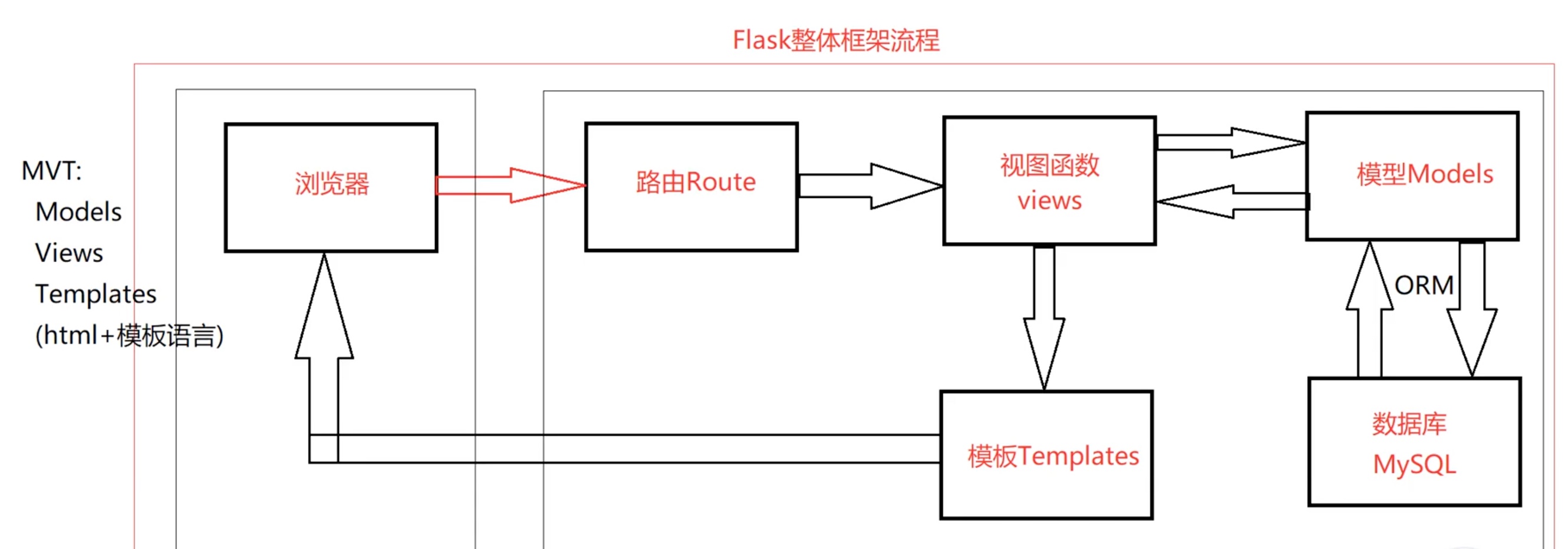
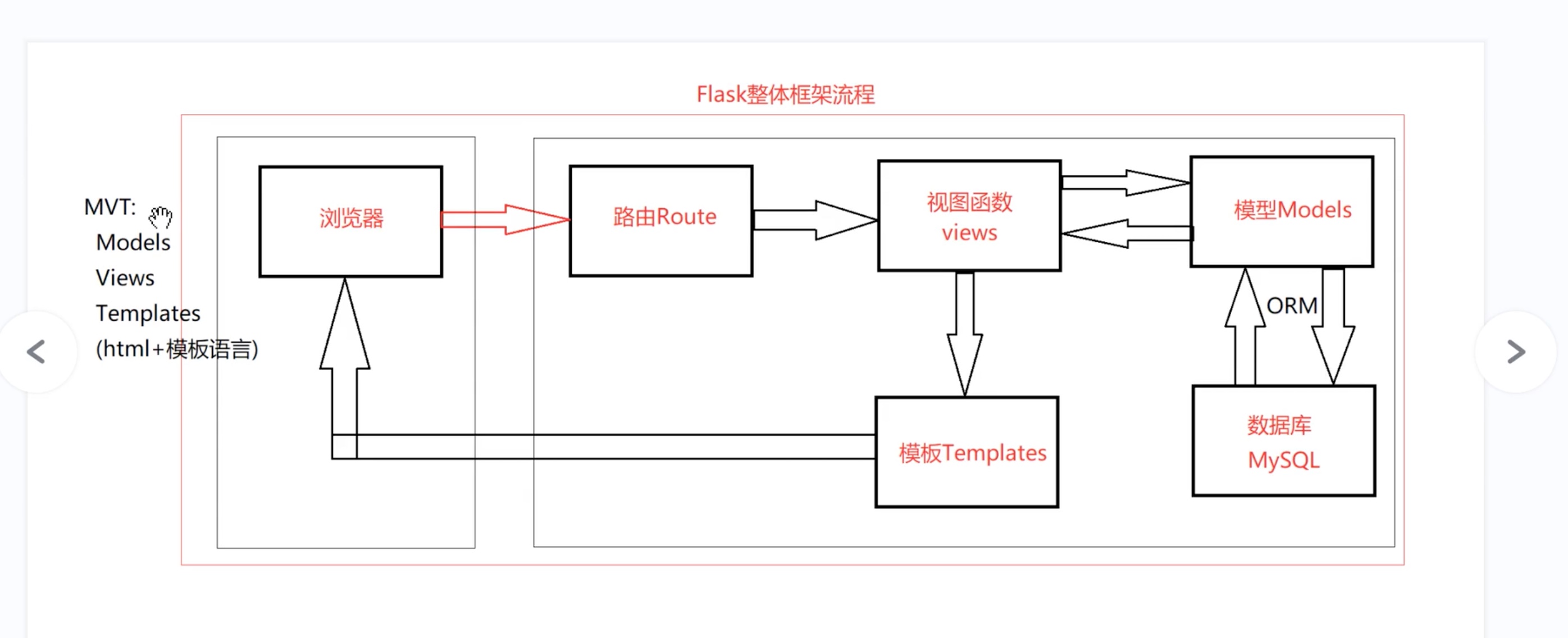
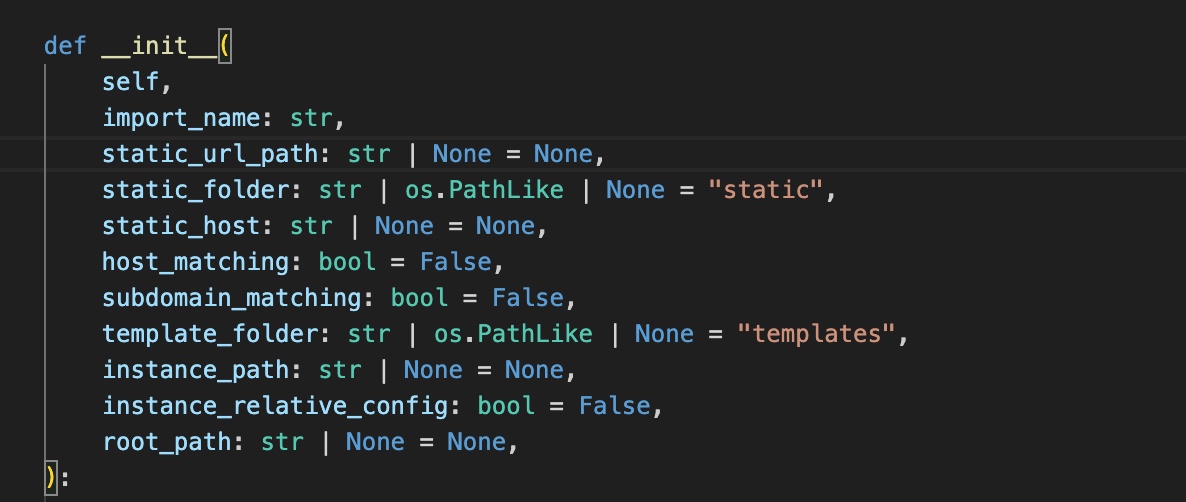
Flask整体框架流程
简单例子 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 from flask import Flask app = Flask(__name__) @app.route("/" def hello_world (): return "<p>Hello,world!</p>" @app.route('/index' def index_test (): return 'Index 页面' if __name__=='__main__' : app.run()
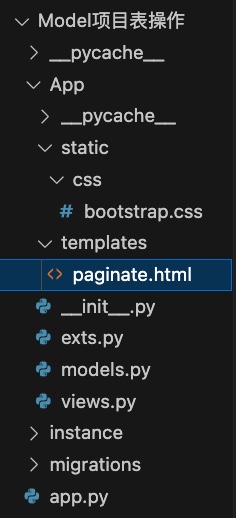
建立一个项目,项目下由app.py、templates/index.html、static/index.css 组成。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 from flask import Flask, jsonify, render_templateapp = Flask(__name__) @app.route("/" def home (): return "<b>Flask Home</b>" @app.route('/index' def index_test (): return render_template('index.html' ,name='法外狂徒' ) if __name__=='__main__' : app.run(debug=True ,port=5000 ,host='0.0.0.0' )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Title</title > <link rel ="stylesheet" href ="{{ url_for('static',filename='index.css')}}" > </head > <body > <h2 > Index</h2 > <hr > <h4 > name: {{ name }}</h4 > </body > </html >
注意上面的 app = Flask(__name__) 是在 “第一个flask项目” 下创建的,app对象实际上的执行 是发生在“第一个flask项目”下的。
项目的拆分
直接从App包 下调用 init .py 中的方法创建app对象就 好了。一个 App 就是一个 flask 应用。
app.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 from App import create_app app = create_app() if __name__ == '__main__' : app.run(debug=True )
App/ init .py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 from flask import Flask from .views import blue def create_app (): app = Flask(__name__) app.register_blueprint(blueprint=blue) return app
App/views.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 from flask import Blueprint blue = Blueprint('user' ,__name__) blue2 = Blueprint('product' ,__name__) @blue.route('/' def index (): return 'home' @blue2.route('/goods' def index (): return 'goods'
路由
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 @blue.route('/string/<string:name>/' def get_string (name ): print (type (name)) return name @blue.route('/int/<int:age>/' def get_int (age ): print (type (age)) return str (age) @blue.route('/getuuid' def get_uuid2 (): import uuid return str (uuid.uuid4()) @blue.route('/uuid/<uuid:id>/' def get_uuid (id print (type (id )) return str (id ) @blue.route('/any/<any(apple,orange,banana):id>/' def get_any (id print (type (id )) return str (id ) @blue.route('/methods' ,methods=['GET' ,'POST' ] def get_methods (): return 'methods'
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 import requests res = requests.get('http://127.0.0.1:5000/methods' ) print (res.text)res = requests.post('http://127.0.0.1:5000/methods' ) print (res.text)
Flask请求request/响应response
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 from flask import Blueprint, Response,jsonify, render_template,requestblue = Blueprint('user' ,__name__) blue1 = Blueprint('product1' ,__name__) blue2 = Blueprint('product2' ,__name__) @blue.route('/request/' ,methods=['GET' ,'POST' ] def get_request (): print ('look here ! this is:' ,request) print (request.method) print (request.args) print (request.args.get('name' )) print (request.form) print (request.form.get('name' )) print (request.cookies) return 'request ok!' @blue.route('/response/' def get_response (): pass html = render_template('index.html' ,name='小城' ,age=100 ) print (html,type (html)) res = Response(html) return res
