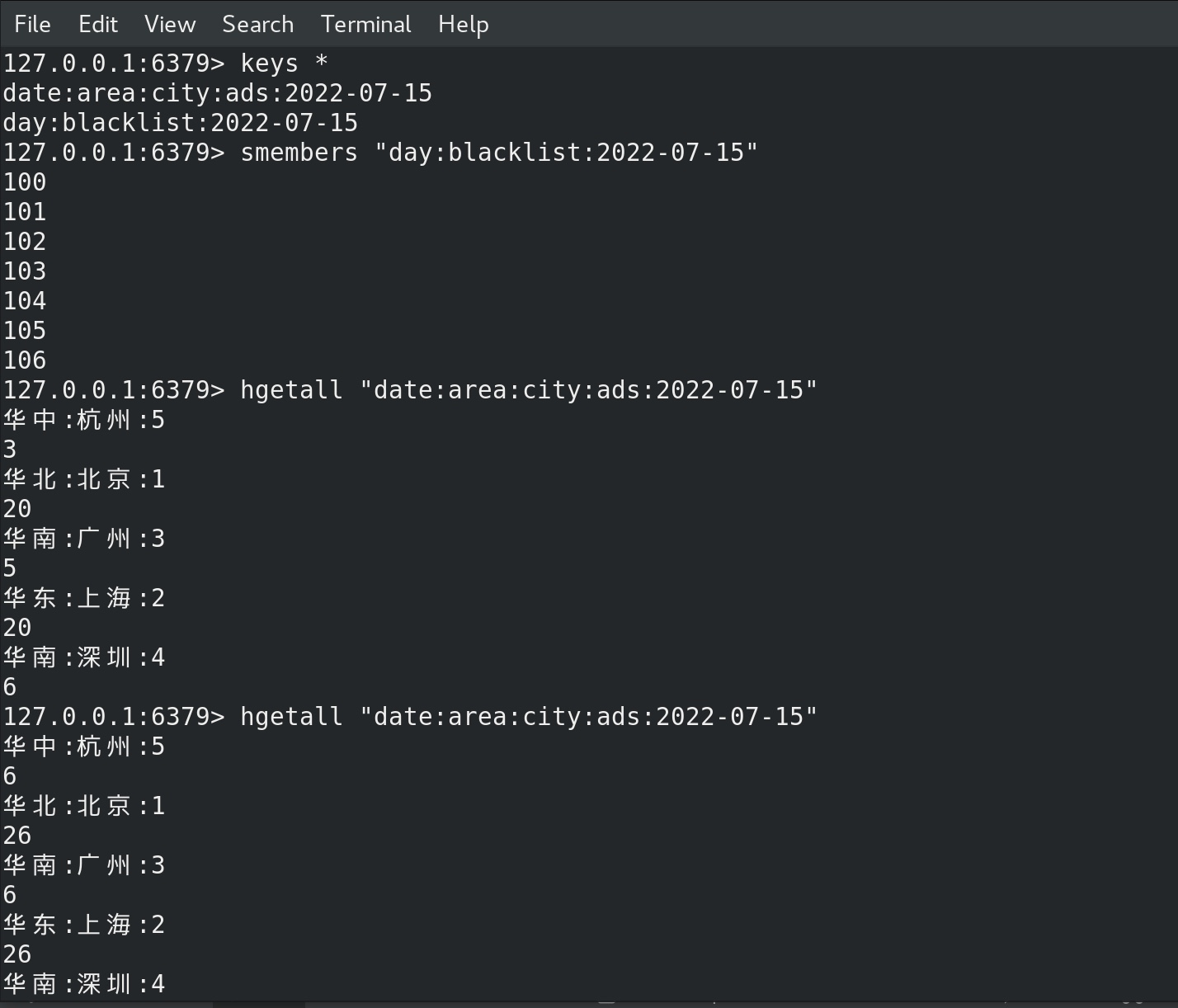
先运行前面的模拟数据模块 mockRealTime,再运行最后一版的RealtimeApp1 ,启动了流式计算的 “两个流”,前一个流写 黑名单入redis,并且返回过滤后的值,后一个流 实时统计每天每地区每城市广告点击量,运行一段时间后,用显示原数据的模式打开redis客户端 redis-cli --raw(为了显示中文) 可见:
等待一会儿,redis 中就有了两个key,一个是黑名单(set类型),一个是最后的统计点击量数据(map类型),我们看见黑名单内数据慢慢增多,最后统计点击量数据 也慢慢增多,在所有数据都入了黑名单之后,最后统计点击量的数据也就不再发生变化。
词频统计 还是以kafka为输入源。
1 2 3 kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server node01:9092 --create --topic kafka-structure-stream --partitions 3 --replication-factor 2 kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list node01:9092 --topic kafka-structure-stream
编写Structured Streaming程序的基本步骤包括:
导入pyspark模块
创建SparkSession对象
创建输入数据源
定义流计算过程
启动流计算并输出结果
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/databricks/kb/streaming/append-output-not-supported-no-watermark
注意事项:spark structure streaming 中 append mode情况下,聚合函数像groupby,参数都要加一个时间戳列,或者窗口函数,来确定是在哪个时间范围内做聚合操作 The aggregation must have an event-time column, or a window on the event-time column.。