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 import requests res = requests.get('http://127.0.0.1:5000/request/?name=lisi&name=zhangsan&age=22' ) print (res.text)res = requests.post('http://127.0.0.1:5000/request/' , data={'name' :'lucy' ,'age' :33 }, cookies={'name' :'hello' }) print (res.text)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Title</title > <link rel ="stylesheet" href ="{{ url_for('static',filename='index.css')}}" > </head > <body > <h2 > Index</h2 > <hr > <p > name: {{ name }}</p > <p > age: {{age}}</p > </body > </html >
重定向 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 from flask import Blueprint, Response,jsonify, redirect, render_template,request, url_forblue = Blueprint('user' ,__name__) blue1 = Blueprint('product1' ,__name__) @blue.route('/request/' ,methods=['GET' ,'POST' ] def get_request (): print ('look here ! this is:' ,request) print (request.method) print (request.args) print (request.args.get('name' )) print (request.form) print (request.form.get('name' )) print (request.cookies) return 'request ok!' @blue.route('/response/' def get_response (): pass html = render_template('index.html' ,name='小城' ,age=100 ) print (html,type (html)) res = Response(html) return res @blue.route('/redirect' def make_redirect (): pass ret = url_for('user.get_response' ,) print ('ret is:' ,ret) ret2 = url_for('user.get_request' ,name='张飞' ,age=100 ) return redirect(ret2)
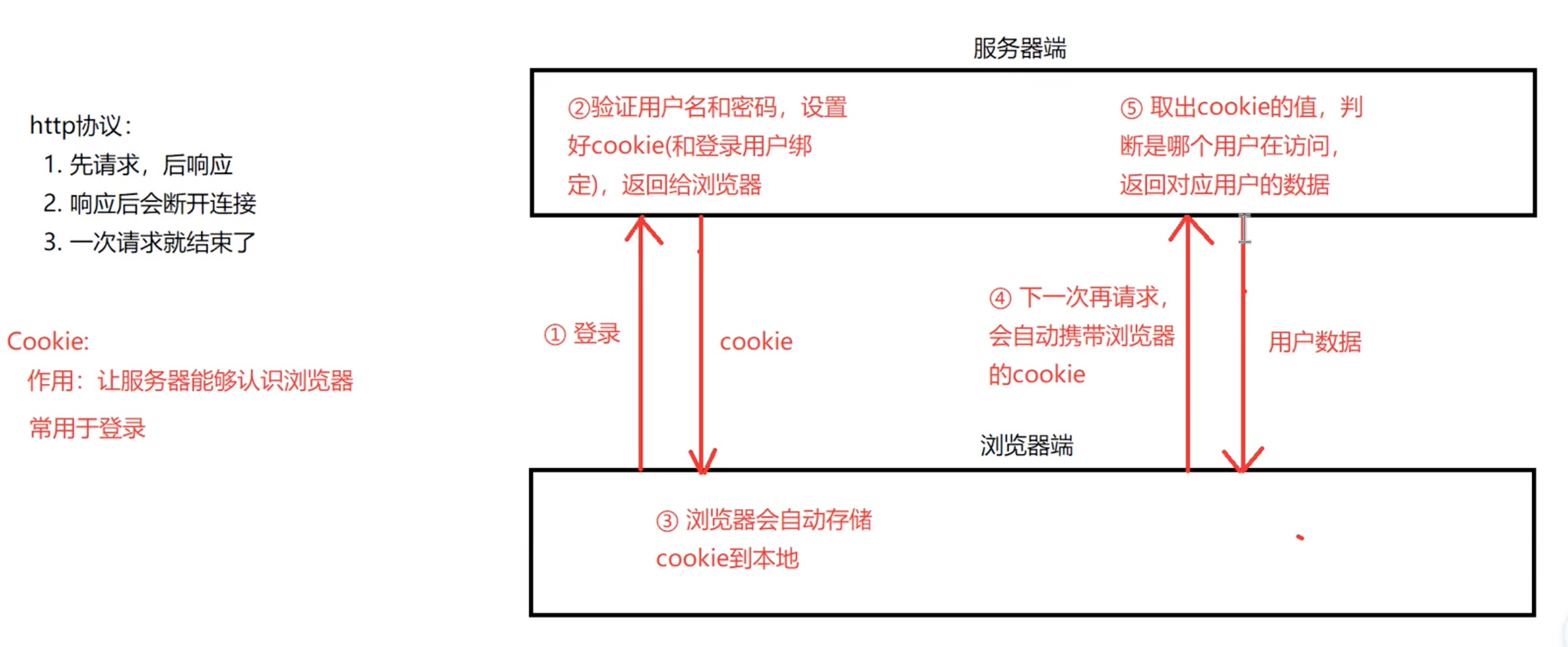
cookie实现 cookie的记忆是基于用户而不是浏览器;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 from flask import Blueprint, redirect, render_template, requestblue = Blueprint('user' ,__name__) @blue.route('/' @blue.route('/home/' def home (): username = request.cookies.get('user' ) return render_template('/home.html' ,username=username) @blue.route('/login/' ,methods=['POST' ,'GET' ] def login (): if request.method == 'GET' : return render_template('login.html' ) elif request.method == 'POST' : pass username = request.form.get('username' ) password = request.form.get('password' ) if username=='chen' and password=='123' : response = redirect('/home' ) print (response,'look here' ) response.set_cookie('user' ,username,max_age=3600 *24 *7 ) return response else : return '用户名或密码错误' @blue.route('/logout' def logout (): response = redirect('/home' ) response.delete_cookie('user' ) return response
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > 首页</title > <link rel ="stylesheet" href ="{{ url_for('static',filename='index.css')}}" > </head > <body > <h2 > 首页</h2 > <hr > {% if username %} <p > 当前用户是:{{username}} <a href ="/logout" > 注销</a > </p > {% else %} <a href ="/login" > 登录</a > {% endif %} </body > </html >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > 登录</title > <link rel ="stylesheet" href ="{{ url_for('static',filename='index.css')}}" > </head > <body > <h2 > 登录</h2 > <hr > <form action ="{{url_for('user.login')}}" method ="post" > <p > 用户名:<input type ="text" name ="username" > </p > <p > 密码:<input type ="password" name ="password" > </p > <p > <button > 提交</button > </p > </form > </body > </html >
session实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 from flask import Blueprint, redirect, render_template, request, sessionblue = Blueprint('user' ,__name__) @blue.route('/' @blue.route('/home/' def home (): username = session.get('user' ) return render_template('/home.html' ,username=username) @blue.route('/login/' ,methods=['POST' ,'GET' ] def login (): if request.method == 'GET' : return render_template('login.html' ) elif request.method == 'POST' : pass username = request.form.get('username' ) password = request.form.get('password' ) if username=='chen' and password=='123' : response = redirect('/home/' ) session['user' ] = username session.permanent = True return response else : return '用户名或密码错误' @blue.route('/logout' def logout (): response = redirect('/home' ) session.pop('user' ) return response
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 import datetimefrom flask import Flask from .views import bluedef create_app (): app = Flask(__name__) app.register_blueprint(blueprint=blue) print (app.config) app.config['SECRET_KEY' ] = '123' app.config['PERMANENT_SESSION_LIFETIME' ] = datetime.timedelta(days=8 ) return app
template Flask 使用 jinja2模版引擎。
view.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 from flask import Blueprint, render_template blue = Blueprint('user' ,__name__) @blue.route('/' def home (): pass data = { 'name' :'ikun ikun ikun' , 'age' :7 , 'likes' :['ball' ,'sing' ,'dance' ,'code' ] } return render_template('child2.html' ,**data)
home.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > 首页</title > </head > <body > <h2 > Home</h2 > <hr > {# 模版语言的注释 #} <h4 > 变量:</h4 > <p > name:{{ name }}</p > <p > age:{{age}}</p > <p > likes:{{likes}}</p > <hr > <h4 > 标签:</h4 > <h5 > if语句</h5 > {% if age >= 18 %} <p > {{name}}已经成年了</p > {% elif age>=6 %} <p > 可以上学了</p > {% else %} <p > {{name}}还是小孩</p > {% endif %} <h5 > for循环</h5 > {% for like in likes %} {% if loop.first %} <p style ="color:red;" > {{like}}</p > {% elif loop.last %} <p style ="color:blue;" > {{like}}</p > {% else %} <p > {{like}}</p > {% endif %} index:{{ loop.index }} index2:{{ loop.index0 }} revindex:{{ loop.revindex }} revindex0:{{ loop.revindex0 }} {% endfor %} </body > </html >
base.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > 父模版</title > {# 在html的head中导入css文件,static中 #} <link rel ="stylesheet" href ="{{url_for('static',filename='css/base.css')}}" > {% block extcss %} {% endblock %} </head > <body > {% block head %} {% endblock %} <hr > {% block content %} {% endblock %} <hr > {% block foot %} {% endblock %} {# 导入js文件,static中 #} <script src ="{{url_for('static',filename='js/base.js')}}" > </script > {% block extjs %} {% endblock %} </body > </html >
child1.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 {% extends 'base.html' %} {% block head %} <div > <p > ok,ok,ok.</p > </div > {% endblock %}
child2.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 {% extends 'child1.html' %} {# 继承 #} {% block head %} {{ super() }} {# 保留父辈block head内容 #} <p > python</p > {# 如果没有super就,覆盖重写了 #} {% endblock %} {% block content %} {% include 'child2_include.html' %} {# 导入include内容 #} <p > Flask content </p > {% endblock %} {% macro person(name,age) %} <b > 姓名 : {{name}}, 年龄 : {{age}} </b > {% endmacro %} {% block foot %} {{ person('小鸟',100) }} {# 过滤器 #} <p > {{name | capitalize }}</p > <p > {{name | title }}</p > <p > {{name | upper }}</p > <p > {{name | upper | first |lower }}</p > {% endblock %}
child2_include.html
1 <div > 我是child2中include的内容</div >
模型 ORM object relational mapping 对象关系映射;
数据库的表 映射到对象,对对象操作。
pip install flask-sqlalchemy pip install flask-migrate pip install pymysql
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 from flask import Flask from .views import bluefrom .exts import init_exitdef create_app (): app = Flask(__name__) app.register_blueprint(blueprint=blue) db_uri = 'sqlite:///sqlite3.db' app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI' ] = db_uri init_exit(app=app) return app
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemyfrom flask_migrate import Migratedb = SQLAlchemy() migrate = Migrate() def init_exit (app ): db.init_app(app=app) migrate.init_app(app=app,db=db)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 from .exts import db class User (db.Model): __tablename__ = 'tb_user' id = db.Column(db.Integer,primary_key=True ,autoincrement=True ) name = db.Column(db.String(30 ),unique=True ,index=True ) age = db.Column(db.Integer,default=1 ) sex = db.Column(db.Boolean,default=True ) salary = db.Column(db.Float,default=1000000000 ,nullable=False )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 from flask import Blueprint from .models import * blue = Blueprint('user' ,__name__) @blue.route('/' def index (): return 'home' @blue.route('/string/<string:name>/' def get_string (name ): print (type (name)) return name
进入 app.py 文件夹所在的目录,执行
flask db init(创建迁移文件夹migrates;只调用一次) flask db migrate (生成迁移文件;自动搜索继承了db.Model的类) flask db upgrade (把类都转换成表) flask db downgrade (撤回把类都转换成表)
每一次执行 flask db migrate 都会在migrations/versions 中生成新的py文件,在表格变动的时候记得生成,然后 再 upgrade 变成表,在instance 下的db文件可见这些表。
注意:
Flask使用migrate迁移后,无法检测到models,无法生成表,则 *只需要在 app.py 中导入 models.py 中的类即可。*
模型表操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 from operator import and_from flask import Blueprint, render_template, requestfrom sqlalchemy import desc from .models import *blue = Blueprint('user' ,__name__) blue1 = Blueprint('product1' ,__name__) blue2 = Blueprint('product2' ,__name__) @blue.route('/useradd' def user_add (): u = User() u.name = 'kun' u.age = 24 db.session.add(u) db.session.commit() return 'success!' @blue.route('/useradds' def user_adds (): users = [] for i in range (10 ,30 ): u = User() u.name = '斌斌' + str (i) u.age = i users.append(u) try : db.session.add_all(users) db.session.commit() except Exception as e: db.session.rollback() db.session.flush() return 'fail !' + str (e) return 'success !!' @blue.route('/userdel' def user_del (): u = User.query.first() db.session.delete(u) db.session.commit() return 'success !' @blue.route('/userupdate' def user_update (): u = User.query.first() u.age = 1000 db.session.commit() return 'success !' @blue.route('/userget/' def user_get (): users = User.query.all () users = User.query.filter () user = User.query.get(8 ) users = User.query.filter (User.age==20 ) users = User.query.filter_by(age=20 ) users = User.query.filter (User.age>20 ) print (list (users)) users = User.query.offset(3 ).limit(4 ) print (list (users)) users = User.query.order_by('age' ) users = User.query.order_by(desc('age' )) print (list (users)) users = User.query.filter (and_(User.age>20 ,User.age<25 )) print (list (users)) users = User.query.filter (User.name.contains('3' )) print (list (users)) users = User.query.filter (User.name.in_([10 ,20 ,30 ,40 ])) print (list (users)) return 'success !' @blue.route('/paginate/' def get_paginate (): page = int (request.args.get('page' ,1 )) per_page = int (request.args.get('per_page' ,5 )) print (page,type (page)) print (per_page,type (per_page)) p = User.query.paginate(page=page,per_page=per_page,error_out=False ) print (p.items) print (p.has_next) print (p.has_prev) print (p.total) return render_template('paginate.html' ,p=p)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 from .exts import db class User (db.Model): __tablename__ = 'user1' id = db.Column(db.Integer,primary_key=True ,autoincrement=True ) name = db.Column(db.String(30 ),unique=True ) age = db.Column(db.Integer,default=1 ) def __repr__ (self ) -> str : return self.name
先去bootstrap官网下载文件,把对应的bootstrap.css 文件放到app/static/css文件夹下。照着文档指导配合自己的逻辑关系写即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 <link rel ="stylesheet" href ="{{ url_for('static',filename='css/bootstrap.css')}}" > </head > <body > <div class ="container" > <h2 > 分页演示</h2 > <hr > <ul class ="list-group" > {% for user in p.items %} <li class ="list-group-item" > {{ user.name }}</li > {% endfor %} </ul > </div > <hr > <ul class ="pagination" > <li class ="page-item" > {% if p.has_prev %} <a class ="page-link" href ="/paginate/?page={{ p.prev_num }}&per_page=3" aria-label ="Previous" > {% else %} <a class ="page-link" href ="javascript:;" aria-label ="Previous" > {% endif %} <span aria-hidden ="true" > « </span > </a > </li > {% for i in range(p.pages) %} {% if p.page == i+1 %} <li class ="page-item active" > {% else %} <li class ="page-item" > {% endif %} <a class ="page-link" href ="/paginate/?page={{ i+1 }}&per_page=3" > {{ i + 1 }}</a > </li > {% endfor %} <li class ="page-item" > {% if p.has_next %} <a class ="page-link" href ="/paginate/?page={{ p.next_num }}&per_page=3" aria-label ="Next" > {% else %} <a class ="page-link" href ="javascript:;" aria-label ="Next" > {% endif %} <span aria-hidden ="true" > » </span > </a > </li > </ul > </body > </html >
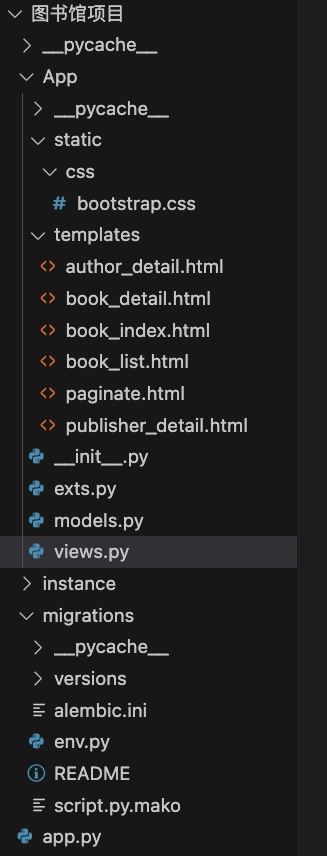
图书馆测试项目
app.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 from App import create_app from App.models import *app = create_app() if __name__ == '__main__' : app.run(debug=True )
__init__.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 from flask import Flask from .views import bluefrom .exts import init_extsdef create_app (): app = Flask(__name__) app.register_blueprint(blueprint=blue) db_uri = 'mysql+pymysql://root:cys123456@localhost:3306/bookdb' app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI' ] = db_uri app.config['SQLALCHEMY_TRACK_MODIFICATIONS' ] = False init_exts(app=app) return app
exes.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemyfrom flask_migrate import Migratedb = SQLAlchemy() migrate = Migrate() def init_exts (app ): db.init_app(app=app) migrate.init_app(app=app,db=db)
models.py 定义模型结构
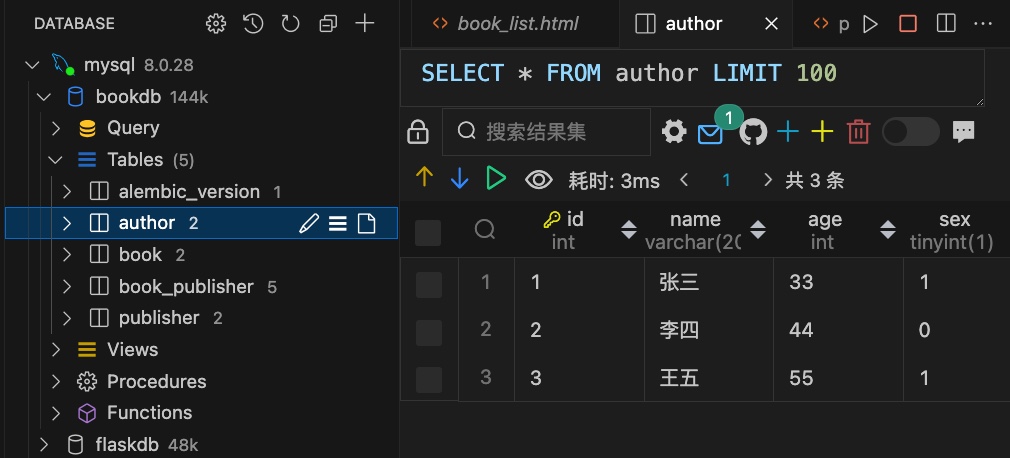
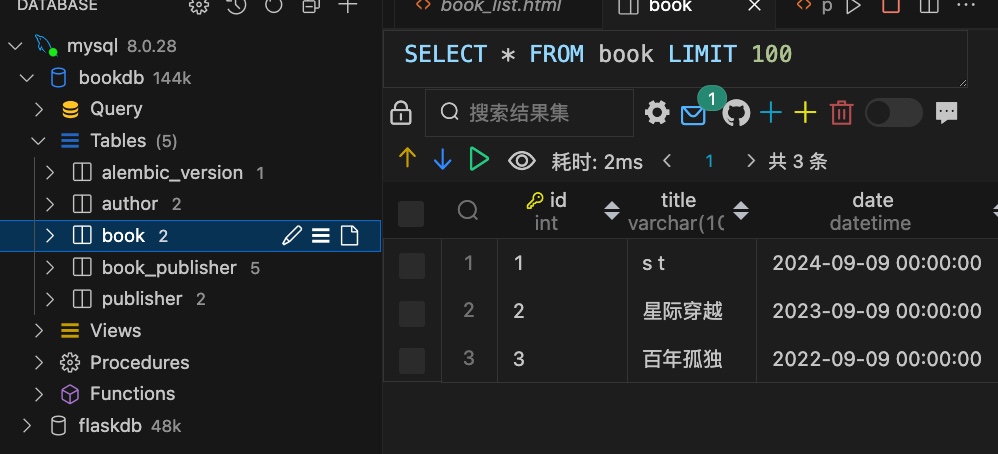
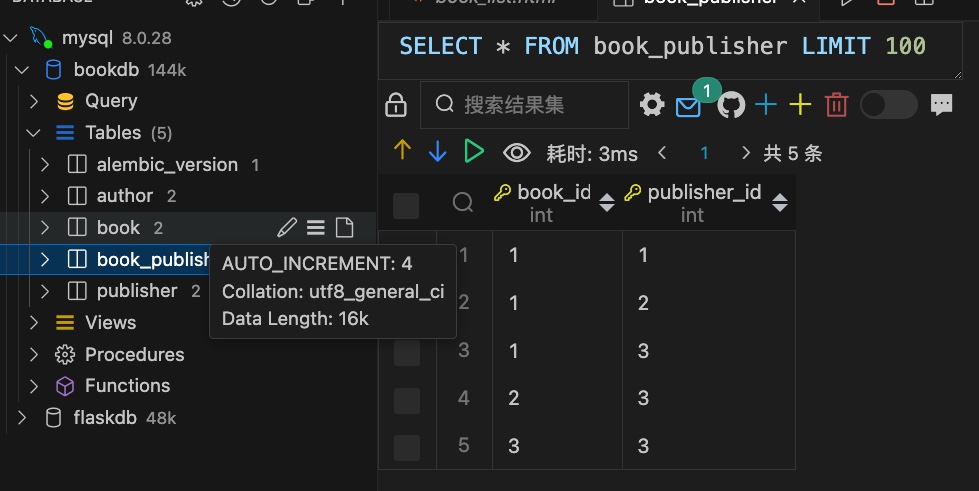
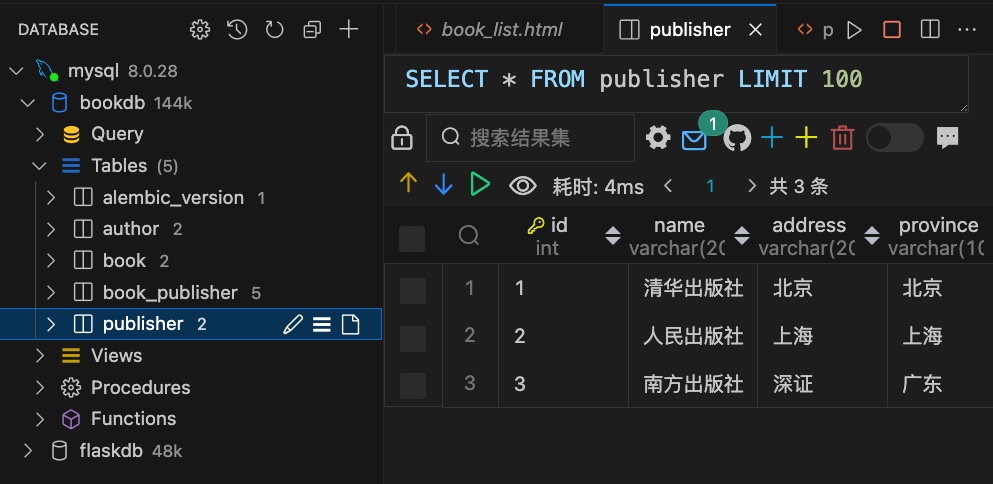
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 from .exts import db class Author (db.Model): id = db.Column(db.Integer,primary_key=True ,autoincrement=True ) name = db.Column(db.String(20 ) ) age = db.Column(db.Integer,default=1 ) sex = db.Column(db.Boolean,default=True ) email = db.Column(db.String(200 )) books = db.relationship('Book' ,backref='auther' ,lazy='dynamic' ) class Book (db.Model): id = db.Column(db.Integer,primary_key=True ,autoincrement=True ) title = db.Column(db.String(100 ),unique=True ) date = db.Column(db.DateTime) author_id = db.Column(db.Integer,db.ForeignKey(Author.id )) book_publisher = db.Table('book_publisher' , db.Column('book_id' ,db.Integer,db.ForeignKey('book.id' ),primary_key=True ), db.Column('publisher_id' ,db.Integer,db.ForeignKey('publisher.id' ),primary_key=True )) class Publisher (db.Model): id = db.Column(db.Integer,primary_key=True ,autoincrement=True ) name = db.Column(db.String(20 ),unique=True ) address = db.Column(db.String(200 )) province = db.Column(db.String(100 )) country = db.Column(db.String(100 )) website = db.Column(db.String(100 )) books = db.relationship('Book' ,backref='publishers' , secondary=book_publisher,lazy='dynamic' )
模型构建好以后,就可以进入 app.py 文件夹所在的目录,执行
flask db init(创建迁移文件夹migrates;只调用一次) flask db migrate (生成迁移文件;自动搜索继承了db.Model的类) flask db upgrade (把类都转换成表) flask db downgrade (撤回把类都转换成表)
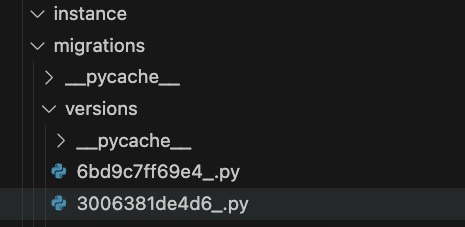
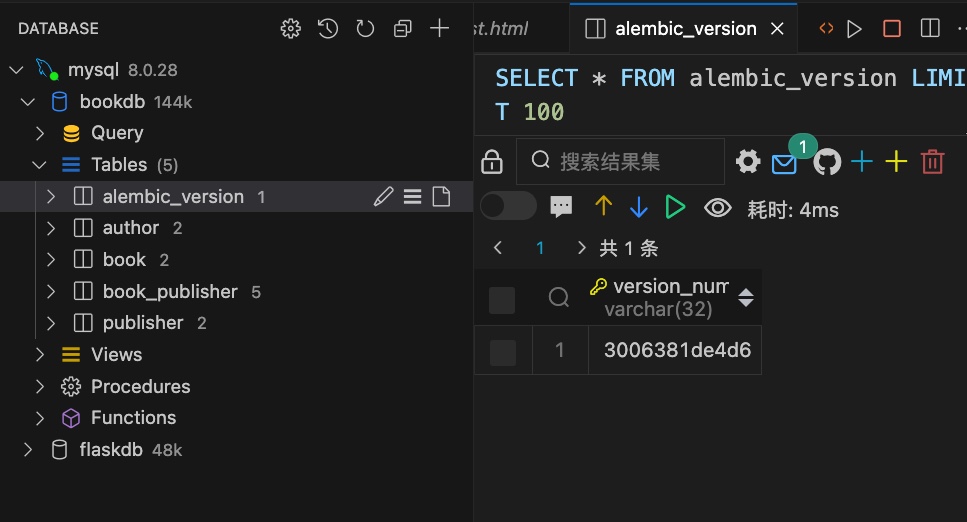
构建完表之后,就可以往表内写各种内容了。如果是vscode插件操作mysql可能出现数据库同步出现问题,此时需要找到migrations文件夹下最下面也就是最新的一个.py文件的名称,此名称去掉下划线,放入mysql数据库的alembic_version中。
通过模型让mysql构建好表的结构之后,我们在表内写入数据。
view.py 视图脚本,基于视图脚本写各个html的前端逻辑
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 from operator import and_from flask import Blueprint, render_template, requestfrom sqlalchemy import desc from .models import *blue = Blueprint('book' ,__name__) @blue.route('/' @blue.route('/bookindex/' def book_index (): return render_template('book_index.html' ) @blue.route('/booklist/' def book_list (): books = Book.query.all () return render_template('book_list.html' ,books = books) @blue.route('/bookdetail/<int:bid>/' def book_detail (bid ): book = Book.query.get(bid) return render_template('book_detail.html' ,book=book) @blue.route('/authordetail/<int:aid>/' def author_detail (aid ): author = Author.query.get(aid) return render_template('author_detail.html' ,author=author) @blue.route('/publisherdetail/<int:pid>/' def publisher_detail (pid ): publisher = Publisher.query.get(pid) return render_template('publisher_detail.html' ,publisher=publisher)
book_index.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > 书籍</title > </head > <body > <h2 > 书籍首页</h2 > <hr > <a href ="/booklist/" > 查看所有书籍</a > </body > </html >
book_list.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > 书籍</title > </head > <body > <h2 > 书籍列表</h2 > <hr > <ul > {% for book in books %} <li > <a href ="{{ url_for('book.book_detail',bid=book.id) }}" > {{ book.title }}</a > </li > {% endfor %} </ul > </body > </html >
book_detail.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > 书籍</title > </head > <body > <h2 > 书籍详情</h2 > <hr > <p > 书籍标题:{{ book.title }}</p > <p > 书籍出版时间:{{ book.date }}</p > <p > 作者: <a href ="/authordetail/{{ book.auther.id }}" > {{ book.auther.name }}</a > </p > <p > 出版社: {% for publisher in book.publishers %} <a href ="/publisherdetail/{{ publisher.id }}" > {{ publisher.name }}</a > {% endfor %} </p > </body > </html >
author_detail.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > 书籍</title > </head > <body > <h2 > 作者详情</h2 > <hr > <p > 作者名称:{{ author.name }}</p > <p > 作者年龄:{{ author.age }}</p > <p > 作者性别:{{ author.sex }}</p > <p > 作者Email:{{ author.email }}</p > <hr > <p > 我的作品 {% for book in author.books %} <a href ="/bookdetail/{{ book.id }}" > {{ book.title }}</a > {% endfor %} </p > </body > </html >
publisher_detail.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > 书籍</title > </head > <body > <h2 > 出版社详情</h2 > <hr > <p > 出版社名称:{{ publisher.name }}</p > <p > 出版社名称:{{ publisher.address }}</p > <p > 出版社名称:{{ publisher.city }}</p > <p > 出版社名称:{{ publisher.province }}</p > <p > 出版社名称:{{ publisher.website }}</p > <hr > <p > 出版社的出版书籍 {% for book in publisher.books %} <a href ="/bookdetail/{{ book.id }}" > {{ book.title }}</a > {% endfor %} </p > </body > </html >
插件使用 缓存例子
使用flask插件 就三个步骤,先下载,再ext.py中初始化,最后再视图中使用。
中间件(钩子) 切面编程
views.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 from operator import and_import timefrom flask import Blueprint, render_template, requestfrom sqlalchemy import desc from .models import *from .exts import cache blue = Blueprint('book' ,__name__) @blue.route('/' @cache.cached(timeout=20 ) def index (): print ('index111' ) time.sleep(5 ) print ('Index' ) return 'index' @blue.before_request def before (): print ('before request.' ) print (request.path) print (request.method) print (request.remote_addr) ip = request.remote_addr if cache.get(ip): return 'please stop 爬虫!!!' else : cache.set (ip,'value' ,timeout=1 )
spider.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 import requests res = requests.get('http://127.0.0.1:5000/' ) print (res.text) for i in range (10 ): res = requests.get('http://127.0.0.1:5000/' ) print (res.text)
flask四大内置对象 g :global,突破变量存储位置限制,例如在 before_request装饰的钩子函数产生了一个后续用得到的变量就可以保存在g对象中,在视图函数中就可以用这个数据。
request :请求对象,可以获取客户端提交过来的请求信息。
session :会话技术,服务端会话技术的接口。
current_app :app的配置信息,app对象获取,一定要在初始化之后使用。
1 2 g.star = 'jack' print (current_app)
静态文件目录static和模版文件目录templates 需要去 Flask.py文件中去修改,才能变 templates的配置。但是我们不推荐在这里改。
给一个改动的例子,把app文件下的 static 和 templates 改到外面一层的文件。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 import os BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))) def create_app (): static_folder = os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'static' ) template_folder = os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'template' ) app = Flask(__name__,static_folder=static_folder, template_folder=template_folder)
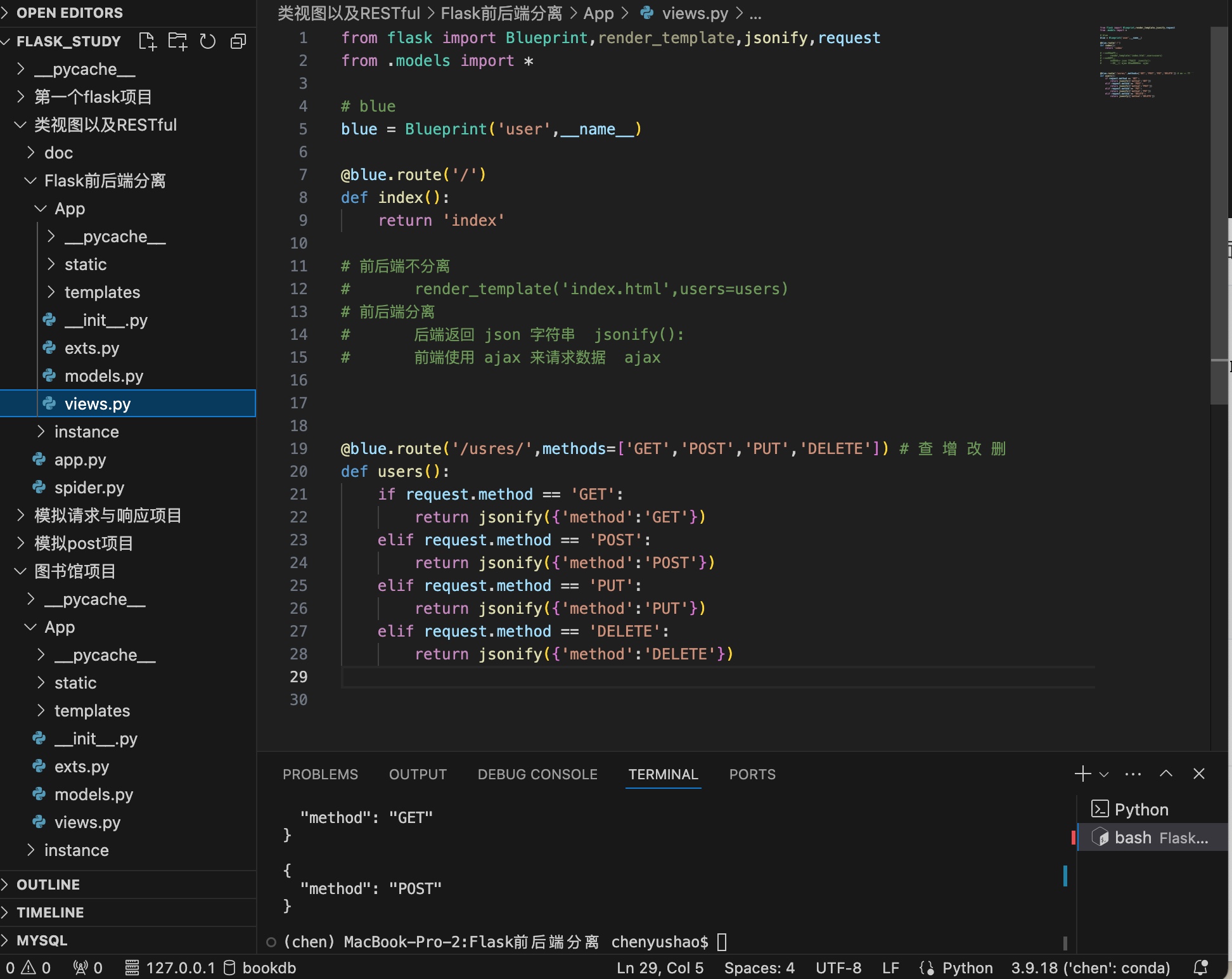
前后端分离
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 from flask import Blueprint,render_template,jsonify,request from .models import *blue = Blueprint('user' ,__name__) @blue.route('/' def index (): return 'index' @blue.route('/usres/' ,methods=['GET' ,'POST' ,'PUT' ,'DELETE' ] def users (): if request.method == 'GET' : return jsonify({'method' :'GET' }) elif request.method == 'POST' : return jsonify({'method' :'POST' }) elif request.method == 'PUT' : return jsonify({'method' :'PUT' }) elif request.method == 'DELETE' : return jsonify({'method' :'DELETE' })
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 import requestsres = requests.get('http://127.0.0.1:5000/usres/' ) print (res.text)res = requests.post('http://127.0.0.1:5000/usres/' ) print (res.text)
Flask类视图和RESTful 我们删除 view模块,新建一个 apis.py模块,对 上面的代码 修改,使用 api接口开发。
先说一下 思路,就是在 exts模块中引入restful包的api,然后在 写入exts的初始化的方法中,在初始化的时候把 app对象 和 这个插件api 对象绑定,把我们想要写的逻辑写进一个名叫 apis的模块的 函数中(充当视图函数),新建一个 urls模块 作路由用,这个路由模块中需要 关联上 apis模块中我们的逻辑 和 插件api对象,让索引能够找到 我们apis模块中 视图函数。(但是请在__init__模块中import 一下,不然urls模块不会执行)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemyfrom flask_migrate import Migratefrom flask_restful import Apidb = SQLAlchemy() migrate = Migrate() api = Api() def init_exts (app ): db.init_app(app=app) migrate.init_app(app=app,db=db) api.init_app(app=app)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 from flask import jsonifyfrom flask_restful import Resourceclass HelloResouce (Resource ): def get (self ): return jsonify({'msg' :'get 请求' }) def post (self ): return jsonify({'msg' :'post 请求' })
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 from .exts import apifrom .apis import *api.add_resource(HelloResouce,'/hello/' )
字段格式化及参数解析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 from flask import jsonifyfrom flask_restful import Resource,fields,marshal_with,reqparsefrom .models import *class HelloResouce (Resource ): def get (self ): return jsonify({'msg' :'get 请求' }) def post (self ): return jsonify({'msg' :'post 请求' }) ret_field = { 'id' :fields.Integer, 'name' :fields.String, 'age' :fields.Integer, 'like' :fields.String(default='ball' ), 'url' :fields.Url(endpoint='id' ,absolute=True ) } class UserResource (Resource ): @marshal_with(ret_field ) def get (self ): return { 'status' :1 , 'msg' :'ok' , 'data' :'chenyushao' } ret_field2 = { 'status' :fields.Integer, 'msg' :fields.String, 'data' :fields.Nested(ret_field) } class User2Resource (Resource ): @marshal_with(ret_field2 ) def get (self ): user = User.query.first() return { 'status' :1 , 'msg' :'ok' , 'data' :user } ret_field3 = { 'name' :fields.String, 'age' :fields.Integer, } ret_field4 = { 'status' :fields.Integer, 'msg' :fields.String, 'data' :fields.List (fields.Nested(ret_field3)) } class User3Resource (Resource ): @marshal_with(ret_field4 ) def get (self ): user = User.query.first() return { 'status' :1 , 'msg' :'ok' , 'data' :user } parser = reqparse.RequestParser() parser.add_argument('name' ,type =str ,required=True ,help ='name是必须的参数。' ) parser.add_argument('age' ,type =int ,required=True ,action='append' ) parser.add_argument('BAIDUID' ,type =str ,location='cookies' ) class User4Resource (Resource ): def get (self ): args = parser.parse_args() name = args.get('name' ) age = args.get('age' ) BAIDUID = args.get('BAIDUID' ) return {'name' :name,'age' :age,'BAIDUID' :BAIDUID}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 import requestsres = requests.get('http://127.0.0.1:5000/user4/' , json={'name' :'lisi' ,'age' :'30' }, headers={'Content-Type' :'application/json' , 'Cookie' :'BAIDUID=DBF491F84E3AC8F568BC6F6E3D8DF37C' }) print (res.text)
实验部分
项目分析 数据库设计